Arcesium interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Arcesium
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them
Tip 4 : One should have strong DSA skills and knowledge of Basic OOPS. Its not necessary to learn OS and DBMS if it's not taught in your college yet.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration45 minutes
Interview date12 Jul 2021
Coding problem2
It was an online coding round where we were supposed to solve 2 coding questions in 45 minutes.
1. Maximum meetings
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the schedule of 'N' meetings with their start time 'Start[i]' and end time 'End[i]'.
You have only 1 meeting room. So, you need to return the maximum number of meetings you can organize.
Note:
The start time of one chosen meeting can’t be equal to the end time of the other chosen meeting.
For example:
'N' = 3, Start = [1, 3, 6], End = [4, 8, 7].
You can organize a maximum of 2 meetings. Meeting number 1 from 1 to 4, Meeting number 3 from 6 to 7.
Problem approach
Greedy approach can be applied to solve this problem. We sort the start and end time pairs for each meeting on the basis of the end time. Then we compare if the next meeting's start time is greater than the previous meeting's end time. If the start time is greater, we can count this meeting and we increase our meeting counter otherwise this meeting can't take place. In this manner, we traverse through all the meeting pairs, comparing in a greedy fashion and checking if the meeting can take place or not.
Time Complexity : O(nlogn)
2. Connect N Ropes With Minimum Cost
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given 'N' ropes of different lengths, we need to connect these ropes into one rope. The cost to connect two ropes is equal to sum of their lengths. We need to connect the ropes with minimum cost.
The test-data is such that the result will fit into a 32-bit integer.
Problem approach
Concept of min heap can be applied here. In each iteration, we need to pick the rope with minimum length because the value picked first will be included in the final answer multiple times. Hence, for minimum cost, we pick the longer length ropes later.
Approach :
First of all, build minHeap (priority queue) from the given array of rope length.
In each iteration:
1) Extract two ropes with minimum length from the minHeap.
2) add the length of both the ropes to the cost.
3) add the cost to the result and push the cost (sum of length of two ropes) again in the minHeap.
The final result will be the minimum cost.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date14 Jul 2021
Coding problem3
The interview was conducted online. The interviewer asked me 2 programming questions and questions on OOPS concepts.
1. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
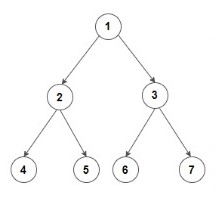
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
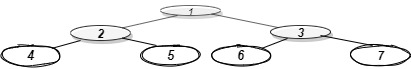
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
The basic idea is to use modified pre-order traversal. In this modified pre-order traversal, we keep track of horizontal distance of the node being visited from the root. We also keep track of height of that node. During this traversal, we use an ordered map that stores node's horizontal distance as key and value as tuple (current node's value, current node's level) if the node being visited is the bottommost node seen at its horizontal distance.
Algorithm :
1. Perform a preorder traversal to calculate the level of each node of the binary tree.
2. Consider a hash map and store the height into the map, where the key is the horizontal distance of the ith node and the value is a pair (p, q), where p is the value of the node and q is the height of the node.
3. For every node:
Add the node to the resultant map if it is the first node to have the current horizontal distance.
Else, if a node is already present for the particular distance, replace the previous node with the current node, if the node has a height greater than the previous node.
2. Serialize/Deserialize The Binary Tree
Hard
15m average time
85% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have been given a binary tree of integers. You are supposed to serialize and deserialize (refer to notes) the given binary tree.
You can choose any algorithm to serialize/deserialize the given binary tree. You only have to ensure that the serialized string can be deserialized to the original binary tree.
Note :
Serialization is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted (for example, across a computer network) and reconstructed later. The opposite operation, that is, extracting a data structure from stored information, is deserialization.
Problem approach
DFS can be used for serializing and de-serializing. Process root node and then make recursive calls for left and right child.
For serializing the tree into a list :
1. If node is null, store -1 in list to denote a null link. Return.
2. Store the data at current node in list.
3. Call function recursively for left and right subtrees.
4. Return the list.
If we serialize using preorder traversal, apply the same preorder procedure to recursively build the tree. Take the keys from the array one by one and build the tree accordingly. The de-serialize function takes two arguments, i.e., the list of values and an index.
1. The base case would be true either when index passed is out of bound or if the value at index position is -1, return NULL in that case.
2.Create new node for storing current element.
3. Call function recursively for left and right subtrees.
4. Return the tree.
3. OOPS Question
Virtual destructors in C++
Problem approach
Using a virtual destructor, we can release the memory allocated by a derived class object or instance. In addition, we can delete instances of the derived class using a base class object pointer. The base class destructor uses the virtual keyword so that both the base class and the derived class destructor will be called at run time. However, the derived class will be called first and then the base class to free up the memory.
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date14 Jul 2021
Coding problem0
This was a HR based round where the interviewer asked questions to know more about me. Questions were related to mu resume, my projects and my vision for the next 5 years.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3713 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
1469 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
1435 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
954 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2335 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
2275 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2094 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





