Cashfree Payments interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Cashfree Payments
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started coding two years ago when I was in my second year. I learned that to secure an internship, coding skills were essential. I began with basic coding and practiced on various platforms, gradually increasing the difficulty of the problems. Later, I transitioned to solving problems categorized by difficulty, starting with easy, then medium, and eventually tackling hard ones. I ensured to cover all the standard problems for each topic.
Application story
Cashfree Payments came to our college on August 10 to hire final year students for SDE-1 roles. There were a total of 4 rounds, and I was rejected in round 3.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was asked a very difficult design question, and I couldn't figure out the solution. Since I lack knowledge in system design, I didn't know how to approach such types of questions, resulting in rejection.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Dynamic Programming (DP), Arrays, Linked Lists, Stacks and Queues, Trees
Tip
Tip 1: Be consistent.
Tip 2: Try to do a variety of questions.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 8 cgpa and above
Resume tip
Tip 1: Have at least 1 project on your resume.
Tip 2: Ensure your resume is strictly one page only.
Tip 3: Include achievements, such as achieving a good rank in a coding contest, to help you stand out
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration80
Interview date13 Aug 2022
Coding problem2
It was at 2 pm in the afternoon time.
1. Dijkstra's shortest path
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an undirected graph of ‘V’ vertices (labeled 0,1,..., V-1) and ‘E’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes (‘X’,’Y’) will have a weight denoting the distance between node ‘X’ and node ‘Y’.
Your task is to find the shortest path distance from the source node, which is the node labeled as 0, to all vertices given in the graph.
Example:
Input:
4 5
0 1 5
0 2 8
1 2 9
1 3 2
2 3 6
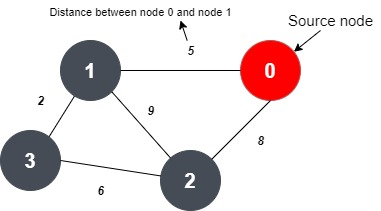
In the given input, the number of vertices is 4, and the number of edges is 5.
In the input, following the number of vertices and edges, three numbers are given. The first number denotes node ‘X’, the second number denotes node ‘Y’ and the third number denotes the distance between node ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
As per the input, there is an edge between node 0 and node 1 and the distance between them is 5.
The vertices 0 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 8.
The vertices 1 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 9.
The vertices 1 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 2.
The vertices 2 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 6.
Note:
1. There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
2. There can be parallel edges i.e. two vertices can be directly connected by more than 1 edge.
Problem approach
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
Create a set sptSet (shortest path tree set) that keeps track of vertices included in the shortest-path tree, i.e., whose minimum distance from the source is calculated and finalized. Initially, this set is empty.
Assign a distance value to all vertices in the input graph. Initialize all distance values as INFINITE. Assign the distance value as 0 for the source vertex so that it is picked first.
While sptSet doesn’t include all vertices
Pick a vertex u which is not there in sptSet and has a minimum distance value.
Include u to sptSet.
Then update distance value of all adjacent vertices of u.
To update the distance values, iterate through all adjacent vertices.
For every adjacent vertex v, if the sum of the distance value of u (from source) and weight of edge u-v, is less than the distance value of v, then update the distance value of v.
Note: We use a boolean array sptSet[] to represent the set of vertices included in SPT. If a value sptSet[v] is true, then vertex v is included in SPT, otherwise not. Array dist[] is used to store the shortest distance values of all vertices.
2. Longest Subarray With Sum K.
Moderate
30m average time
50% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja and his friend are playing a game of subarrays. They have an array ‘NUMS’ of length ‘N’. Ninja’s friend gives him an arbitrary integer ‘K’ and asks him to find the length of the longest subarray in which the sum of elements is equal to ‘K’.
Ninjas asks for your help to win this game. Find the length of the longest subarray in which the sum of elements is equal to ‘K’.
If there is no subarray whose sum is ‘K’ then you should return 0.
Example:
Input: ‘N’ = 5, ‘K’ = 4, ‘NUMS’ = [ 1, 2, 1, 0, 1 ]
Output: 4
There are two subarrays with sum = 4, [1, 2, 1] and [2, 1, 0, 1]. Hence the length of the longest subarray with sum = 4 is 4.
Problem approach
An efficient solution is while traversing the array, storing sum so far in currsum. Also, maintain the count of different values of currsum in a map. If the value of currsum is equal to the desired sum at any instance increment count of subarrays by one.
The value of currsum exceeds the desired sum by currsum – sum. If this value is removed from currsum then the desired sum can be obtained. From the map, find the number of subarrays previously found having sum equal to currsum-sum. Excluding all those subarrays from the current subarray, gives new subarrays having the desired sum.
So increase count by the number of such subarrays. Note that when currsum is equal to the desired sum then also check the number of subarrays previously having a sum equal to 0. Excluding those subarrays from the current subarray gives new subarrays having the desired sum. Increase the count by the number of subarrays having sum 0 in that case.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60
Interview date13 Aug 2022
Coding problem2
After the OA, the results were declared shortly, and I was informed that my interview would be at 5 pm, so I was ready. The interviewer has 3 years of experience. They asked about my internship experience, then presented 2 dynamic programming questions to solve on HackerRank CodePair. Afterward, they inquired about my hobbies.
1. Add One to Linked List
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given a number that is represented in the form of a linked list such that each digit corresponds to a node. He has been asked to add 1 to it and return the updated list.
For Example:
1234 is represented as (1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4) and adding 1 to it should change it to (1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5).
Note:
The input Linked list does not have any trailing zeros.
Problem approach
We can recursively reach the last node and forward the carry to previous nodes. A recursive solution doesn’t require reversing the linked list. Alternatively, we can use a stack in place of recursion to temporarily hold nodes.
2. Maximum In Sliding Windows Of Size K
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array/list of integers of length ‘N’, there is a sliding window of size ‘K’ which moves from the beginning of the array, to the very end. You can only see the ‘K’ numbers in a particular window at a time. For each of the 'N'-'K'+1 different windows thus formed, you are supposed to return the maximum element in each of them, from the given array/list.
Problem approach
Create a Deque, Qi, with capacity K, that stores only the useful elements of the current window of size K. An element is considered useful if it is in the current window and is greater than all other elements to its right within the window. Process all array elements one by one and maintain Qi to contain the useful elements of the current window, sorted in ascending order. The element at the front of Qi is the largest, and the element at the rear/back of Qi is the smallest of the current window.
03
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration70
Interview date13 Aug 2022
Coding problem2
The interview was conducted by an experienced individual with 7 years of experience. He introduced himself and then asked me to do the same. He inquired about some object-oriented programming concepts and then asked about my internship experience. Following that, he questioned why I didn't receive a PPO offer from my previous company and asked about my overall experience there. He also asked about my corporate experience.
Later, he presented a coding question. After I attempted to solve it, he asked me to design a URL shortener. Since I lacked knowledge in system design, this question was completely new and challenging for me. I tried to provide a solution, but it wasn't satisfactory, as I didn't have enough knowledge in the area.
1. Connect Nodes at Same Level
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



A binary tree is a tree where each node has at most two children i.e left child and right child.
You are given a binary tree, where the structure of the node is as follow -:
class BinaryTreeNode {
int data; // Value of the node.
BinaryTreeNode *left; // Pointer to left child node.
BinaryTreeNode *right; // Pointer to right child node.
BinaryTreeNode *next; // Pointer to next right node at same level.
}
Your task is to connect all the adjacent nodes at the same level in the given binary tree. You can do this by populating each 'next' pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL. Initially, all the next pointers are set to NULL.
For Example:
Consider the figure shown below. The left part represents the initial binary tree and right part represents the binary tree after connecting adjacent nodes at the same level.
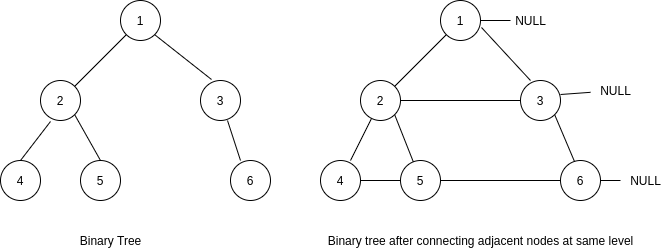
In the tree shown in the picture above -:
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 2 is connected to the node having value 3.
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 4 is connected to the node having value 5.
The ‘next’ pointer of the node having value 5 is connected to the node having value 6.
The ‘next’ pointer of nodes having value 1, 3, 6 will have a value NULL as there are no next right nodes in their cases.
Note:
1. The structure of the ‘Node’ of a binary tree is already defined. You should not change it.
2. The root of the binary tree is known to you.
3. There is at least one node in the given binary tree.
4. You may only use constant extra space.
Problem approach
Follow the below steps to Implement the idea:
1.Initialize a node pointer Prev to NULL and a queue of node pointer Q.
2.Traverse the tree in Breadth-first search order starting from the root.
3.Calculate the size sz of the Q and run a for loop from 0 to sz – 1.
4.If prev is Null then set prev to the current node.
5.Else set prev’s next to the current node and prev to the current node.
6.Set prev’s next to Null and prev to Null.
7.If the current node’s left is not null push it into the queue.
8.If the current node’s right is not null push it into the queue.
2. Designing a Scalable URL Shortener System
Design a URL shortener capable of handling a large load
Tell me which data structures you would use and why.
How can you optimize it.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Cashfree Payments
2994 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6544 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6316 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2180 views
0 comments
0 upvotes









