CSG interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
CSG
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
In my second year, I took a course in competitive programming from Coding Ninjas, which helped me dive deep into DSA. I then started practising problems on online coding platforms.
Application story
It was an off-campus drive with three rounds, including a technical interview and a managerial round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I prepared for DSA using the Coding Ninjas platform and took a course that helped me master it.
Preparation
Duration: 3 Months
Topics: Dynamic Programming, Graphs, DSA, OS, Networking, OOPs
Tip
Tip 1: Focus on DSA
Tip 2: Study CS fundamentals (mainly OOP and DBMS)
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: 8 CGPA, (Salary Package: 12 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Don't include false information in your resume.
Tip 2: Be prepared to discuss your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date10 Jan 2024
Coding problem2
It was a managerial round where the manager asked me about my journey and past experiences.
1. Sort Array
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array consisting of 'N' positive integers where each integer is either 0 or 1 or 2. Your task is to sort the given array in non-decreasing order.
Note :
1. The array consists of only 3 distinct integers 0, 1, 2.
2. The array is non-empty.
Problem approach
Prepare some sorting algorithms before going.
2. Count All Subarrays With Given Sum
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an integer array 'arr' of size 'N' and an integer 'K'.
Your task is to find the total number of subarrays of the given array whose sum of elements is equal to k.
A subarray is defined as a contiguous block of elements in the array.
Example:
Input: ‘N’ = 4, ‘arr’ = [3, 1, 2, 4], 'K' = 6
Output: 2
Explanation: The subarrays that sum up to '6' are: [3, 1, 2], and [2, 4].
Problem approach
1. Initialize the map.
2. Iterate through the array and check if the required subarray is found; if so, increment the answer by 1.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date12 Jan 2024
Coding problem2
Problem solving.
1. Merge Intervals
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given N number of intervals, where each interval contains two integers denoting the start time and the end time for the interval.
The task is to merge all the overlapping intervals and return the list of merged intervals sorted by increasing order of their start time.
Two intervals [A,B] and [C,D] are said to be overlapping with each other if there is at least one integer that is covered by both of them.
For example:
For the given 5 intervals - [1, 4], [3, 5], [6, 8], [10, 12], [8, 9].
Since intervals [1, 4] and [3, 5] overlap with each other, we will merge them into a single interval as [1, 5].
Similarly, [6, 8] and [8, 9] overlap, merge them into [6,9].
Interval [10, 12] does not overlap with any interval.
Final List after merging overlapping intervals: [1, 5], [6, 9], [10, 12].
Problem approach
Intuition
If we sort the intervals by their start value, each set of intervals that can be merged will appear as a contiguous "run" in the sorted list.
2. Detect Cycle In A Directed Graph
Moderate
30m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a directed graph having ‘N’ nodes. A matrix ‘EDGES’ of size M x 2 is given which represents the ‘M’ edges such that there is an edge directed from node EDGES[i][0] to node EDGES[i][1].
Find whether the graph contains a cycle or not, return true if a cycle is present in the given directed graph else return false.
For Example :
In the following directed graph has a cycle i.e. B->C->E->D->B.
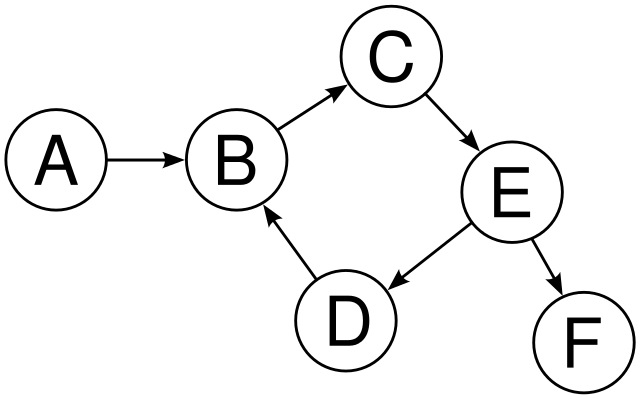
Note :
1. The cycle must contain at least two nodes.
2. It is guaranteed that the given graph has no self-loops in the graph.
3. The graph may or may not be connected.
4. Nodes are numbered from 1 to N.
5. Your solution will run on multiple test cases. If you are using global variables make sure to clear them.
Problem approach
To find cycle in a directed graph we can use the Depth First Traversal (DFS) technique. It is based on the idea that there is a cycle in a graph only if there is a back edge [i.e., a node points to one of its ancestors in a DFS tree] present in the graph.
To detect a back edge, we need to keep track of the visited nodes hat are in the current recursion stack [i.e., the current path that we are visiting]. Please note that all ancestors of a node are present in recursion call stack during DFS. So if there is an edge to an ancestor in DFS, then this is a back edge.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date22 Oct 2024
Coding problem3
Problem solving.
1. Target Sum
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘ARR’ of ‘N’ integers and a target number, ‘TARGET’. Your task is to build an expression out of an array by adding one of the symbols '+' and '-' before each integer in an array, and then by concatenating all the integers, you want to achieve a target. You have to return the number of ways the target can be achieved.
For Example :
You are given the array ‘ARR’ = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], ‘TARGET’ = 3. The number of ways this target can be achieved is:
1. -1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
2. +1 - 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
3. +1 + 1 - 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
4. +1 + 1 + 1 - 1 + 1 = 3
5. +1 + 1 + 1 + 1 - 1 = 3
These are the 5 ways to make. Hence the answer is 5.
Problem approach
The very basic approach is to generate all the possible pairs and check if any pair exists whose sum is equals to given target value, then increment the count variable.
2. Cache & CDN
What is cache, and how does a CDN work?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8771 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
938 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7923 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4395 views
1 comments
0 upvotes






