Arcesium interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Senior Software Engineer
Arcesium
4 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 Months
Topics: Data Structure(Mainly Graphs and DP), Algorithms, LLD, Design Pattern, Operating System, OOPs
Tip
Tip 1 : OOPs concept is a must have/ design patterns is a plus.
Tip 2 : Prepare Graphs and DP well, this will outshine you from crowd.
Tip 3 : If experienced, prepare your project well and be ready to manage surprises(deep knowledge is a must have)
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 2 years of experience
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Mention your achievements. (after all, you need to sell your skills )
Tip 2 : In case not having relevant experience, start developing from free resources, preferably using spring boot.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jun 2021
Coding problem3
This was a medium level online Hackerrank assessment test. Only 60 minutes was allowed time and there was no time to search online. Camera was not there but full screen access was taken. 3 days window was given to attempt the test.
1. Inform Employees
Hard
0/120
Asked in companies



You are in a company with ‘N’ employees each with a unique ID from ‘0 to N - 1’. You are given a list of managers, where ‘manager[i]’ is the direct manager of ‘ith’ employee. You are also given an array ‘timeToInform’ where ‘timeToInform[i]’ is the time it takes for ‘ith’ employee to send information to all his subordinates. Your task is to find out how much time it will take for any piece of information to reach all employees. You are also given ‘headId’ that is the ID of the head of the company.
For example:
You are given ‘manager’ = [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1], ‘timeToInform’ = [1, 1, 0, 0, 0], ‘headId’ = [0],
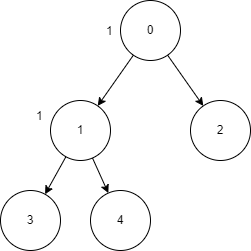
We can see employee ‘0’ will take 1 time to inform their subordinates, that are employee 1, and employee 2, and employee 1 will take 1 time to inform their subordinates that are employee 3 and employee 4. The total time taken is 2. Hence the answer is 2.
Problem approach
In this approach, we can create a tree out of the given information and traverse it. For any node, the time taken is the maximum time taken by its subordinates and the timeToInform of that node.
We will create a dfs(employeeId, subordinates, timeToInform), where employeeId is the id of the employee we are currently looking, ‘subordinates’ is the map containing the list of all subordinates of any employee, and ‘timeToInform is the array given in the problem.
2. Longest sub-array with positive product
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘ARR’ of ‘N’ integers, you need to find the maximum length of the sub-array such that the product of elements of the sub-array is positive.
For Example:
Let us say we have array 'ARR' =[-1,3,5,-2,4,-9]. The longest sub-array with the positive product is [3,5,-2,4,-9].
Problem approach
It was a DP problem. The idea here is to maintain the count of positive elements and negative elements such that their product is positive. Was a hard problem.
Initialize the variable, say res, to store the length of the longest subarray with the positive product.
Initialize two variables, Pos and Neg, to store the length of the current subarray with the positive and negative products respectively.
Iterate over the array.
If arr[i] = 0: Reset the value of Pos and Neg.
If arr[i] > 0: Increment Pos by 1. If at least one element is present in the subarray with the negative product, then increment Neg by 1.
If arr[i] < 0: Swap Pos and Neg and increment the Neg by 1. If at least one element is present in the subarray with the positive product, then increment Pos also.
Update res=max(res, Pos).
3. Min Steps to one
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a positive integer 'N’. Your task is to find and return the minimum number of steps that 'N' has to take to get reduced to 1.
You can perform any one of the following 3 steps:
1) Subtract 1 from it. (n = n - 1) ,
2) If n is divisible by 2, divide by 2.( if n % 2 == 0, then n = n / 2 ) ,
3) If n is divisible by 3, divide by 3. (if n % 3 == 0, then n = n / 3 ).
For example:
Given:
‘N’ = 4, it will take 2 steps to reduce it to 1, i.e., first divide it by 2 giving 2 and then subtract 1, giving 1.
Problem approach
The idea is to use recursion to find all possible cases and then, out of them, choose the minimum. As there are maximum ‘N’ states, we can use a ‘dp’ array to store the recurring sub-problems, where ‘dp[N]’ represents the minimum number of steps it takes to convert ‘N’ to 1.
02
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Oct 2021
Coding problem1
I was told to give my brief intro. Then they asked me to find the maximum path sum between two leaves of a binary tree question.
Was asked about the time and space complexity in detail. Then interviewer asked about my work experience in previous organization. Then few questions were asked related to java (Garbage Collector).
1. Maximum Path Sum Between Two Leaves
Hard
50m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a non-empty binary tree where each node has a non-negative integer value. Return the maximum possible sum of path between any two leaves of the given tree.
The path is also inclusive of the leaf nodes and the maximum path sum may or may not go through the root of the given tree.
If there is only one leaf node in the tree, then return -1.
Problem approach
1) Find maximum sum from leaf to root in left subtree of X.
2) Find maximum sum from leaf to root in right subtree of X.
3) Add the above two calculated values and X->data and compare the sum with the maximum value obtained so far and update the maximum value.
4) Return the maximum value.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date15 Nov 2021
Coding problem1
It was the second technical round. I was asked a graph question. It is a standard question but my approach was a bit different. Mostly my time went proving the interviewer that my approach was also correct.
1. Rotting Oranges
Moderate
20m average time
78% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You have been given a grid containing some oranges. Each cell of this grid has one of the three integers values:
Every second, any fresh orange that is adjacent(4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Your task is to find out the minimum time after which no cell has a fresh orange. If it's impossible to rot all the fresh oranges then print -1.
Note:
1. The grid has 0-based indexing.
2. A rotten orange can affect the adjacent oranges 4 directionally i.e. Up, Down, Left, Right.
Problem approach
--> I made an auxiliary 2D array and initialized all empty places with maximum possible value.
Then I used BFS to get my solution, the algorithm was as follow:
1. Pick a cell where rotten fruit was placed.
For all neighbors of that cell(arr[i][j]), I set the value = minimum(arr[i][j], value of rotten cell +1).
The minimum function will make sure that neighbor cells should get the minimum possible value ,ie, the fruit in cell should get rotten from nearest rotten fruit cell.
04
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 Nov 2021
Coding problem1
It was the third technical round where I was interviewed by a panel of 2 senior members. I was asked a graph related problem and was also asked to share previous company experience, tech-stack and projects.
1. Minimum walk
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There are ‘N’ cities in the Ninja world that are connected via ‘M’ bi-directional roads. Alice wants to take a tour in the Ninja world, but she doesn’t have so much time, so she chooses any city as a source, visits some cities, and gets back to where she started. In her journey, she doesn’t walk through any road more than once.
Your task is to find the minimum possible distance she needs to walk such that she ends in the same city where she started and doesn’t walk any road more than once. If no such path is found, return -1.
Note :-
Any pair of cities (x, y) have at most one road connecting them directly.
A city ‘x’ is reachable by any other city ‘y’ via some group of roads.
In input data, cities are numbered from [0, 1, ……. N-1].
Problem approach
Approach: Take the given network as a connected graph with ‘N’ vertices and ‘M’ edges.
Let’s assume that the given graph is a rooted tree (with loops), and each loop must have the root node in its path. For such cases, loops can be easily detected with BFS / DFS traversal. But the lengths of loops are also needed, so BFS is preferred.
While traversing the tree, if any node ‘x’ is visited more than once, then it’s in a loop, and the length of the loop will be [previous distance of node ‘x’ from root + current distance of ‘x’ from root].
Using the above assumption, we can find lengths of all loops passing through the ‘root’ node. Now, we take each vertex of the graph as the root node one by one and run a BFS traversal.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Senior Software Engineer
1 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3792 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
2017 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
5079 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
3077 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
Senior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 20 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
3680 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





