Bloomreach interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Bloomreach
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 2 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, React, Java, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Try to build solution during interview going from brute force to more optimised ones
Tip 2 : Write clean, modular, understandable code for your approach and be ready with both iterative and recursive approaches if question demands
Tip 3 : Understand question before trying to solve it, clear any doubts with interviewer before/during solving
Application process
Where: Company Website
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Should have awesome side/personal projects
Tip 2 : DSA is not enough development projects are a must
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date7 Jan 2020
Coding problem2
1. Inorder Traversal
Easy
32m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to return the In-Order traversal of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
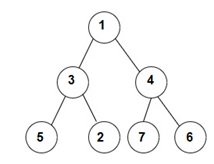
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
Problem approach
We do simple Inorder Traversal. While doing the traversal, we keep track of count of nodes visited so far. When count becomes n, we print the node
2. Reverse Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
Problem approach
Implemented standard iterate and recursive solutions
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date7 Jan 2020
Coding problem2
1. LCA In A BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary search tree of integers with N nodes. You are also given references to two nodes 'P' and 'Q' from this BST.
Your task is to find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of these two given nodes.
The lowest common ancestor for two nodes P and Q is defined as the lowest node that has both P and Q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself)
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For example:
'P' = 1, 'Q' = 3
tree = 2 1 4 -1 -1 3 -1 -1 -1,
The BST corresponding will be-
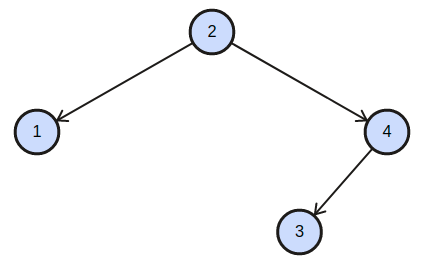
Here, we can clearly see that LCA of node 1 and node 3 is 2.
Problem approach
Implemented standard solution:
1. Create a recursive function that takes a node and the two values n1 and n2.
2. If the value of the current node is less than both n1 and n2, then LCA lies in the right subtree. Call the recursive function for the right subtree.
3. If the value of the current node is greater than both n1 and n2, then LCA lies in the left subtree. Call the recursive function for the left subtree.
4. If both the above cases are false then return the current node as LCA.
2. Trapping Rain Water
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a long type array/list 'arr’ of size 'n’.
It represents an elevation map wherein 'arr[i]’ denotes the elevation of the 'ith' bar.
Print the total amount of rainwater that can be trapped in these elevations.
Note :
The width of each bar is the same and is equal to 1.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 6, ‘arr’ = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4].
Output: 10
Explanation: Refer to the image for better comprehension:

Note :
You don't need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Approach: The idea is to traverse every array element and find the highest bars on the left and right sides. Take the smaller of two heights. The difference between the smaller height and height of the current element is the amount of water that can be stored in this array element.
Algorithm:
Traverse the array from start to end.
For every element, traverse the array from start to that index and find the maximum height (a) and traverse the array from the current index to end, and find the maximum height (b).
The amount of water that will be stored in this column is min(a,b) – array[i], add this value to the total amount of water stored
Print the total amount of water stored.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Bloomreach
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes









