BNY Mellon interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
BNY Mellon
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
Effort is the road to success. My path to BNY Mellon began with learning programming basics in C/C++ through the Coding Ninjas platform, my first tutor, and creating projects in web development and machine learning. Passing the interview was possible only through daily study, consistent practice, and a never-give-up attitude. The biggest challenge was time management—balancing the study of core subjects with practising DSA.
Application story
I applied on-campus for the Software Developer role at BNY Mellon. The criteria for applying were that there should be no active backlogs, and candidates needed to have a CGPA of 7 or higher to clear the cutoff. Since I have a CGPA of 9.5, meeting the cutoff was easy for me, and then the process was initiated.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected for the role because I aligned with the company values and effectively answered the questions during the interview. I presented myself as team-centric, which I believe was a significant factor in my selection.
Preparation
Duration: 12 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Graphs, Operating System, DBMS, OOPS, Machine Learning
Tip
Tip 1: Focus on problem-solving and unique projects.
Tip 2: Regularly review algorithms and apply them to real-world scenarios.
Tip 3: Effective time management is crucial in DSA and development.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA, No active Backlogs, (Salary Package: 25 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Projects should focus on problem-solving, and you should include at least two projects.
Tip 2: Mention only those technologies in which you have significant experience.
Tip 3: Also, include some co-curricular activities beyond your technical background.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Hard
Online Coding Interview
Duration120 minutes
Interview date26 Aug 2023
Coding problem4
Timing: The round was held in the evening from 4 to 6 PM.
The environment was quite stressful, as it took place in college.
The round was fully proctored by invigilators, and cameras were used to monitor the candidates, with code plagiarism also being checked.
1. Count Distinct Subarrays With At Most K Odd Elements
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of 'N' integers. Your task is to return the total number of distinct subarrays of 'arr' having 'k' odd elements.
Example :
If arr = [3,2,3], and k = 1
then there are 4 subarrays with 1 odd elements:
[3], [3,2], [2,3] & [3].
Problem approach
Algorithm:
Step 1: For each element in the array, maintain two helper arrays: prefix (stores leftmost occurrence of a set bit) and suffix (stores rightmost occurrence of a set bit).
Step 2: Traverse the array to populate the prefix and suffix arrays.
Step 3: For each element, determine the number of valid subarrays using the prefix and suffix arrays.
Step 4: Accumulate the count of valid subarrays.
2. Count User Logins
You are given a list of login records consisting of a username, time, and date. You need to count how many times each user logged in on a specific date. If the date or time is invalid, ignore that login record. (Practice)
Problem approach
Algorithm :
Step 1: Parse each login record to extract the user, time, and date.
Step 2: Use maps to store user login counts based on valid date entries.
Step 3: For each user, increment the login count for the specific date if the record is valid.
3. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
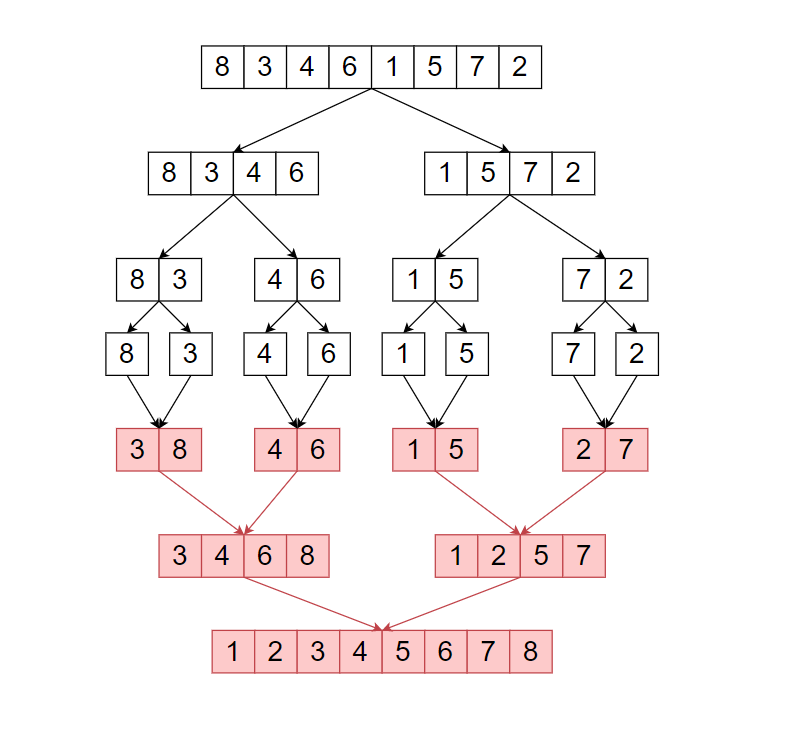
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
Algorithm :
Step 1: Apply merge sort to the array, splitting it into subarrays.
Step 2: Count inversions during the merge step by comparing left and right subarrays. If an element from the left is greater than the right, it forms an inversion.
Step 3: Accumulate inversion counts from each merge operation.
4. Reverse Edges
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a directed graph of ‘N’ nodes and ‘M’ edges. Also, you have two nodes ‘A’ and ‘B’. Your task is to make at least one valid path from ‘A’ to ‘B’ by doing the below operations a minimum number of times.
Choose two nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’, such that there exists an edge from ‘X’ to ‘Y’.
Delete edge ‘X’ to ‘Y’.
Add edge ‘Y’ to ‘X’.
You need to print the minimum operations that you have done.
Problem approach
Algorithm :
Step 1: Use two DFS traversals:
First DFS (dfs1) computes how many reversals are needed to make the tree rooted at node 0 unidirectional.
Second DFS (dfs2) calculates the minimum reversals needed for the entire tree by considering parent-child relationships and adjusting based on the direction of each edge.
Step 2: Return the minimum reversal count.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date29 Aug 2023
Coding problem3
Timing - The round was in morning
The interviewer was very helpful and guided althrough my interview time and was very considerate and very knowledgeable person
1. Construct The String
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Your friend gave you a challenge. He gave you a string ‘S’ of length ‘N’ consisting only of lowercase English alphabets. He asked you to construct the given string using the minimum number of operations. In each operation, you can do one of the steps.
1) Add a lowercase English alphabet at the end of the string.
2) Create a copy of the string and concatenate both of the strings.
Initially, you have an empty string. So if you perform the second operation, you will get an empty string.
For example: If the current string is “abc”, then after performing the second operation, the current string will be “abcabc”.
Problem approach
Approach
The approach is based on Dynamic Programming (DP).
First, a check is made to see if zero is greater than one. If this is the case, we call the same function but swap zero and one. This is because the types of characters (0 or 1) are interchangeable, and we want to ensure that zero is less than or equal to one for the following steps.
Next, we initialize a DP array dp of size high + 1, where dp[i] represents the number of "good strings" of length i that we can build. We set dp[0] = 1, as there is one way to create a string of length zero: an empty string.
We then iterate over i from 1 to high:
If i is greater than or equal to one, we set dp[i] to dp[i - zero] + dp[i - one]. This update signifies the ways to build strings of length i by appending a '0' to strings of length i - zero and a '1' to strings of length i - one, while adhering to the maximum consecutive counts.
If i is less than one but greater than or equal to zero, we set dp[i] to dp[i - zero]. This optimization is made because, after some iterations, i will always be greater than zero, and execution will not fall into this branch again.
If i is greater than or equal to low, we update our answer ans by adding dp[i]. Strings of length i contribute to our final count of good strings.
Finally, we return ans modulo MOD, as the problem asks for the answer modulo 109+710^9 + 7109+7.
2. DBMS
- What is normalization? (Learn)
- Normalize a given table to 3NF.
- Write a SQL query to find the second highest salary. (Practice)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Thoroughly revise DBMS
Tip 2: Practice SQL frequently.
3. Puzzle
Light bulbs are numbered from 1 to 100 and are initially kept off. The first person comes and toggles all the bulbs that are multiples of 1, meaning they switch all the bulbs to 'ON'. The second person toggles all the multiples of 2, turning the even-numbered bulbs 'OFF'. The third person comes and toggles all the multiples of 3. This process continues until the 100th person has completed their part. After this, how many bulbs are 'ON'?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Just solve it with the right intuition.
Tip 2: Solve all the puzzles available online.
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration40 minutes
Interview date29 Aug 2023
Coding problem2
Timing: It was held in the afternoon after 12 PM.
This round was conducted online, where a mix of questions was asked by the interviewer.
The interview included HR questions, some problem-solving questions with puzzles, and mostly resume-based questions.
1. Puzzle
One container has 7 litres and another has 3 litres. How can we measure 5 litres of milk?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice all puzzles.
Tip 2: Always give a logical answer.
2. Operating System
- What are paging and segmentation? (Learn)
- What is deadlock, and what are the techniques to prevent it?
- Explain memory management. (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Do read and implement OS.
Tip 2: Explain the answers in brief.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
1981 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
1382 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
2659 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by HCL Technologies
1862 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






