DTCC interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
DTCC
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I have done my BTech during my studies I started doing the coding questions and participating in the interview mocks.Till then i have done a numbers of questions in all the practicing websites.
Application story
This is an on-campus opportunity for me company visited to my campus for the placement. They have given a CGPA-wise cutoff also
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because i was not able to provide the accurate solution for the question given to me.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, Object-Oriented Programming System, Operating system, Database Management System
Tip
Try to do Data Structures and Algorithms based questions and firstly attempt it yourself before going to the solution, also try to do it as quickly as you can. Also prepare for theory subjects like Operating system, Database Management System, etc which I prepared through Coding Ninjas subjective notes and they are very accurate and up to mark
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2: Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 mins
Interview date25 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Level order traversal
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the level order traversal of the given tree.
For example:
For the given binary tree
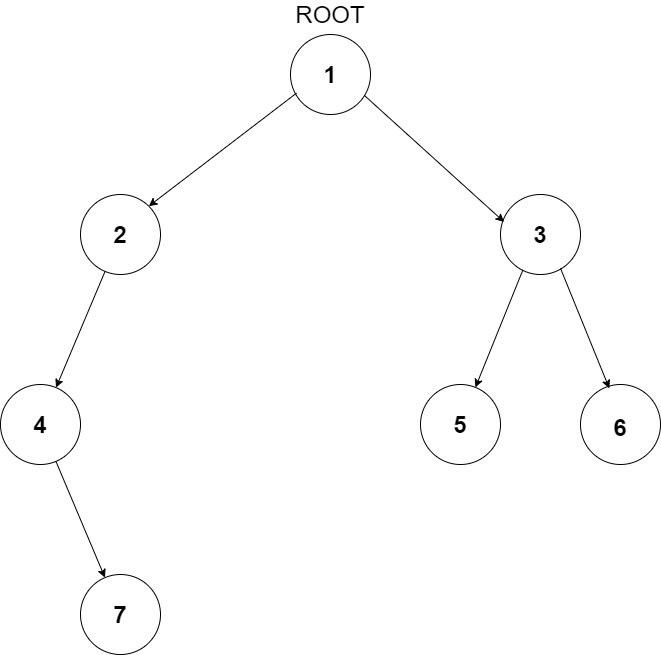
The level order traversal will be {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}.
Problem approach
You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the level order traversal of the given tree.
2. Maximum meetings
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the schedule of 'N' meetings with their start time 'Start[i]' and end time 'End[i]'.
You have only 1 meeting room. So, you need to return the maximum number of meetings you can organize.
Note:
The start time of one chosen meeting can’t be equal to the end time of the other chosen meeting.
For example:
'N' = 3, Start = [1, 3, 6], End = [4, 8, 7].
You can organize a maximum of 2 meetings. Meeting number 1 from 1 to 4, Meeting number 3 from 6 to 7.
Problem approach
You are given the schedule of N meetings with their start time Start[i] and end time End[i]. But you have only 1 meeting room. So, you need to tell the meeting numbers you can organize in the given room, such that the number of meetings organized is maximum.
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 mins
Interview date25 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Longest Consecutive Sequence
Moderate
40m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an unsorted array/list 'ARR' of 'N' integers. Your task is to return the length of the longest consecutive sequence.
The consecutive sequence is in the form ['NUM', 'NUM' + 1, 'NUM' + 2, ..., 'NUM' + L] where 'NUM' is the starting integer of the sequence and 'L' + 1 is the length of the sequence.
Note:
If there are any duplicates in the given array we will count only one of them in the consecutive sequence.
For example-
For the given 'ARR' [9,5,4,9,10,10,6].
Output = 3
The longest consecutive sequence is [4,5,6].
Follow Up:
Can you solve this in O(N) time and O(N) space complexity?
Problem approach
Your task is to return the length of the longest consecutive sequence.
2. N-th Fibonacci Number
Moderate
40m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an integer ‘N’, your task is to find and return the N’th Fibonacci number using matrix exponentiation.
Since the answer can be very large, return the answer modulo 10^9 +7.
Fibonacci number is calculated using the following formula:
F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2),
Where, F(1) = F(2) = 1.
For Example:
For ‘N’ = 5, the output will be 5.
Problem approach
The value N is a Positive integer that should be read from STDIN. The Nth term that is calculated by the program should be written to STDOUT. Other than the value of Nth term, no other characters/strings or message should be written to STDOUT.
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 mins
Interview date25 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Permutations
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



A permutation is a mathematical technique that determines the number of possible arrangements in a set when the order of the arrangements matters. A string of length 'N' has 'N'! permutations.
Given an array of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations of the array.
Example:
'ARR[]' = [1, 2]
The size of the array is 2. So, the total number of permutations is 2! = 2. The possible permutations are [1, 2] (the array itself) and [2,1] where the position of element 1 in the original array is swapped with element 2 and vice-versa.
Note:
1. All the numbers in the array are unique.
2. You can return the answer in any order.
3. The original array is also a permutation of the given array.
Problem approach
Maintain two variables num and den to store numerator and denominator.
We need to find n! and (n-r)!.
Traverse from 1 to n and multiple i by num to find n!.
Traverse from 1 to (n-r) and multiply i by den to find (n-r)!.
num/den is the final answer
2. Sort Array
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array of size ‘n’ to find the minimum number of steps to either convert it into either non-decreasing or non-increasing array. In one step you can either increment or decrement the element of the array.
Problem approach
Repeatedly swap 2 adjacent elements if arr[j] > arr[j+1] .
Here, the maximum element of the unsorted array reaches the end of the unsorted array after each iteration.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by DTCC
1005 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by DTCC
1102 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by DTCC
1503 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






