BYJUS interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
BYJUS
2 rounds | 3 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice from Leetcode, solve Leetcode medium level problems.
Tip 2 : Brush up computer fundamentals from subjects like OS, DBMS and CN.
Tip 3 : Have a good project or good internship experience and have in-depth knowledge regarding what you have done.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 6 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 mins
Interview date31 Aug 2022
Coding problem1
1. LFU Cache
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



Design and implement a Least Frequently Used(LFU) Cache, to implement the following functions:
1. put(U__ID, value): Insert the value in the cache if the key(‘U__ID’) is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least frequently used item before inserting the new item.
2. get(U__ID): Return the value of the key(‘U__ID’), present in the cache, if it’s present otherwise return -1.
Note:
1) The frequency of use of an element is calculated by a number of operations with its ‘U_ID’ performed after it is inserted in the cache.
2) If multiple elements have the least frequency then we remove the element which was least recently used.
You have been given ‘M’ operations which you need to perform in the cache. Your task is to implement all the functions of the LFU cache.
Type 1: for put(key, value) operation.
Type 2: for get(key) operation.
Example:
We perform the following operations on an empty cache which has capacity 2:
When operation 1 2 3 is performed, the element with 'U_ID' 2 and value 3 is inserted in the cache.
When operation 1 2 1 is performed, the element with 'U_ID' 2’s value is updated to 1.
When operation 2 2 is performed then the value of 'U_ID' 2 is returned i.e. 1.
When operation 2 1 is performed then the value of 'U_ID' 1 is to be returned but it is not present in cache therefore -1 is returned.
When operation 1 1 5 is performed, the element with 'U_ID' 1 and value 5 is inserted in the cache.
When operation 1 6 4 is performed, the cache is full so we need to delete an element. First, we check the number of times each element is used. Element with 'U_ID' 2 is used 3 times (2 times operation of type 1 and 1-time operation of type 1). Element with 'U_ID' 1 is used 1 time (1-time operation of type 1). So element with 'U_ID' 1 is deleted. The element with 'U_ID' 6 and value 4 is inserted in the cache.
Problem approach
Design and implement a Least Frequently Used(LFU) Cache, to implement the following functions:
1. put(U__ID, value): Insert the value in the cache if the key(‘U__ID’) is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least frequently used item before inserting the new item.
2. get(U__ID): Return the value of the key(‘U__ID’), present in the cache, if it’s present otherwise return -1
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 mins
Interview date31 Aug 2022
Coding problem2
1. Preorder traversal of a BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values.
Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties:
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note:
It is guaranteed that a BST can be always constructed from the given preorder traversal. Hence, the answer will always exist.
Example:
From PREORDER = [20, 10, 5, 15, 13, 35, 30, 42] , the following BST can be constructed:
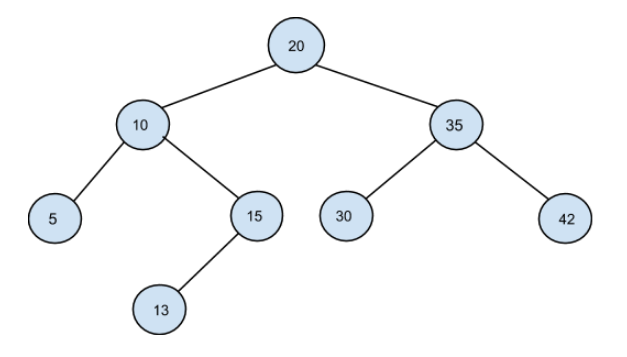
Problem approach
You have been given an array/list 'PREORDER' representing the preorder traversal of a BST with 'N' nodes. All the elements in the given array have distinct values.
Your task is to construct a binary search tree that matches the given preorder traversal.
2. Check if number is Binary
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a string of integers ‘bin’. Return 'true' if the string represents a valid binary number, else return 'false'. A binary number is a number that has only 0 or 1 in it.
Problem approach
Given a string of integers ‘bin’. Return 'true' if the string represents a valid binary number, else return 'false'. A binary number is a number that has only 0 or 1 in it.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BYJUS
0 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by BYJUS
664 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by BYJUS
659 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BYJUS
555 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes








