EPAM Systems interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer Intern
EPAM Systems
4 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My journey has been a mix of consistency, self-belief, and structured preparation. I started with the basics of programming and gradually moved towards mastering DSA, databases, operating systems, and system design concepts while simultaneously building projects to strengthen my practical knowledge. Along the way, I created a roadmap for myself that balanced coding practice, concept revision, and mock interviews.
Cracking the EPAM interview wasn’t just about one day. It was about challenging myself; I transitioned from coding in C++ to Java within a month, specifically for EPAM. Thumb Rule: Solving at least 2 DSA questions every day.
Application story
It was an on-campus opportunity, and I was excited to apply for this role. I filled out the application form and was shortlisted for the initial online assessment round, which I successfully qualified, and moved on to the Group Discussion. After that, I appeared for the technical round, followed by the HR round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected in the end because I was confident about my skills, and at the same time, I was willing to learn and contribute to this field without restricting myself to any particular technology, language, or domain.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: DSA, OOPS, Graph Algorithms, DBMS, OS, JavaScript, NextJS, SQL
Tip
Tip 1: Solve at least two DSA questions every day.
Tip 2: Keep notes of the approach and revise twice a week.
Tip 3: Keep core concepts (OS, DBMS) at fingertips.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 60% in 10th 12th & 70% in graduation, (Salary Package: 8.48 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Use action keywords to rank your resume better.
Tip 2: Use numerical indicators to show the results or impacts of your projects.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration70 minutes
Interview date18 Jul 2025
Coding problem2
It was an afternoon shift for me. The exam was closely proctored. The questions were easy to medium level.
1. Rotation
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given an array 'arr' having 'n' distinct integers sorted in ascending order. The array is right rotated 'r' times
Find the minimum value of 'r'.
Right rotating an array means shifting the element at 'ith' index to (‘i+1') mod 'n' index, for all 'i' from 0 to ‘n-1'.
Example:
Input: 'n' = 5 , ‘arr’ = [3, 4, 5, 1, 2]
Output: 3
Explanation:
If we rotate the array [1 ,2, 3, 4, 5] right '3' times then we will get the 'arr'. Thus 'r' = 3.
Problem approach
I went for a straightforward brute force approach. Since the array is originally sorted in ascending order, I simply traversed the array once while keeping track of the minimum element and its index. The index at which this minimum element occurred was the answer.
2. String Mismatch Finder
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given two strings, s1 and s2, which are guaranteed to be of the same length.
Your task is to compare these two strings character by character and identify all the positions (indices) where they differ. You need to return a list of these 0-indexed positions.
Problem approach
My approach is simple and linear. I initialize a counter to zero and then traverse both strings character by character. At each index, I check if the characters are different, and if they are, I increment the counter. After completing the traversal, the counter gives the total number of differing positions.
02
Round
Medium
Group Discussion
Duration30 minutes
Interview date4 Aug 2025
Coding problem1
1. Effects of the US Tariffs on India
Topic: Effects of the US Tariffs on India (Focus: Ground-level effects on Indian Manufacturers).
There were 10 participants in GD.
Problem approach
I aim to initiate or conclude the discussion and participate at least 2–3 times in between. I try to stay on topic, put forward only relevant points, and highlight key facts and figures.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date5 Aug 2025
Coding problem2
1. Dijkstra's shortest path
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an undirected graph of ‘V’ vertices (labeled 0,1,..., V-1) and ‘E’ edges. Each edge connecting two nodes (‘X’,’Y’) will have a weight denoting the distance between node ‘X’ and node ‘Y’.
Your task is to find the shortest path distance from the source node, which is the node labeled as 0, to all vertices given in the graph.
Example:
Input:
4 5
0 1 5
0 2 8
1 2 9
1 3 2
2 3 6
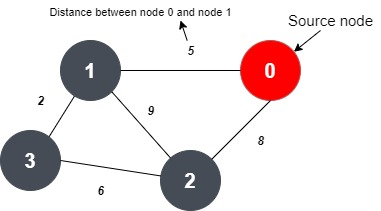
In the given input, the number of vertices is 4, and the number of edges is 5.
In the input, following the number of vertices and edges, three numbers are given. The first number denotes node ‘X’, the second number denotes node ‘Y’ and the third number denotes the distance between node ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
As per the input, there is an edge between node 0 and node 1 and the distance between them is 5.
The vertices 0 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 8.
The vertices 1 and 2 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 9.
The vertices 1 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 2.
The vertices 2 and 3 have an edge between them and the distance between them is 6.
Note:
1. There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
2. There can be parallel edges i.e. two vertices can be directly connected by more than 1 edge.
Problem approach
To solve Dijkstra’s algorithm, I first initialize the distance of the source node as 0 and set the distance of all other nodes to infinity, since we don’t yet know the shortest paths. I then use a priority queue (min-heap) to always pick the node with the smallest current distance.
When I pick a node, I look at all of its neighbors. For each neighbor, I check if the distance through the current node is shorter than the previously recorded distance. If it is, I update the neighbor’s distance and push it into the priority queue with this new value.
This process repeats until the priority queue becomes empty. In the end, the distance array will contain the shortest distance from the source to every other node in the graph.
2. Implement Queue Using Linked List
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in company

You are given ‘q’ queries, where each query can be of the following types:
(1) 1 x -> this means to push the element ‘x’ in the queue.
(2) 2 -> This means deleting the front element of the queue and returning it. If there’s no element in the queue, return -1.
Your task is to implement a queue that supports these two queries.
You must write an algorithm whose time complexity is O(1), and whose space complexity is O(1).
Note:
In the output, you will see the output of queries of type 2.
In the queries, there will be at least one type 2 query.
You will be given two functions, ‘push’, and ‘pop’.
Your task is to implement the two functions.
Example:
Input: ‘q’ = 5
‘queries’ = [[1 3], [2], [1 4], [2], [2]]
Output: 3 4 -1
Explanation: After the first query, the queue is {3}. After the second query, the queue is {}, and we returned 3. After the third query, the queue is {4}. After the fourth query, the queue is {}, and we returned 4. After the fifth query, the queue is {}, and we returned -1(since there was no element at the time of the pop statement).
Problem approach
To implement a queue using a doubly linked list, I maintain two pointers front and rear. Enqueue operation is done by inserting a new node at the rear end, and dequeue operation is done by removing the node from the front end. Since the doubly linked list allows constant-time insertion and deletion at both ends, both operations run in O(1) time.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date5 Aug 2025
Coding problem1
Basic HR questions and behavioural & situational questions were asked in this round.
1. HR Questions
Can you describe a situation where you had to make a difficult choice? What choice did you make, and why?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Choose from your experience.
Tip 2: Don't Bluff.
Tip 3: Highlight what you learnt from the situation.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Junior Software Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by EPAM Systems
2111 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by EPAM Systems
2037 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by EPAM Systems
824 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Junior Software Engineer
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by EPAM Systems
1258 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer Intern
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1249 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer Intern
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
606 views
1 comments
0 upvotes




