Expedia Group interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 2
Expedia Group
4 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I got a call from an Expedia recruiter, and he explained the whole process, which includes three rounds of interviews after clearing the test. The test has three DSA questions. I took one week to prepare well for the rounds, specifically the LLD round. I brushed up on my skills and cleared the test.
Application story
I have made my profile on Naukri and various other job portals. Expedia recruiter shortlisted my resume from there and called me regarding the first round, the online test. He asked me for basic details like a current project, expected CTC, and preferred location and sent me a test link.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected after giving all the rounds. I solved 3 DSA questions out of 4, and my design round also went well. The feedback I received was that the one question I could not think of even brute force, and due to that, I was rejected.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, System Design (LLD), Algorithms, SQL, HLD BASICS
Tip
Tip 1: Runnable code is expected in the interview. SO practice that in committed time.
Tip 2: Focus on LLD & HLD explanation using some online tool.
Tip 3: Having projects on GitHub will be a plus point.
Application process
Where: Naukri
Resume tip
Tip 1: Mention personal projects if you have one. (will be a plus)
Tip 2: Mention microservice concerts and projects and if you handled a team (1-2 people also) then mention that.
Tip 3: Keep it 1 pager, include only relevant skills & projects.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date8 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
There were 2 DSA coding questions which were to be completed in 90 minutes. You must score more than 60% to be considered for further rounds. So, I would recommend you attempt both questions because the weightage for the second question is more than that of the first question.
1. Guess Price
Easy
10m average time
63% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Your friends gifted you a lot of things on your birthday, and now it's your turn to give some return gifts to them. You went to a gift store and decided to buy some Binary Search Trees (BST).
There is no salesperson in the store. So you are supposed to guess the price of a given BST, which is the minimum value in its nodes.
Problem approach
Approach: A binary search tree (BST) follows a property that for each node, its left child can only have a smaller value than the parent, and a right child can only have a greater value. Thus, we don't need to check the right child at any instance.
Start from the root and move in only the left direction. The leftmost leaf node in the tree is our answer.
If the tree is left-skewed, this optimized approach works the same as the normal traversal, shown in Approach-1.
Algorithm:
A pointer to the root node is given.
While the current node is not a leaf node.
Move the pointer to the left child of the current node.
Return the current node's value, which is the leftmost leaf node of the tree.
2. Maximum Sum BST
Hard
50m average time
55% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree ‘root’. The given Binary Tree may or may not be a Binary Search Tree(BST) itself. Your task is to find the maximum sum of node values of any subtree that is a Binary Search Tree(BST).
Binary Search Tree is defined as follows:
1) If the left subtree exists it should contain only nodes with values less than the current node's value.
2) If the right subtree exists it should contain only nodes with values greater than the current node's value.
3) Both the left and right subtrees should also be Binary Search Tree.
Example :
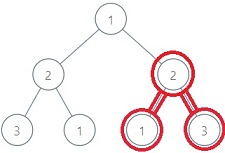
For the above binary tree, the BST with the maximum possible sum is marked with RED colour, the sum of this BST is equal to 6.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date11 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
After clearing the test, I received a call from the recruiter regarding the next three rounds, which were to be scheduled on a single day. Based on my availability, my interviews were scheduled. During the interviews, I was asked two coding questions: one easy and one medium level. I was able to solve both of them with optimized solutions.
1. Maximum Difference
Hard
40m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an integer array ‘arr’ of size ‘N’. Your task is to find the maximum difference between two consecutive elements in the sorted form of the array ‘arr’.
If the ‘arr’ contains less than two elements, return 0.
For example:
You are given arr = {1, 3, 8, 6, 7}, then our answer will be 3.
Sorted form of arr = {1, 3, 6, 7, 8}. The maximum absolute difference between two consecutive elements is 6 - 3 = 3, which is the correct answer.
2. Row with max 1s
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 2D matrix 'ARR' (containing either ‘0’ or ‘1’) of size 'N' x 'M', where each row is in sorted order.
Find the 0-based index of the first row with the maximum number of 1's.
Note :
If two rows have the same number of 1’s, return the row with a lower index.
If no row exists where at-least one '1' is present, return -1.
Example:
Input: ‘N’ = 3, 'M' = 3
'ARR' =
[ [ 1, 1, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 1 ],
[ 0, 0, 0 ] ]
Output: 0
Explanation: The 0th row of the given matrix has the maximum number of ones.
Problem approach
First I started with a brute force approach and later on interviewer asked me to optimise it further.
A simple method is to do a row-wise traversal of the matrix, count the number of 1s in each row, and compare the count with the max. Finally, return the index of the row with a maximum of 1s. The time complexity of this method is O(m*n) where m is the number of rows and n is the number of columns in the matrix.
The following method works in O(m+n) time complexity in the worst case.
Step 1: Get the index of first (or leftmost) 1 in the first row.
Step 2: Do the following for every row after the first row
…IF the element on the left of the previous leftmost 1 is 0, ignore this row.
…ELSE Move left until a 0 is found. Update the leftmost index to this index and max_row_index to be the current row.
The time complexity is O(m+n) because we can go as far left as we came ahead in the first step.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
In this round, two DSA coding questions were asked, one of which was easy, while the other was harder, focusing on the topic of dynamic programming.
1. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'prices' where the elements of the array represent the prices of the stock as they were yesterday and indices of the array represent minutes. Your task is to find and return the maximum profit you can make by buying and selling the stock. You can buy and sell the stock only once.
Note:
You can’t sell without buying first.
For Example:
For the given array [ 2, 100, 150, 120],
The maximum profit can be achieved by buying the stock at minute 0 when its price is Rs. 2 and selling it at minute 2 when its price is Rs. 150.
So, the output will be 148.
Problem approach
public:
int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length == 1)
return 0;
int min=prices[0];
int profit=0;
for(int i=1; i if(prices[i] < min)
min = prices[i];
else
profit = Math.max(profit, prices[i] - min);
}
return profit;
}
}2. Possible Words From A Phone Number
Hard
55m average time
45% success
0/120
Asked in companies



After years of research, Ninja is finally able to invent the time machine, and now he is back to the good old days when T9 keypads were being used in mobile phones.
Being a curious person, Ninja wants to find out all possible strings that can be formed by pressing the keys of the phone.
Formally, you are given a string S, that consists of digits from 2-9 (both inclusive), your task is to find out all the possible strings that can be formed from the input string by mapping the digits to the letters as in a T9 keypad. Then, print the strings in a lexicographically sorted order.

For Example:
If S = “34”, then all the possible letters that can be formed from string S are {“dg”, “dh”, “di”, “eg”, “eh”, “ei”, “fg”, “fh”, “fi”}.
04
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2023
Coding problem1
After completing the initial three rounds, a fourth round of system design was scheduled. To be eligible for this round, they checked that I had solved at least three out of four questions in the previous rounds. The interviewer asked me about basic LLD concepts and presented a problem. He was interested in the right approach rather than in-depth knowledge, as expected at the SDE2 level.
1. System Design
The goal of this exercise is to design a system like Google Search, which accepts a query string and returns a set of documents to the user. We are given the following: a UI that accepts the query and can make an RPC out to another server, which will accept a query and return a list of the top 10 documents related to it. The goal is to focus on the overall system architecture, not any specifics of ranking or information retrieval.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Read up on LLD concepts like load balancer, sharding, and scaling.
Tip 2: Understand what downstream is and how application servers work.
Tip 3: Clarify the requirements and ask questions to ensure an understanding of what exactly is being sought.
Tip 4: Utilize design patterns whenever applicable.
Tip 5: Apply object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts effectively.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
1857 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
1053 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Walmart
29739 views
8 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
6727 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
6 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
5225 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




