Ciena interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
UI Developer 2
Ciena
5 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, JavaScript, TypeScript, Angular, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Focus on JS core concepts, don't rush to learn the framework directly.
Tip 2 : Practice writing coding solutions, don't just memorise the solution
Application process
Where: Naukri
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Make a single page resume
Tip 2 : Add only those skills about which you feel confident
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date1 Mar 2021
Coding problem2
It was an online round on codility platform with 2 problems to be attempted in 90 minutes. Two problems were based on Data Structures - Tree and Graph and one on UI concepts.
1. Count Complete Binary Tree Nodes
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a complete binary tree, you are supposed to return the number of nodes in the given tree.
In a complete binary tree every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes in the last level are as far left as possible.
For example:
For the binary trees in the image below.
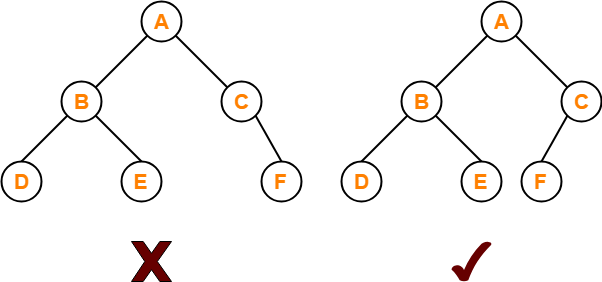
The left tree in the image is not a complete binary tree that’s why it is invalid and the right tree in the image is a valid complete binary tree which contains total 6 nodes.
Problem approach
Step 1 : The approach is to first traverse the tree. To see the maximum value in the given path, the pre-order traversal is used to traverse the given binary tree.
Step 2 : While traversing the tree, keep the track of the maximum value of the node that we have seen so far. If the current node is greater or equal to the max value, then increment the count of the visible node and update the max value with the current node value.
function solution(T) {
if (!T) {
return 0;
}
let leftSubTreeVisibleNodes = getVisibleNodes(T.l, T.x);
let rightSubTreeVisibleNodes = getVisibleNodes(T.r, T.x);
return leftSubTreeVisibleNodes + rightSubTreeVisibleNodes + 1;
}
function getVisibleNodes(tree, prevMax) {
if (!tree) {
return 0;
}
// pass max value upto current node to check for visibility
let leftCount = getVisibleNodes(tree.l, Math.max(prevMax, tree.x));
let rightCount = getVisibleNodes(tree.r, Math.max(prevMax, tree.x));
if (tree.x >= prevMax) {
return leftCount + rightCount + 1;
} else {
return leftCount + rightCount;
}
}
2. Frontend Development
There is a list of elements in the UI with a comment count. Fetch the comments from an API and render them in an optimised manner.
Problem approach
function solution() {
$('.comment-list').each(function () {
const commentCount = +$(this).attr('data-count');
$(this).text('Loading...');
fetch(`https://www.example.com/comments?count=${commentCount}`)
.then(response => response.json())
.then((comments) => {
// make a document fragment and then add fragment as a whole instead of adding individual comments to DOM to improve rendering performance
let fragment = $(document.createDocumentFragment());
comments.forEach((comment) => {
fragment.append($(createCommentItem(comment)));
});
$(this).text('');
$(this).append(fragment);
})
.catch(error => $(this).text(''))
});
}
function createCommentItem(comment) {
return `
${comment.username}
${comment.message}
`;
}
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Mar 2021
Coding problem3
This round was majorly based on JS Core concepts and some DS problems.
1. JS Concepts
- What is Prototypal Inheritance?
- Explain Hoisting, Event Loop?
- What is the difference between Shallow and Deep Copy?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Focus on JS concepts and o/p questions.
Tip 2 : Cross check your solution thoroughly before discussing with the interviewer.
Tip 3 : Study theory as well as keep examples ready.
2. Middle Of Linked List
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of 'N' nodes. The objective is to determine the middle node of a singly linked list. However, if the list has an even number of nodes, we return the second middle node.
Note:
1. If the list is empty, the function immediately returns None because there is no middle node to find.
2. If the list has only one node, then the only node in the list is trivially the middle node, and the function returns that node.
Problem approach
Step 1 : Traverse linked list using two-pointers.
Step 2 : Move one pointer by one and the other pointers by two. When the fast pointer reaches the end, the slow pointer will reach the middle of the linked list.
3. Add Linked Lists
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given two numbers represented by linked lists. Your task is find the sum list and return the head of the sum list.
The sum list is a linked list representation of addition of two numbers.
Problem approach
Step 1 : Calculate sizes of given two linked lists.
Step 2 : If sizes are same, then calculate sum using recursion. Hold all nodes in recursion call stack till the rightmost node, calculate the sum of rightmost nodes and forward carry to the left side.
Step 3 : If size is not same, then follow below steps:
a) Calculate difference of sizes of two linked lists. Let the difference be diff
b) Move diff nodes ahead in the bigger linked list. Now use step 2 to calculate the sum of the smaller list and right sub-list (of the same size) of a larger list. Also, store the carry of this sum.
c) Calculate the sum of the carry (calculated in the previous step) with the remaining left sub-list of a larger list. Nodes of this sum are added at the beginning of the sum list obtained the previous step.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date9 Mar 2021
Coding problem2
This round was based on JS Concepts like Promises, Is JS compiled or interpreted. Some TypeScript concepts like type vs inheritance was also asked. Designing of classes was also discussed.
1. System Design
Show usage of interface in creating classes and what is the advantage of the same. Coding problem on the same as well.
Problem approach
We can use an interface for multiple similar classes having similar functionality. It helps us to define a contract and also we can assign instance of any class to that interface type item at runtime.
2. JS Question
Convert a callback approach to a promise based approach
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Study the concept of promises and its advantage over callback.
Tip 2 : Study promise APIs like all, any etc.
04
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Mar 2021
Coding problem2
This round was based on DS and JS.
1. Right View
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers.
Your task is to print the Right view of it.
The right view of a Binary Tree is a set of nodes visible when the tree is viewed from the Right side and the nodes are printed from top to bottom order.
Problem approach
Step 1 : Level order traversal is used.
Step 2 : Print the right most node of every level. So, do a level order traversal on the tree and print the last node at every level.
2. JS Question
Write a custom deecopy function in JS.
Problem approach
function deepCopy(obj) {
const copyObj = {}
for (const key in obj) {
if (typeof obj[key] === 'object') {
copyObj[key] = deepCopy(obj[key]);
} else {
copyObj[key] = obj[key];
}
}
return copyObj
}
05
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration30 minutes
Interview date12 Mar 2021
Coding problem1
This was a managerial round.
1. Basic HR Questions
- Tell me about yourself
- Why are you looking for a change?
- What are your strengths?
- Where do you see yourself in the upcoming 5 years?
Problem approach
Prepare for some behavioural questions as well.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Ciena
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Ciena
1298 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
UI/UX Engineer 2
5 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Ciena
428 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





