Epsilon interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 2
Epsilon
3 rounds | 14 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Java , Design Patterns, Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 2 years of experience
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Jul 2021
Coding problem8
This round had 1 question related to DSA and then the majority of the questions were revolving around Java.
1. Intersection Point in 2 Linked List
Easy
25m average time
73% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two Singly Linked Lists of integers, which may have an intersection point.
Your task is to return the first intersection node. If there is no intersection, return NULL.
Example:-
The Linked Lists, where a1, a2, c1, c2, c3 is the first linked list and b1, b2, b3, c1, c2, c3 is the second linked list, merging at node c1.

Problem approach
Approach (Using 2-pointers) :
1) Initialize two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 at the head1 and head2.
2) Traverse through the lists,one node at a time.
3) When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then redirect it to the head2.
4) Similarly when ptr2 reaches the end of a list, redirect it the head1.
5) Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be equidistant from the collision point
6) If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is the intersection node.
7) After second iteration if there is no intersection node it returns NULL.
TC : O(m+n) where m=Length of LL-1 and n=Length of LL-2
SC : O(1)
2. Java Question
What is Garbage collector in JAVA?
Problem approach
1) Garbage Collection in Java is a process by which the programs perform memory management automatically.
2) The Garbage Collector(GC) finds the unused objects and deletes them to reclaim the memory.
3) In Java, dynamic memory allocation of objects is achieved using the new operator that uses some memory and the memory remains allocated until there are references for the use of the object.
4) When there are no references to an object, it is assumed to be no longer needed, and the memory, occupied by the object can be reclaimed.
5) There is no explicit need to destroy an object as Java handles the de-allocation automatically.
The technique that accomplishes this is known as Garbage Collection. Programs that do not de-allocate memory can eventually crash when there is no memory left in the system to allocate. These programs are said to have memory leaks.
Garbage collection in Java happens automatically during the lifetime of the program, eliminating the need to de-allocate memory and thereby avoiding memory leaks.
In C language, it is the programmer’s responsibility to de-allocate memory allocated dynamically using free() function.
This is where Java memory management leads.
3. Java Question
Why Java is platform independent and JVM platform dependent?
Problem approach
JVM is platform dependent because it takes java byte code and generates byte code for the current operating system. So Java software is platform dependent but Java language is platform-independent because different operating system have different JVMs.
4. Java Question
What do you understand by marker interfaces in Java?
Problem approach
Marker interfaces, also known as tagging interfaces are those interfaces that have no methods and constants defined in them. They are there for helping the compiler and JVM to get run time-related information regarding the objects.
5. Java Question
How would you differentiate between a String, StringBuffer, and a StringBuilder?
Problem approach
1) Storage area : In string, the String pool serves as the storage area. For StringBuilder and StringBuffer, heap memory is the storage area.
2) Mutability : A String is immutable, whereas both the StringBuilder and StringBuffer are mutable.
3) Efficiency : It is quite slow to work with a String. However, StringBuilder is the fastest in performing operations. The speed of a StringBuffer is more than a String and less than a StringBuilder. (For example, appending a character is fastest in StringBuilder and very slow in String because a new memory is required for the new String with appended
character.)
4) Thread-safe : In the case of a threaded environment, StringBuilder and StringBuffer are used whereas a String is not used. However, StringBuilder is suitable for an environment with a single thread, and a StringBuffer is suitable for multiple threads.
6. Java Question
Explain the use of final keyword in variable, method and class.
Problem approach
In Java, the final keyword is used as defining something as constant /final and represents the non-access modifier.
1) final variable :
i) When a variable is declared as final in Java, the value can’t be modified once it has been assigned.
ii) If any value has not been assigned to that variable, then it can be assigned only by the constructor of the class.
2) final method :
i) A method declared as final cannot be overridden by its children's classes.
ii) A constructor cannot be marked as final because whenever a class is inherited, the constructors are not inherited. Hence, marking it final doesn't make sense. Java throws compilation error saying - modifier final not allowed here
3) final class :
i) No classes can be inherited from the class declared as final. But that final class can extend other classes for its usage.
7. Java Question
What are the advantages of Packages in Java?
Problem approach
There are various advantages of defining packages in Java.
i) Packages avoid the name clashes.
ii) The Package provides easier access control.
iii) We can also have the hidden classes that are not visible outside and used by the package.
iv) It is easier to locate the related classes.
8. Java Question
Which among String or String Buffer should be preferred when there are a lot of updates required to be done in the data?
Problem approach
StringBuffer is mutable and dynamic in nature whereas String is immutable. Every updation / modification of String creates a new String thereby overloading the string pool with unnecessary objects. Hence, in the cases of a lot of updates, it is always preferred to use StringBuffer as it will reduce the overhead of the creation of multiple String objects in the string pool.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date20 Jul 2021
Coding problem2
This round specifically focused more on DSA and the interviewer asked me 2 coding problems and told me to solve them as optimally as possible. I was able to solve both the questions and the interviewer was also quite impressed.
1. Count ways to reach the n’th stair.
Moderate
30m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a number of stairs. Initially, you are at the 0th stair, and you need to reach the Nth stair.
Each time, you can climb either one step or two steps.
You are supposed to return the number of distinct ways you can climb from the 0th step to the Nth step.
Note:
Note: Since the number of ways can be very large, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
Example :
N=3
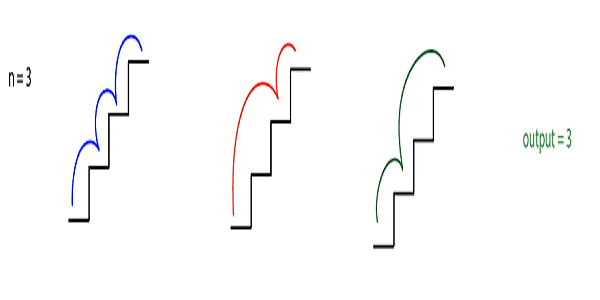
We can climb one step at a time i.e. {(0, 1) ,(1, 2),(2,3)} or we can climb the first two-step and then one step i.e. {(0,2),(1, 3)} or we can climb first one step and then two step i.e. {(0,1), (1,3)}.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DP) :
1) We reach “currStep” step in taking one step or two steps :
1.1) We can take the one-step from (currStep-1)th step or,
1.2) We can take the two steps from (currStep-2)th step.
2) So the total number of ways to reach “currStep” will be the sum of the total number of ways to reach at (currStep-1)th and the total number of ways to reach (currStep-2)th step.
3) Let dp[currStep] define the total number of ways to reach “currStep” from the 0th. So, dp[ currStep ] = dp[ currStep-1 ] + dp[ currStep-2 ]
4) The base case will be, If we have 0 stairs to climb then the number of distinct ways to climb will be one (we are already at Nth stair that’s the way) and if we have only one stair to climb then the number of distinct ways to climb will be one, i.e. one step from the beginning.
TC : O(N), Where ‘N’ is the number of stairs.
SC : O(N)
2. Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list, you have to detect the loop and remove the loop from the linked list, if present. You have to make changes in the given linked list itself and return the updated linked list.
Expected Complexity: Try doing it in O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity. Here, n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Problem approach
Approach 1(Using Hashing) :
We are going to maintain a lookup table(a Hashmap) that basically tells if we have already visited a node or not, during the course of traversal.
Steps :
1) Visit every node one by one, until null is not reached.
2) Check if the current node is present in the loop up table, if present then there is a cycle and will return true, otherwise, put the node reference into the lookup table and repeat the process.
3) If we reach at the end of the list or null, then we can come out of the process or loop and finally, we can say the loop doesn't exist.
TC : O(N), where N is the total number of nodes.
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 (Using Slow and Fast Pointers) :
Steps :
1) The idea is to have 2 pointers: slow and fast. Slow pointer takes a single jump and corresponding to every jump slow pointer takes, fast pointer takes 2 jumps. If there exists a cycle, both slow and fast pointers will reach the exact same node. If there is no cycle in the given linked list, then fast pointer will reach the end of the linked list well before the slow pointer reaches the end or null.
2) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
3) Start moving slow to every next node and moving fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
4) If after adjusting slow and fast, if they are referring to the same node, there is a cycle otherwise repeat the process
5) If fast reaches the end or null then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
TC : O(N), where N is the total number of nodes.
SC : O(1)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Jul 2021
Coding problem4
This round majorly focused on past projects and experiences from my Resume and some standard System Design + LLD questions + some basic questions from Design Pattern which a SDE-2 is expected to know. At the end, after all these technical questions the interviewer asked me if I was willing to solve a puzzle to which I said yes and so he also asked me an interesting puzzle at the end.
1. System Design Question
Design a URL Shortener
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Firstly, remember that the system design round is extremely open-ended and there’s no such thing as a standard answer. Even for the same question, you’ll have a totally different discussion with different interviewers.
Tip 2 : Before you jump into the solution always clarify all the assumptions you’re making at the beginning of the interview. Ask questions to identify the scope of the system. This will clear the initial doubt, and you will get to know what are specific detail the interviewer wants to consider in this service.
Some standard requirements for this problem would be :
1) Given a long URL, the service should generate a shorter and unique alias of it.
2) When the user hits a short link, the service should redirect to the original link.
3) Links will expire after a standard default time span.
4) The system should be highly available. This is really important to consider because if the service goes down, all the URL redirection will start failing.
5) URL redirection should happen in real-time with minimal latency.
6) Shortened links should not be predictable.
Tip 3: Now knowing about the requirements, note down all the important factors to take into consideration while solving this problem. Most common factors include :
1)Traffic
2) URL Length
3) Data Capacity Modeling
4) URL Shortening Logic (Encoding basically) - Standard Hashing Techniques like Base62, MD5 should be known
5) Choice of Database - SQL vs NoSQL
Finally, for acing System Design Rounds I would suggest watching Gaurav Sen's System Design Videos on YouTube and for hands-on practice there is a Guided Path solely for System Design on CodeStudio which is very useful while preparing for these types of rounds.
2. Design Pattern Question
What is a Bridge Design Pattern?
Problem approach
1) The bridge pattern is a type of structural design pattern that lets to split large class or closely related classes into 2 hierarchies - abstraction and implementation.
2) These hierarchies are independent of each other and are used whenever we need to decouple an abstraction from implementation.
3) This is called a Bridge pattern because it acts as a bridge between the abstract class and the implementation class.
4) In this pattern, the abstract classes and the implementation classes can be altered or modified independently without affecting the other one.
5) There are 4 main elements of Bridge Pattern. They are:
1) Abstraction – This is the core of the pattern and it defines its crux. This contains a reference to the implementer.
2) Refined Abstraction – This extends the abstraction and takes refined details of the requirements and hides it from the implementors.
3) Implementer – This is the interface for the implementation classes.
4) Concrete Implementation – These are the concrete implementation classes that implement the Implementer interface.
3. Design Pattern Question
What are some of the design patterns used in Java’s JDK library?
Problem approach
Following are some design patterns used in Java’s JDK library:
1) Decorator pattern are used by the Wrapper classes.
2) Singleton pattern is used in classes like Calendar and Runtime.
3) Factory pattern is used for methods like Integer.valueOf methods in wrapper classes.
4) Observer pattern is used for handling event frameworks like awt, swing etc.
4. Puzzle
Two wire burning puzzle
Problem approach
If we light a stick, it takes 60 minutes to burn completely. What if we light the stick from both sides? It will take exactly half the original time, i.e. 30 minutes to burn completely.
1) 0 minutes – Light Stick 1 on both sides and Stick 2 on one side.
2) 30 minutes – Stick 1 will be burnt out. Light the other end of Stick 2.
3) 45 minutes – Stick 2 will be burnt out. Thus 45 minutes is completely measured.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Lead Developer
3 rounds | 22 problems
Interviewed by Epsilon
1474 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Testing Engineer
3 rounds | 19 problems
Interviewed by Epsilon
1465 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
9654 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
1811 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HashedIn
1921 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







