Compro Technologies interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Associate Software Engineer
Compro Technologies
4 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started learning web development using available resources on the internet and created a small project to add to my resume. After that, I joined a classroom course at Coding Ninjas and began DSA preparation in JAVA, which significantly aided me in cracking the technical rounds of the interview.
Application story
I applied on campus, and there was an online round that included DSA, OOPS-related MCQs, and two coding questions. Post clearing that, there were 2-3 rounds based on your performance in technical interview rounds.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
My understanding of web development and background processing, how things happen, like caching, storing user data, and networking, was impressive, according to the interviewer. I was able to create a decent-looking form quickly, which helped me clear the interview sooner than others.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: OOPS, Computer networks, Data Structures, Web Development, DBMS
Tip
Tip 1: A good understanding of HTML, CSS, JS, and any framework is necessary to create a decent project that you can showcase during the interview.
Tip 2: Sorting algorithms are priority 1.
Tip 3: Easy-medium questions on arrays, HashMap, and lists.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 8 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Include your project link.
Tip 2 : Only add skills that you are confident of. Never add them just to fill the space.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date2 Feb 2022
Coding problem2
1. 3Sum
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list ARR consisting of N integers. Your task is to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to a given number K.
An array is said to have a triplet {ARR[i], ARR[j], ARR[k]} with sum = 'K' if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=j and ARR[i] + ARR[j] + ARR[k] = 'K'.
Note:
1. You can return the list of values in any order. For example, if a valid triplet is {1, 2, -3}, then {2, -3, 1}, {-3, 2, 1} etc is also valid triplet. Also, the ordering of different triplets can be random i.e if there are more than one valid triplets, you can return them in any order.
2. The elements in the array need not be distinct.
3. If no such triplet is present in the array, then return an empty list, and the output printed for such a test case will be "-1".
2. Top View of the Binary Tree
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the top view of the given binary tree.
Top view of the binary tree is the set of nodes which are visible when we see the tree from the top.
For example:
For the given binary tree
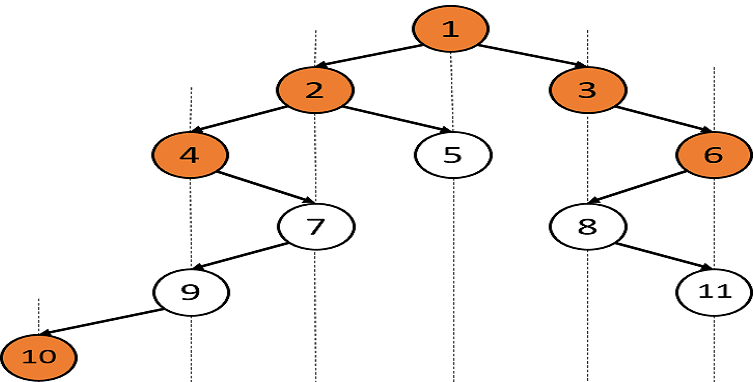
The top view of the tree will be {10, 4, 2, 1, 3, 6}.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date4 Feb 2022
Coding problem2
1. Covid Spread
Hard
45m average time
55% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a city which contains 'N' x 'M' houses, where each house can have one of the following three conditions :
1. The value ‘0’ represents an empty house,
2. The value ‘1’ represents a non-infected person,
3. The value ‘2’ represents an infected person.
It takes one day to propagate the infection from an infected house to its adjacent (Front, Back, Left, Right) non-empty and non-infected house. An empty house can only break the line of propagation of infection.
You need to return the minimum number of days Covid will take to infect each and every house in the city. And for the God’s sake if this is impossible, return -1 instead.
2. Puzzle Question
You are blindfolded and 10 coins are placed in front of you on the table. You are allowed to touch the coins but can’t tell which way up they are by feel. It is told to you that there are 5 coins head up and 5 coins tails up, but not which ones are which. Can you make two piles of coins, each with the same number of heads up? You can flip the coins any number of times.(Learn)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date11 Feb 2022
Coding problem3
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
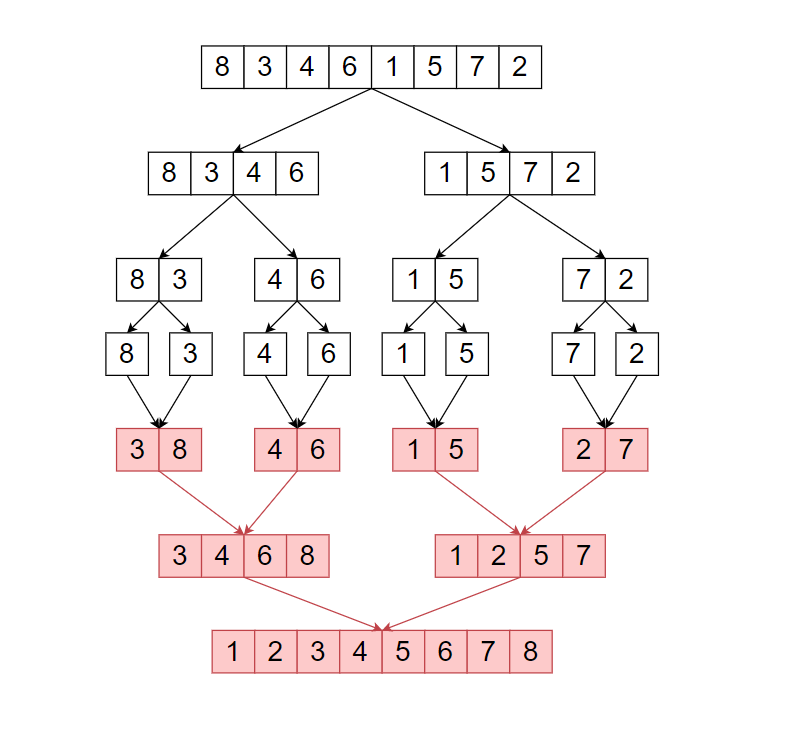
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
// C++ program for Merge Sort
#include
using namespace std;
// Merges two subarrays of array[].
// First subarray is arr[begin..mid]
// Second subarray is arr[mid+1..end]
void merge(int array[], int const left, int const mid,
int const right)
{
int const subArrayOne = mid - left + 1;
int const subArrayTwo = right - mid;
// Create temp arrays
auto *leftArray = new int[subArrayOne],
*rightArray = new int[subArrayTwo];
// Copy data to temp arrays leftArray[] and rightArray[]
for (auto i = 0; i < subArrayOne; i++)
leftArray[i] = array[left + i];
for (auto j = 0; j < subArrayTwo; j++)
rightArray[j] = array[mid + 1 + j];
auto indexOfSubArrayOne = 0, indexOfSubArrayTwo = 0;
int indexOfMergedArray = left;
// Merge the temp arrays back into array[left..right]
while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne
&& indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) {
if (leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne]
<= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo]) {
array[indexOfMergedArray]
= leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne];
indexOfSubArrayOne++;
}
else {
array[indexOfMergedArray]
= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo];
indexOfSubArrayTwo++;
}
indexOfMergedArray++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of
// left[], if there are any
while (indexOfSubArrayOne < subArrayOne) {
array[indexOfMergedArray]
= leftArray[indexOfSubArrayOne];
indexOfSubArrayOne++;
indexOfMergedArray++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of
// right[], if there are any
while (indexOfSubArrayTwo < subArrayTwo) {
array[indexOfMergedArray]
= rightArray[indexOfSubArrayTwo];
indexOfSubArrayTwo++;
indexOfMergedArray++;
}
delete[] leftArray;
delete[] rightArray;
}
// begin is for left index and end is right index
// of the sub-array of arr to be sorted
void mergeSort(int array[], int const begin, int const end)
{
if (begin >= end)
return;
int mid = begin + (end - begin) / 2;
mergeSort(array, begin, mid);
mergeSort(array, mid + 1, end);
merge(array, begin, mid, end);
}
void printArray(int A[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << A[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Given array is \n";
printArray(arr, arr_size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr_size - 1);
cout << "\nSorted array is \n";
printArray(arr, arr_size);
return 0;
}
2. Heap Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘ARR’ consisting of 'N' integers, and your task is to sort the given array in non-decreasing order using the Heap sort algorithm.
Problem approach
// C++ program for implementation of Heap Sort
#include
using namespace std;
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i
// which is an index in arr[].
// n is size of heap
void heapify(int arr[], int N, int i)
{
// Initialize largest as root
int largest = i;
// left = 2*i + 1
int l = 2 * i + 1;
// right = 2*i + 2
int r = 2 * i + 2;
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < N && arr[l] > arr[largest])
largest = l;
// If right child is larger than largest
// so far
if (r < N && arr[r] > arr[largest])
largest = r;
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
swap(arr[i], arr[largest]);
// Recursively heapify the affected
// sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
// Main function to do heap sort
void heapSort(int arr[], int N)
{
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (int i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// One by one extract an element
// from heap
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// A utility function to print array of size n
void printArray(int arr[], int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
heapSort(arr, N);
cout << "Sorted array is \n";
printArray(arr, N);
}
3. Puzzle Question
There are 25 horses among which you need to find out the fastest 3 horses. You can conduct a race among at most 5 to find out their relative speeds. At no point can you find out the actual speed of the horses in a race. Find out the minimum number of races required to determine the top 3 horses. (Learn)
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration45 minutes
Interview date15 Feb 2022
Coding problem1
1. Basic HR Questions
Tell me about yourself.
Why do you want to join us?
What are your future plans?
Problem approach
Tip 1: stay calm and take your time before answering any questions.
Tip 2: Pre-prepare some general HR ques.
Tip 3: have some content ready beforehand

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4781 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 11 problems
Interviewed by Compro Technologies
216 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Amdocs
2391 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2728 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 15 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2382 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







