CargoFlash Info Tech interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Associate Software Engineer
CargoFlash Info Tech
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
At the starting, I was a very bad student in terms of data structure and algorithm but when I realized that this is the only way to get placement then I started preparation in this field.
Application story
I applied to the company when the company come to our college for the placements .
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because i was not able to answer all the questions which were asked in the exam
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : You should be well versed with basic OOPS principles
Tip 2 : You should be confident and have profound knowledge about the projects you worked on
Tip 3 : Basic DB concepts like joins, normalisation
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date2 Nov 2022
Coding problem2
1. Next Greater Element
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'a' of size 'n'.
Print the Next Greater Element(NGE) for every element.
The Next Greater Element for an element 'x' is the first element on the right side of 'x' in the array, which is greater than 'x'.
If no greater elements exist to the right of 'x', consider the next greater element as -1.
For example:
Input: 'a' = [7, 12, 1, 20]
Output: NGE = [12, 20, 20, -1]
Explanation: For the given array,
- The next greater element for 7 is 12.
- The next greater element for 12 is 20.
- The next greater element for 1 is 20.
- There is no greater element for 20 on the right side. So we consider NGE as -1.
Problem approach
For a given array/list of integers of size N, print the Next Greater Element(NGE) for every element. The Next Greater Element for an element X is the first element on the right side of X in the array, which is greater than X. If no greater elements exist to the right of X, consider the next greater element as -1.
2. Copy List with Random Pointer
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a linked list having two pointers in each node. The first one points to the next node of the list, however, the other pointer is random and can point to any node of the list or null. The task is to create a deep copy of the given linked list and return its head. We will validate whether the linked list is a copy of the original linked list or not.
A deep copy of a Linked List means we do not copy the references of the nodes of the original Linked List rather for each node in the original Linked List, a new node is created.
For example,
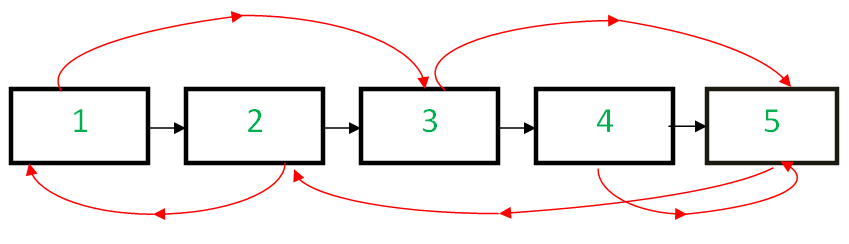
Random pointers are shown in red and next pointers in black.
Problem approach
Given a linked list having two pointers in each node. The first one points to the next node of the list, however, the other pointer is random and can point to any node of the list or null. The task is to create a deep copy of the given linked list and return its head. We will validate whether the linked list is a copy of the original linked list or not.
A deep copy of a Linked List means we do not copy the references of the nodes of the original Linked List rather for each node in the original Linked List, a new node is created.
02
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date2 Nov 2022
Coding problem2
1. Smallest Window
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings S and X containing random characters. Your task is to find the smallest substring in S which contains all the characters present in X.
Example:
Let S = “abdd” and X = “bd”.
The windows in S which contain all the characters in X are: 'abdd', 'abd', 'bdd', 'bd'.
Out of these, the smallest substring in S which contains all the characters present in X is 'bd'.
All the other substring have a length larger than 'bd'.
Problem approach
You are given two strings S and X containing random characters. Your task is to find the smallest substring in S which contains all the characters present in X.
2. Connect Nodes at Same Level
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



A binary tree is a tree where each node has at most two children i.e left child and right child.
You are given a binary tree, where the structure of the node is as follow -:
class BinaryTreeNode {
int data; // Value of the node.
BinaryTreeNode *left; // Pointer to left child node.
BinaryTreeNode *right; // Pointer to right child node.
BinaryTreeNode *next; // Pointer to next right node at same level.
}
Your task is to connect all the adjacent nodes at the same level in the given binary tree. You can do this by populating each 'next' pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL. Initially, all the next pointers are set to NULL.
For Example:
Consider the figure shown below. The left part represents the initial binary tree and right part represents the binary tree after connecting adjacent nodes at the same level.
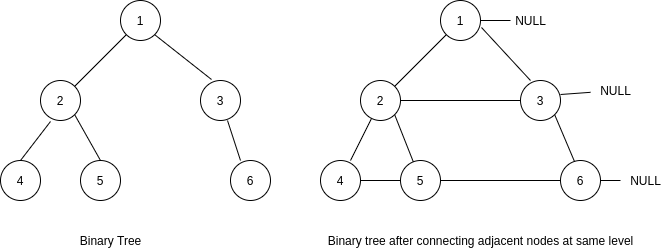
In the tree shown in the picture above -:
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 2 is connected to the node having value 3.
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 4 is connected to the node having value 5.
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 5 is connected to the node having value 6.
The ‘next’ pointer of nodes having value 1, 3, 6 will have a value NULL as there are no next right nodes in their cases.
Note:
1. The structure of the ‘Node’ of a binary tree is already defined. You should not change it.
2. The root of the binary tree is known to you.
3. There is at least one node in the given binary tree.
4. You may only use constant extra space.
Problem approach
A binary tree is a tree where each node has at most two children i.e left child and right child.
You are given a binary tree, where the structure of the node is as follow -:
class BinaryTreeNode {
int data; // Value of the node.
BinaryTreeNode *left; // Pointer to left child node.
BinaryTreeNode *right; // Pointer to right child node.
BinaryTreeNode *next; // Pointer to next right node at same level.
}
Your task is to connect all the adjacent nodes at the same level in the given binary tree. You can do this by populating each 'next' pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL. Initially, all the next pointers are set to NULL.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date2 Nov 2022
Coding problem2
1. Nearest Pallindrome
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a string ‘S' representing a number. Your task is to find the closest palindromic number from this integer represented by 'S'. The closest number is defined as the one for which the absolute difference between the given integer represented by 'S' and the palindrome number is minimum. If more than one number have the same difference then return the smaller integer.
Example:
Let 'S' is 121. Then the nearest integers are 111 and 131 which are palindrome. Both have the same absolute difference but 111 is smaller. Hence 111 is the answer.
Problem approach
You have been given a string ‘S' representing a number. Your task is to find the closest palindromic number from this integer represented by 'S'. The closest number is defined as the one for which the absolute difference between the given integer represented by 'S' and the palindrome number is minimum. If more than one number have the same difference then return the smaller integer.
2. System Design
What is CAP theorem?
Problem approach
CAP(Consistency-Availability-Partition Tolerance) theorem says that a distributed system cannot guarantee C, A and P simultaneously. It can at max provide any 2 of the 3 guarantees. Let us understand this with the help of a distributed database system.
Consistency: This states that the data has to remain consistent after the execution of an operation in the database. For example, post database updation, all queries should retrieve the same result.
Availability: The databases cannot have downtime and should be available and responsive always.
Partition Tolerance: The database system should be functioning despite the communication becoming unstable.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the result of len([1, 2, 3, 4])?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4822 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CargoFlash Info Tech
360 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CargoFlash Info Tech
411 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3584 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Associate Software Engineer
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
807 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







