Cadence Design Systems interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Cadence Design Systems
3 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration75 minutes
Interview date12 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
This was an online coding round where I had 2 questions to solve under 75 minutes. Both the coding questions were related to DP and were of Medium to Hard level of difficulty.
1. Longest Common Prime Subsequence
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja got a very long summer vacation. Being very bored and tired about it, he indulges himself in solving some puzzles.
He encountered a problem in which he was given two arrays of integers of length ‘N’ and ‘M’ respectively and he had to find the longest common prime subsequence.
Ninja wants help in solving the problem as he is not getting the approach so he approaches you as he knows that you are very good at building logics. Help Ninja!
Note:
A subsequence is a sequence that can be derived from another sequence by zero or more elements, without changing the order of the remaining elements.
Problem approach
Algorithm :
1) Generate all the prime numbers in the range of values of the given array using Sieve Of Eratosthenes.
2) Now make an iteration for ‘arr1’ and check the elements in ‘arr1’ which are prime and store the elements in an array, say ‘finalA’.
3) Now make an iteration for ‘arr2’ and check the elements in ‘arr2’ which are prime and store the elements in an array, say ‘finalB’.
4) Now calculate the LCS for the two arrays: ‘finalA’ and ‘finalB’ with the help of ‘lcs()’ function using Dynamic Programming.
5) Return the array after calculating the longest common subsequence.
TC : O(N*M) , where N=size of array 1 and M=size of array 2
SC : O(N*M)
2. Maximum Sum
Moderate
35m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array “ARR” of N integers. You are required to perform an operation on the array each time until it becomes empty. The operation is to select an element from the array(let’s say at ith index i.e ARR[i]) and remove one occurrence of the selected element from the array and remove all the occurrences of (ARR[i]-1) and (ARR[i]+1) from the array(if present). Your task is to maximize the sum of selected elements from the array.
For example, let’s say the given array is [2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5].
The maximum possible sum for the given array would be 14. Because if we select one of the 3’s from the array, then one 3 and all occurrences of (3-1) and (3+1) i.e 2 and 4 will be deleted from the array. Now we left with {3,3,5} elements in the array. Then again we select 3 in the next two steps and in both steps 3 will be deleted also (3-1) and (3+1) doesn't exist in the array so nothing extra to delete in both steps. Now we left with only {5} and in the next step, we select the 5 and delete it. Then the array becomes empty. Thus the sum of selected elements will be 3+3+3+5 = 14.
Problem approach
Algorithm:
1) Find the maximum number max in the array.
2) Create a new auxiliary array dp of size max+1 and store frequencies of unique elements in the array, where dp[i] denotes the number of times i as an element is present in the input array.
3) Iterate the dp array(we will use this array to store the results), now for each index i from 2 to MAX we have two choices: dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], dp[i-2] + dp[i]*i).
4) Return dp[MAX], which have the maximum sum of the selected numbers.
TC : O(max(MAX, N)), where “MAX” is the maximum element and N is the size of the array.
SC : O(MAX)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Aug 2021
Coding problem4
This round had 2 Algorithmic questions wherein I was supposed to code both the problems after discussing their approaches and respective time and space complexities . After that , I was grilled on some OOPS concepts related to C++.
1. Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
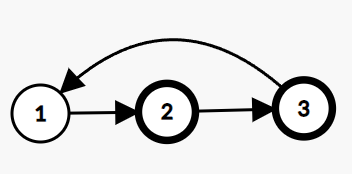
Problem approach
Approach 1(Using Hashing) :
We are going to maintain a lookup table(a Hashmap) that basically tells if we have already visited a node or not, during the course of traversal.
Steps :
1) Visit every node one by one, until null is not reached.
2) Check if the current node is present in the loop up table, if present then there is a cycle and will return true, otherwise, put the node reference into the lookup table and repeat the process.
3) If we reach at the end of the list or null, then we can come out of the process or loop and finally, we can say the loop doesn't exist.
TC : O(N), where N is the total number of nodes.
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 (Using Slow and Fast Pointers) :
Steps :
1) The idea is to have 2 pointers: slow and fast. Slow pointer takes a single jump and corresponding to every jump slow pointer takes, fast pointer takes 2 jumps. If there exists a cycle, both slow and fast
pointers will reach the exact same node. If there is no cycle in the given linked list, then fast pointer will reach the end of the linked list well before the slow pointer reaches the end or null.
2) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
3) Start moving slow to every next node and moving fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
4) If after adjusting slow and fast, if they are referring to the same node, there is a cycle otherwise repeat the process
5) If fast reaches the end or null then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
TC : O(N), where N is the total number of nodes.
SC : O(1)
2. Check If Preorder Traversal Is Valid
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' of positive integers. Your task is to check whether the array 'ARR' is a valid Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree.
A binary search tree (BST), also called an ordered or sorted binary tree, is a rooted binary tree whose internal nodes each store a value greater than or equal all the values in the node's left subtree and less than those in its right subtree.
For Example
Consider the array ARR = [ 7, 4, 8 ] having 3 elements.
This array represents the pre-order traversal of the below tree.
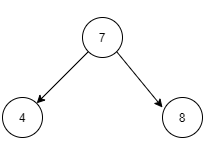
Hence, the above array 'ARR' is a valid Preorder Traversal of a Binary Search Tree.
Problem approach
Approach (Using Stack) :
1) Initialize an empty stack of integers.
2) Initialize a variable lowerBound to store the value of the root of the current tree. Initialize is as INT_MIN.
3) Iterate through i = 0 to N - 1
3.1) If ARR[i] is smaller than lowerBound, then we will return 0.
3.2) Repeatedly,
If the stack is non-empty, then remove the element at the top of the stack if it is smaller than ARR[i] and make the removed element as the new lowerBound.
3.3) Push ARR[i] to the stack. Note that the stack will always contain elements sorted in descending order.
4) Return 1 if we have not returned 0 till now.
TC : O(N), where N = size of the array
SC : O(N)
3. OOPS Question
What is Vtable and VPTR in C++?
Problem approach
Vtable : It is a table that contains the memory addresses of all virtual functions of a class in the order in which they are declared in a class. This table is used to resolve function calls in dynamic/late binding manner. Every class that has virtual function will get its own Vtable.
VPTR : After creating Vtable address of that table gets stored inside a pointer i.e. VPTR (Virtual Pointer). When you create an object of a class which contains virtual function then a hidden pointer gets created automatically in that object by the compiler. That pointer points to a virtual table of that particular class.
Some important points about Vtable and VPTR are as follows :
1) Vtable is created by compiler at compile time.
2) VPTR is a hidden pointer created by compiler implicitly.
3) If base class pointer pointing to a function which is not available in base class then it will generate error over there.
4) Memory of Vtable and VPTR gets allocated inside the process address space.
5) Vtable gets created for each class which has virtual functions.
6) To achieve run time polymorphism effect there should be single level inheritance in our code.
4. OOPS Question
What Friend Functions in C++?
Problem approach
1) Friend functions of the class are granted permission to access private and protected members of the class in C++. They are defined globally outside the class scope. Friend functions are not member functions of the class.
2) A friend function is a function that is declared outside a class but is capable of accessing the private and protected members of the class.
3) There could be situations in programming wherein we want two classes to share their members. These members may be data members, class functions or function templates. In such cases, we make the desired function, a friend to both these classes which will allow accessing private and protected data members of the class.
4) Generally, non-member functions cannot access the private members of a particular class. Once declared as a friend function, the function is able to access the private and the protected members of these classes.
Some Characteristics of Friend Function in C++ :
1) The function is not in the ‘scope’ of the class to which it has been declared a friend.
2) Friend functionality is not restricted to only one class
3) Friend functions can be a member of a class or a function that is declared outside the scope of class.
4) It cannot be invoked using the object as it is not in the scope of that class.
5) We can invoke it like any normal function of the class.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Aug 2021
Coding problem4
This was also a DS/Algo round where I was given 2 questions to solve and I was expected to come up with the optimal approach as far as possible. I solved both the questions with the optimal time and space complexities and then I was asked some more questions related to DBMS towards the end of the interview.
1. Top View of a Binary Tree
Moderate
42m average time
61% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree. Print the Top View of Binary Tree. Print the nodes from left to right order.
Example:
Input:
Output: 2 35 2 10 2
Problem approach
Approach 1 :
1) Like vertical Order Traversal, we need to put nodes of same horizontal distance together.
2) We do a level order traversal so that the topmost node at a horizontal node is visited before any other node of same horizontal distance below it.
3) Hashing is used to check if a node at given horizontal distance is seen or not.
TC : O(N*log(N)), where N = number of nodes in the binary tree
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 :
1) This approach is based on the level order traversal.
2) We’ll keep record of current max so far left, right horizontal distances from the root.
3) And if we found less distance (or greater in magnitude) then max left so far distance then update it and also push data on this node to a stack (stack is used because in level order traversal the left nodes will appear in reverse order), or if we found greater distance then max right so far distance then update it and also push data on this node to a vector.
In this approach, no map is used.
TC : O(N), where N = number of nodes in the binary tree
SC : O(N)
2. Count number of Palindromic Substrings
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a string STR. Your task is to find the total number of palindromic substrings of STR.
Example :
If the input string is "abbc", then all the possible palindromic substrings would be: ["a", "b", "b", c", "bb"] and hence, the output will be 5 since we have 5 substrings in total which form a palindrome.
Note :
A string is said to be a 'Palindrome' if it is read the same forwards and backwards.
For example, “abba” is a palindrome, but “abbc” is not.
A 'Substring' is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
For example, "a", "b", "c", "ab", "bc", "abc" are substrings of "abc".
Problem approach
I solved it using DP as I was able to figure out what my dp table would store and the dp transition state .
Approach :
1) Create a 2-D dp boolean vector(with all false initially) where dp[i][j] states whether s[i...j] is a palindrome or not .
2) Base Case : For every i from 0 to n-1 fill dp[i][i]=1 ( as a single character is always a palindrome )and increment the counter where counter=0 initially
3) Now, run 2 loops first one from i=n-1 to i=0 (i.e., tarverse from the back of the string) and the second one from j=i+1 to n .
4) For every s[i]==s[j] , check if(j-i==1 i.e., if s[i] and s[ j] are two consecutive same letters) or if(dp[i+1][j-1]==1 or not i.e., if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is palindrome or not .
5) Because if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is a palindrome and s[i]==s[j] then s[i] and s[j] can be appended at the starting and the ending position of s[i+1,...j-1] and s[i...j] will then be a palindrome , so mark dp[i][j]=1 and increment the counter
6) Finally return the counter
TC : O(N^2) where N=length of the string s
SC : O(N^2)
3. DBMS Question
Difference between the DELETE and TRUNCATE command in a DBMS.
Problem approach
DELETE command :
1) This command is needed to delete rows from a table based on the condition provided by the WHERE clause.
2) It can be rolled back if required.
3) It maintains a log to lock the row of the table before deleting it and hence it’s slow.
TRUNCATE command :
1) This command is needed to remove complete data from a table in a database. It is like a DELETE command which
has no WHERE clause.
2) It removes complete data from a table in a database.
3) It can be rolled back even if required.
4) It doesn’t maintain a log and deletes the whole table at once and hence it’s fast.
4. DBMS Question
What is meant by normalization and denormalization?
Problem approach
NORMALIZATION :
1) Normalization is a process of reducing redundancy by organizing the data into multiple tables.
2) Normalization leads to better usage of disk spaces and makes it easier to maintain the integrity of the database.
DENORMALIZATION :
1) Denormalization is the reverse process of normalization as it combines the tables which have been normalized into a single table so that data retrieval becomes faster.
2) JOIN operation allows us to create a denormalized form of the data by reversing the normalization.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Cadence Design Systems
2770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Cadence Design Systems
2624 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
QA Engineer
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Cadence Design Systems
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Cadence Design Systems
1230 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2180 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







