Flash Tech Company interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Web Developer
Flash Tech Company
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My journey started in 2nd year of college, and I saw my friends practicing coding questions, learning new coding languages, and developing some individual projects. After seeing them, I should learn more and practice coding questions. When I practiced coding questions on platforms like Codechef and Hackerrank, it made me realize that I need to think more to solve complex problems, and due to that, I developed a habit of solving them.
Application story
I was practicing DSA regularly when I saw a small advertisement on Leetcode. I opened it and found that the company is looking for an SDE-intern for some freshers. I applied for the role, and after some rounds, I got selected.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I think I was on point with my coding solutions to the questions asked in the interviews. I provided the optimal solutions and I was giving correct explanations to some theory questions asked.
Preparation
Duration: 8 months
Topics: Topics: I covered major data structure topics like Arrays, Stacks, Queues, Linked List, Trees, Graphs, backtracking, Dynamic Programming. After reading each topic, I tried to practice maximum questions on the concerned topic from Coding Ninjas, geeksforgeeks, Hackerrank and when stuck on a question, I preferred watching solution videos provided by Coding Ninjas.
Tip
Tip 1: It is essential to practice coding consistently because it enables you to solve interview questions in the stipulated time. But before this, it is essential to have a clear understanding of all the data structures so that they can be easily implemented as and when required to solve a problem. It is also mandatory to clearly understand algorithms' time and space complexities because this is what you are judged upon in actual interviews: good intuition and an excellent approach to solving a problem help to crack the interview of such companies.
Tip 2: They do not judge you upon the number of internships you have done or the number of projects you have made. A single,good-quality project is enough if you have in-depth knowledge. What matters to them is how efficient a learner you are, how good your problem-solving skill is, and how confident you are with your answers.
Tip 3: Practise topic-wise questions, participate in lots of coding contests, and watch lots of YouTube solutions even after you can solve a question because you may find a different approach that is more efficient than yours, and watching video solutions is always a better option than just reading the solution, as it gives a clear and deeper understanding of the logics. Also, pray hard along with your preparation.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep your resume short and clear. Mention your projects and internships with a brief description and year of completion. Mention coding languages are known to you, or other technical skills that you are good at. Do not mention anything that you are not good at. Highlight the topics that you are really good at.
Tip 2 : Be very honest and figure out only those things in your resume that you really know. Anything extra or unknown may have a negative impact upon your interview if asked by the interviewer.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date2 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Climbing the leaderboard
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a leaderboard of a game with the following ranking pattern:
The player with the highest score is ranked number 1 on the leaderboard.
Players who have equal scores receive the same ranking number, and the next player(s) receive the immediately following ranking number.
You are given game scores of a player of ‘M’ rounds. Your task is to return the position obtained in each round.
Note:
The leaderboard scores are in descending order.
The game scores are given in ascending order.
Problem approach
This problem was of easy level and I could easily come up with a solution after identifying a relation between the rank and index of the element.
2. Flatten The Multi-Level Linked List
Moderate
10m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a multi-level linked list of 'N' nodes, each node has a next and child pointer which may or may not point to a separate node. Flatten the multi-level linked list into a singly linked list. You need to return the head of the updated linked list.
Example:
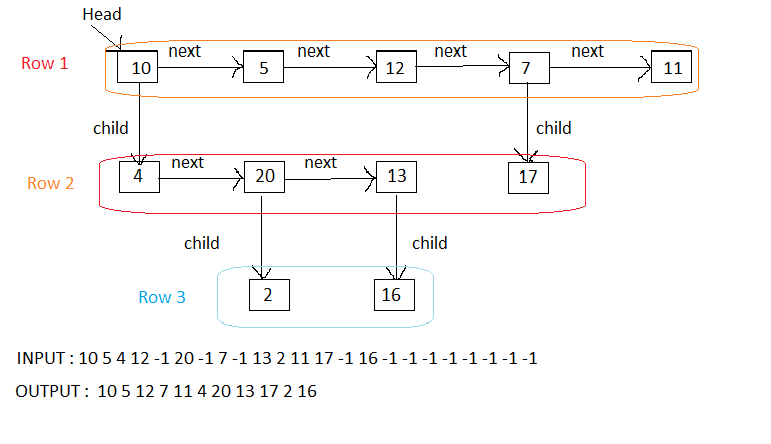
Flatten :
All the different rows are merged into a single row.
Problem approach
Step 1: I first traversed the linked list and on find a child pointer, descended down the list but forgot to keep track of the next pointers of such nodes.
Step 2: It dawned upon me that I need a container to keep hold of all next-pointers, and Stack could be used for this.
Step 3: Then I gave a solution using stack and also flattening the linked-list in O(n) time and the interviewer was happy with me.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
1. Print Nodes at Distance K From a Given Node
Hard
20m average time
80% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary binary tree, a node of the tree, and an integer 'K'. You need to find all such nodes which have a distance K from the given node and return the list of these nodes.
Distance between two nodes in a binary tree is defined as the number of connections/edges in the path between the two nodes.
Note:
1. A binary tree is a tree in which each node has at most two children.
2. The given tree will be non-empty.
3. The given tree can have multiple nodes with the same value.
4. If there are no nodes in the tree which are at distance = K from the given node, return an empty list.
5. You can return the list of values of valid nodes in any order. For example if the valid nodes have values 1,2,3, then you can return {1,2,3} or {3,1,2} etc.
Example :
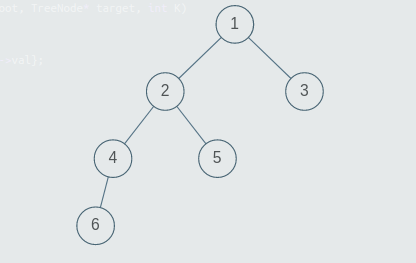
Consider this tree above. The target node is 5 and K = 3. The nodes at distance 1 from node 5 are {2}, nodes at distance 2 from node 5 are {1, 4} and nodes at distance 3 from node 5 are {6, 3}.
Problem approach
Tip 1:We can solve this problem using breadth first search. Main thing to observe in this problem is that if we find two marked nodes which are at largest distance from each other considering all pairs of marked nodes then if a node is at a distance less than K from both of these two nodes then it will be at a distance less than K from all the marked nodes because these two nodes represents the extreme limit of all marked nodes, if a node lies in this limit then it will be at a distance less than K from all marked nodes otherwise not.
As in above example, node-1 and node-4 are most distant marked node so nodes which are at distance less than 3 from these two nodes will also be at distance less than 3 from node 2 also. Now first distant marked node we can get by doing a bfs from any random node, second distant marked node we can get by doing another bfs from marked node we just found from the first bfs and in this bfs we can also found distance of all nodes from first distant marked node and to find distance of all nodes from second distant marked node we will do one more bfs, so after doing these three bfs we can get distance of all nodes from two extreme marked nodes which can be compared with K to know which nodes fall in K-distance range from all marked nodes.
2. Minimum Card Flips
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You are at your friend’s birthday party and one of your friends decided to play a card game with some special type of cards. These cards can have numbers written on both sides.
You are given ‘N’ cards, each card contains some integer number between ‘1’ to ‘10’ written on both sides. You are allowed to flip a card such that the number which was previously on the top now comes at the bottom and vice versa.
Find the minimum flips that need to be performed to make all the numbers equal on either the top sides or the bottom sides. If it is impossible to make all the cards the same on either side then return ‘-1’.
For Example :
If N = 4 and the numbers on the top sides are: { 1, 2, 3, 2 } and the numbers on the bottom sides are: { 2, 4, 2, 2}
Then the minimum number of flips required is equal to 1.
We can flip the 2nd card, the top sides now become: { 1, 4, 3, 2 } and the bottom sides are: { 2, 2, 2, 2}. This results in getting the same numbers on the bottom side.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration30 minutes
Interview date10 Jan 2022
Coding problem1
1. Word Search - l
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 2D board('N' rows and 'M' columns) of characters and a string 'word'.
Your task is to return true if the given word exists in the grid, else return false. The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring.
Note:
The same letter cell should not be used more than once.
For Example:
For a given word “design” and the given 2D board
[[q’, ‘v’, ‘m’, ‘h’],
[‘d’, ‘e’, ‘s’, ‘i’],
[‘d’, ‘g’, ‘f’, ‘g’],
[‘e’, ‘c’, ‘p’, ‘n’]]
The word design can be formed by sequentially adjacent cells as shown by the highlighted color in the 2nd row and last column.
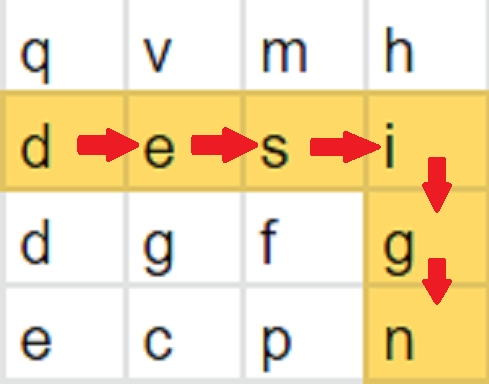
Problem approach
I sat with a pen and paper and used the provided test-case , which helped me to make a tree like structure , which had to be explored until its depth.This is where I realized that Depth First Search could be used to solve the problem.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1012 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







