CGI interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
CGI
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Solve RS Aggarwal Aptitude and Problem Solving Books.
Tip 2 : Practice Coding questions from prepInsta.
Tip 3 : Worked on communication skills
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Mark skills with Bold letters.
Tip 2 : Mention projects on resume
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date7 Oct 2022
Coding problem2
- Morning time
- Environment was good.
- Interviewer was good
1. Segregate Odd-Even
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There is a wedding ceremony at NinjaLand. The bride and groom want everybody to play a game and thus, they have blindfolded the attendees. The people from the bride’s side are holding odd numbers and people from the groom’s side are holding the even numbers. For the game to start quickly, all the bride’s side people should come first, followed by the groom’s side people in the same order.
The attendees of the wedding with their numbers are given in the form of a Singly Linked List, arranged randomly.
A singly linked list is a type of linked list that is unidirectional; that is, it can be traversed in only one direction from head to the last node (tail).
Example:
The attendees holding numbers from 1, 4, 3 are shown:
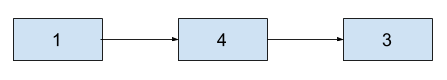
As the organizers are busy, you have to arrange all the people by arranging the bride’s side people first followed by the groom’s side people sequentially.
Note:
For the above example 1 -> 4 -> 3, 1 -> 3 -> 4 is the only correct answer, i.e nodes should be grouped sequentially. Hence, 3 -> 1 -> 4 is the wrong answer as we have to preserve the same order.
Problem approach
Step 1 : Iterate over the loop.
Step 2 : Separate out number divisible by 2 as even.
2. Maximum Subarray Sum
Moderate
35m average time
81% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n', consisting of integers.
A subarray is a contiguous segment of an array. In other words, a subarray can be formed by removing 0 or more integers from the beginning and 0 or more integers from the end of an array.
Find the sum of the subarray (including empty subarray) having maximum sum among all subarrays.
The sum of an empty subarray is 0.
Example :
Input: 'arr' = [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2, -10, 9, 1]
Output: 11
Explanation: The subarray yielding the maximum sum is [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2].
Problem approach
Step 1 : First line of input contains size of array, which is denoted by N and second line of input contains N space separated integers.
Step 2 : First and only line of output should print the maximum subarray sum, N+1.
Step 3 : Apply merge sort
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date16 Sep 2022
Coding problem3
- Morning time
- Environment was good.
- Interviewer was good
1. Colorful Knapsack
Hard
45m average time
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given 'N' stones labeled from 1 to 'N'. The 'i-th' stone has the weight W[i]. There are 'M' colors labeled by integers from 1 to 'M'. The 'i-th' stone has the color C[i] which is an integer between 1 to 'M', both inclusive.
You have been required to fill a Knapsack with these stones. The Knapsack can hold a total weight of 'X'.
You are required to select exactly 'M' stones; one of each color. The sum of the weights of the stones must not exceed 'X'. Since you paid a premium for a Knapsack with capacity 'X', you are required to fill the Knapsack as much as possible.
Write a program to calculate the best way to fill the Knapsack - that is, the unused capacity should be minimized.
Problem approach
s1 : This was solved by me through dynamic programming. Let dp[i][j] denote the maximum possible weight you can fill in the bag with a total capacity of j using exactly one stone of each color from 1 to i.
s2 : Now you can club all same-colored stones in a vector. Then this problem is same as the classical knapsack problem and I passed all test cases and selected for the next round.
2. Merge Point of Two Linked Lists
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



Given two singly linked lists, 'FIRST_HEAD' and 'SECOND_HEAD'. Your task is to find the 'MERGING POINT' i.e. the data of the node at which merging starts. If there is no merging, return -1.
For example:-
The given Linked Lists are merging at node c1.
In this case, c1 is 'MERGING POINT'.
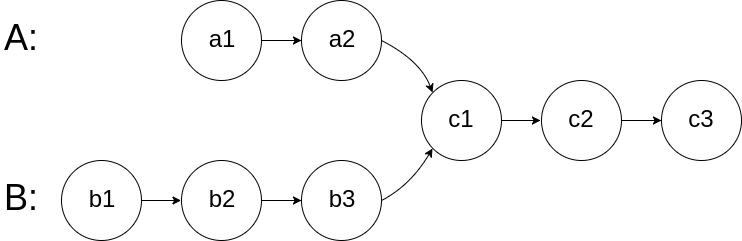
Problem approach
Step 1 : At first I gave the interviewer a complete brute force by considering each element of the first list and comparing it with each element of another list but that was inefficient.
Step 2 : So I gave the interviewer optimal approach by finding difference of lengths of linked list and then traverse bigger linked list to difference. Now start traversing both linked lists till we find the common element. This solution impressed the interviewer.
3. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
Step 1 : Firstly I gave recursion approach but then the interviewer asked me to optimize.
Step 2 : So I gave him a standard DP approach for the longest increasing subsequences by storing the result and use them for future calculations of bigger problem.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration50 minutes
Interview date15 Sep 2022
Coding problem2
- Morning time
- The environment was good.
- Interviewer was good
1. Longest Common Subsequence
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given two Strings “STR1” and “STR2” of characters. Your task is to find the length of the longest common subsequence.
A String ‘a’ is a subsequence of a String ‘b’ if ‘a’ can be obtained from ‘b’ by deletion of several (possibly, zero or all) characters. A common subsequence of two Strings is a subsequence that is common to both Strings.
Problem approach
s1 : By follow approach Binary Search Tree, Check lef and right node leaf
s2 : Compare both nodes by checking which node is smallest
s2 : Merge both nodes
2. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
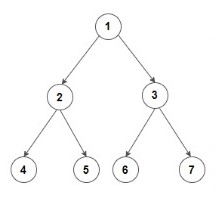
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
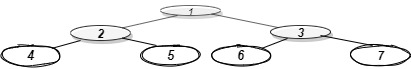
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
Step 1 : Bottom view of the binary tree will be printed on a separate line with all the nodes included in the bottom view separated by a single space.
Step 2 : Interviewer asked me to optimise the solution.
Step 3 : Then I gave solution with merge sort and interviewer was happy.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 16 problems
Interviewed by CGI
1132 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by CGI
527 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CGI
668 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by CGI
716 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








