Directi interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Directi
4 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date16 Mar 2015
Coding problem2
This was a technical round.
1. Find duplicate in array
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'ARR' consisting of N integers, which contains elements only in the range 0 to N - 1. Some of the elements may be repeated in 'ARR'. Your task is to find all such duplicate elements.
Note:
1. All the elements are in the range 0 to N - 1.
2. The elements may not be in sorted order.
3. You can return the duplicate elements in any order.
4. If there are no duplicates present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
Concept of indexing can be used to solve this question.
Traverse the array. For every element at index i,visit a[i]. If a[i] is positive, then change it to negative. If a[i] is negative, it means the element has already been visited and thus it is repeated. Print that element.
Pseudocode :
findRepeating(arr[], n)
{
missingElement = 0
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
element = arr[abs(arr[i])]
if(element < 0){
missingElement = arr[i]
break
}
arr[abs(arr[i])] = -arr[abs(arr[i])]
}
return abs(missingElement)
}2. Find a triplet that sum to a given value
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list ARR consisting of N integers. Your task is to find all the distinct triplets present in the array which adds up to a given number K.
An array is said to have a triplet {ARR[i], ARR[j], ARR[k]} with sum = 'K' if there exists three indices i, j and k such that i!=j, j!=k and i!=j and ARR[i] + ARR[j] + ARR[k] = 'K'.
Note:
1. You can return the list of values in any order. For example, if a valid triplet is {1, 2, -3}, then {2, -3, 1}, {-3, 2, 1} etc is also valid triplet. Also, the ordering of different triplets can be random i.e if there are more than one valid triplets, you can return them in any order.
2. The elements in the array need not be distinct.
3. If no such triplet is present in the array, then return an empty list, and the output printed for such a test case will be "-1".
Problem approach
Sorting can be used to solve this problem. Next, two -pointer technique can be applied on the sorted array.
Traverse the array and fix the first element of the triplet. Now use the Two Pointer technique to find if there is a pair whose sum is equal to x – array[i].
• Algorithm :
1. Sort the given array.
2. Loop over the array and fix the first element of the possible triplet, arr[i].
3. Then fix two pointers, one at i + 1 and the other at n – 1. And look at the sum,
1. If the sum < required sum, increment the first pointer.
2. Else, If the sum > required sum, Decrease the end pointer to reduce the sum.
3. Else, if the sum of elements at two-pointers == required sum, then print the triplet and break.
Time Complexity : O(nlogn)
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date16 Mar 2015
Coding problem2
This was a technical interview round with questions on Programming and algorithms.
1. Box Stacking
Hard
25m average time
65% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a set of ‘n’ types of rectangular 3-D boxes. The height, width, and length of each type of box are given by arrays, ‘height’, ‘width’, and ‘length’ respectively, each consisting of ‘n’ positive integers. The height, width, length of the i^th type box is given by ‘height[i]’, ‘width[i]’ and ‘length[i]’ respectively.
You need to create a stack of boxes that is as tall as possible using the given set of boxes.
Below are a few allowances:
You can only stack a box on top of another box if the dimensions of the 2-D base of the lower box ( both length and width ) are strictly larger than those of the 2-D base of the higher box.
You can rotate a box so that any side functions as its base. It is also allowed to use multiple instances of the same type of box. This means, a single type of box when rotated, will generate multiple boxes with different dimensions, which may also be included in stack building.
Return the height of the highest possible stack so formed.
Note:
The height, Width, Length of the type of box will interchange after rotation.
No two boxes will have all three dimensions the same.
Don’t print anything, just return the height of the highest possible stack that can be formed.
Problem approach
- Make an integer matrix ‘boxes’ of dimension (3*n, 3), we will store all three rotations of each type of boxes in it.
- Generate all 3 rotations for all ‘n’ types of boxes, for simplicity we will consider ‘width’ always smaller than or equal to ‘length’. Store them in matrix ‘boxes’ such that ‘boxes[i][0]’, ‘boxes[i][1]’, ‘boxes[i][2]’ give height, width, length of ‘i’th box respectively.
- Sort the matrix ‘boxes’ in decreasing order of base area. Base area of i^th box is given by ‘boxes[i][1] * boxes[i][2]’.
- Make an integer array ‘maxHeight’ of size 3*n, where maxHeight[i] will give the maximum height of the stack if the ‘i^th’ box after sorting is the topmost box of the stack.
- Initialize an integer variable ‘result’:= 0, it will keep track of the maximum possible height of stack so far.
- Run a loop where ‘i’ ranges from 0 to 3*n-1 and for each ‘i’ perform the following steps-:
- Assign ‘maxHeight[i]’ := ‘boxes[i][0]’.
- Run a loop where j ranges from 0 to i-1. If ‘boxes[j][1]’ and ‘boxes[j][2]’ is strictly greater than ‘boxes[i][1]’ and ‘boxes[i][2]’ respectively, then update ‘maxHeight[i]’ with maximum of its current value and sum of of ‘maxHeight[j]’ + ‘boxes[i][0]’.
- Update ‘result’ with the maximum of its current value and ‘maxHeight[i]’.
- Return ‘result’
TC : O(N ^ 2), where ‘N’ is the number of types of boxes.
2. Maximum Sum Subarray
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array of numbers, find the maximum sum of any contiguous subarray of the array.
For example, given the array [34, -50, 42, 14, -5, 86], the maximum sum would be 137, since we would take elements 42, 14, -5, and 86.
Given the array [-5, -1, -8, -9], the maximum sum would be -1.
Follow up: Do this in O(N) time.
Problem approach
The direct approach to solve this problem is to run two for loops and for every subarray check if it is the maximum sum possible.
Time complexity: O(N^2), Where N is the size of the array.
Space complexity: O(1)
The efficient approach is to use Kadane's algorithm. It calculates the maximum sum subarray ending at a particular index by using the maximum sum subarray ending at the previous position.
Steps :
Declare two variables : currSum which stores maximum sum ending here and maxSum which stores maximum sum so far.
Initialize currSum = 0 and maxSum = INT_MIN.
Now, traverse the array and add the value of the current element to currSum and check :
1. If currSum > maxSum, update maxSum equals to currSum.
2. If currSum < 0, make currSum equal to zero.
Finally, print the value of maxSum.
03
Round
Medium
Telephonic
Duration50 minutes
Interview date16 Mar 2015
Coding problem2
This was a difficult on to face as we have to hold phone and concentrate and explaining is also very difficult.
1. Stock Buy and sell
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'prices' where the elements of the array represent the prices of the stock as they were yesterday and indices of the array represent minutes. Your task is to find and return the maximum profit you can make by buying and selling the stock. You can buy and sell the stock only once.
Note:
You can’t sell without buying first.
For Example:
For the given array [ 2, 100, 150, 120],
The maximum profit can be achieved by buying the stock at minute 0 when its price is Rs. 2 and selling it at minute 2 when its price is Rs. 150.
So, the output will be 148.
Problem approach
The idea is to traverse the given list of prices and find a local minimum of every increasing sequence. We can gain maximum profit if we buy the shares at the starting of every increasing sequence (local minimum) and sell them at the end of the increasing sequence (local maximum).
Steps :
1. Find the local minima and store it as starting index. If not exists, return.
2. Find the local maxima. and store it as an ending index. If we reach the end, set the end as the ending index.
3. Update the solution and Increment count of buy-sell pairs.
4. Repeat the above steps till the end is not reached.
2. Dijikstra Algorithm
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an undirected graph of ‘V’ vertices (labeled 0,1,..., V-1) and ‘E’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes (‘X’,’Y’) will have a weight denoting the distance between node ‘X’ and node ‘Y’.
Your task is to find the shortest path distance from the source node, which is the node labeled as 0, to all vertices given in the graph.
Example:
Input:
4 5
0 1 5
0 2 8
1 2 9
1 3 2
2 3 6
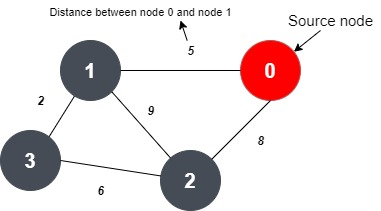
In the given input, the number of vertices is 4, and the number of edges is 5.
In the input, following the number of vertices and edges, three numbers are given. The first number denotes node ‘X’, the second number denotes node ‘Y’ and the third number denotes the distance between node ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
As per the input, there is an edge between node 0 and node 1 and the distance between them is 5.
The vertices 0 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 8.
The vertices 1 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 9.
The vertices 1 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 2.
The vertices 2 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 6.
Note:
1. There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
2. There can be parallel edges i.e. two vertices can be directly connected by more than 1 edge.
Problem approach
Dijkstra's Algorithm basically starts at the source node and it analyzes the graph to find the shortest path between that node and all the other nodes in the graph.
The algorithm keeps track of the currently known shortest distance from each node to the source node and it updates these values if it finds a shorter path.
Once the shortest path between the source node and another node is found, that node is marked as "visited" and added to the path.
The process continues until all the nodes in the graph have been added to the path. This way, we have a path that connects the source node to all other nodes following the shortest path possible to reach each node.
Pseudocode :
function Dijkstra(Graph, source):
2: for each vertex v in Graph: // Initialization
3: dist[v] := infinity // initial distance from source to vertex v is set to infinite
4: previous[v] := undefined // Previous node in optimal path from source
5: dist[source] := 0 // Distance from source to source
6: Q := the set of all nodes in Graph // all nodes in the graph are unoptimized - thus are in Q
7: while Q is not empty: // main loop
8: u := node in Q with smallest dist[ ]
9: remove u from Q
10: for each neighbor v of u: // where v has not yet been removed from Q.
11: alt := dist[u] + dist_between(u, v)
12: if alt < dist[v] // Relax (u,v)
13: dist[v] := alt
14: previous[v] := u
15: return previous[ ]
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date16 Mar 2015
Coding problem1
This was a small interaction just to make us familiar in Mumbai office.
1. Basic HR Questions
1. Introduce Yourself.
2. What do you think about Directi?
3. What are your favourite subjects?
4. Which programming language do you prefer?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Directi
814 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Directi
884 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Directi
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Directi
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





