Arcesium interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Arcesium
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OS, DBMS, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration45 minutes
Interview date16 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
2 coding questions were given to solve in 45 minutes.
1. Left View Of a Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers. You are supposed to find the left view of the binary tree. The left view of a binary tree is the set of all nodes that are visible when the binary tree is viewed from the left side.
Example:
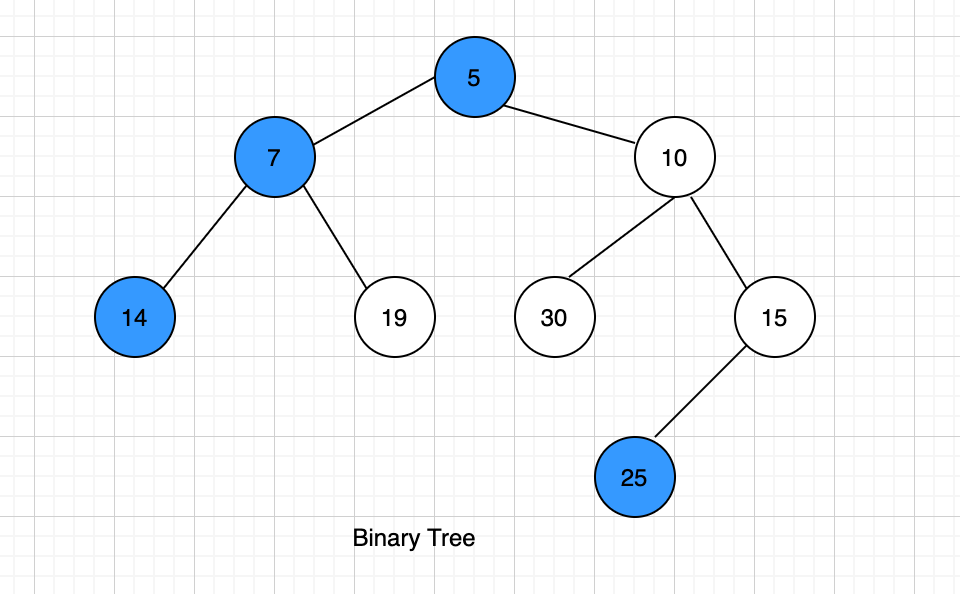
The left view of the above binary tree is {5, 7, 14, 25}.
Problem approach
A level order traversal based solution can be presented here. For each level, we need to print the first node i.e. the leftmost node of that level.
Steps :
1. Make a queue of node type and push the root node in the queue.
2. While the queue is not empty, do :
2.1 Determine the current size of the queue.
2.2 Run a for loop to traverse all nodes of the current level and do :
2.2.1 Remove the topmost node from the queue.
2.2.2 If i==0 (first node of that level) , print it.
2.2.3 Push the left and right child of the node if they exist.
Time Complexity : O(n), where n is number of nodes in binary tree
2. Number of Islands
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a non-empty grid consisting of only 0s and 1s. You have to find the number of islands in the given grid.
An island is a group of 1s (representing land) connected horizontally, vertically or diagonally. You can assume that all four edges of the grid are surrounded by 0s (representing water).
Problem approach
The question boils down to finding the number of connected components in an undirected graph. Now comparing the connected components of an undirected graph with this problem, the node of the graph will be the “1’s” (land) in the matrix.
BFS or DFS can be used to solve this problem. In each BFS call, a component or a sub-graph is visited. We will call BFS on the next un-visited component. The number of calls to BFS function gives the number of connected components. A cell in 2D matrix has 8 neighbors. So for each cell, we process all its 8 neighbors. We keep track of the visited 1s so that they are not visited again using a visited matrix.
Time Complexity : O(m*n) where m*n is the size of the given matrix
Space Complexity : O(min(m,n))
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
This was a 60 min technical interview round. The interviewer asked me to code 2 programming questions.
Tip : Practice more to clear DSA problems. Medium level questions will be enough to clear the rounds.
1. Topological Sort
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



A Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a directed graph that contains no cycles.
Topological Sorting of DAG is a linear ordering of vertices such that for every directed edge from vertex ‘u’ to vertex ‘v’, vertex ‘u’ comes before ‘v’ in the ordering. Topological Sorting for a graph is not possible if the graph is not a DAG.
Given a DAG consisting of ‘V’ vertices and ‘E’ edges, you need to find out any topological sorting of this DAG. Return an array of size ‘V’ representing the topological sort of the vertices of the given DAG.
For example, Consider the DAG shown in the picture.
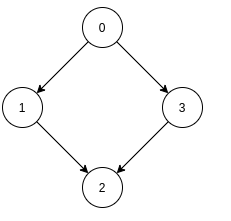
In this graph, there are directed edges from 0 to 1 and 0 to 3, so 0 should come before 1 and 3. Also, there are directed edges from 1 to 2 and 3 to 2 so 1 and 3 should come before 2.
So, The topological sorting of this DAG is {0 1 3 2}.
Note that there are multiple topological sortings possible for a DAG. For the graph given above one another topological sorting is: {0, 3, 1, 2}
Note:
1. It is guaranteed that the given graph is DAG.
2. There will be no multiple edges and self-loops in the given DAG.
3. There can be multiple correct solutions, you can find any one of them.
4. Don’t print anything, just return an array representing the topological sort of the vertices of the given DAG.
Problem approach
Topological sorting of vertices of a Directed Acyclic Graph is an ordering of the vertices v1,v2,v3.....vn in such a way, that if there is an edge directed towards vertex vj from vertex vi , then vi comes before vj. Modified DFS can be used to solve topological sort problem. A stack can be used to implement it. Steps :
1. Make a stack to store the nodes and a Boolean array to mark all visited nodes initialized to false.
2. Now, create a recursive helper function and call it for every unvisited node to store Topological Sort starting from all vertices one by one.
3. In the helper function, mark the current node as visited and recur for all the unvisited vertices adjacent to this vertex. At last, Push current vertex to stack which stores result.
4. After all the nodes are processed, print the contents of the stack.
Time Complexity : O(V+E)
Space Complexity : O(V)
2. N-th Node From The End
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. You have to find the N-th node from end.
For Example
If the given list is (1 -> -2 -> 0 -> 4) and N=2:
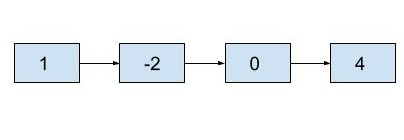
Then the 2nd node from the end is 0.
Problem approach
A direct approach is to traverse the entire linked list and calculate its length. Traverse the list again and return the (length-N+1) node. But this approach involves two traversals of the linked list.
To further optimize the solution, the question can be solved in one traversal only. Two pointers can be used here. Steps :
1. Initialize both the slow pointer and the fast pointer to the head node.
2. First, move fast pointer to n nodes from the head node.
3. Now, move both the pointers one by one until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list.
4. Now, the slow pointer will point to the nth node from the end. This is because when we started advancing pointers 'fast' and 'slow', difference between them was of 'n' nodes which is maintained while advancing these pointers.
Return the slow pointer.
Time Complexity : O(n)

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3713 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
1469 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
2667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
954 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2335 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
2275 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2094 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





