Freshworks interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Graduate Trainee
Freshworks
5 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 7 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, SQL, OOPS, Basics of system design.
Tip
Tip 1 : Make sure that you have good understand of data structures, Algorithm and OOPS
Tip 2 : Practice as many problems as you can in any platform that you are comfortable on.
Tip 3 : Have a decent knowledge on SQL, DBMS, OS, computer networks
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep your resume short preferably 1 page and make sure its communicating all points
Tip 2 : Add only those thing that you are confident on.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Nov 2020
Coding problem3
1. Merge Two Sorted Arrays
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given two sorted integer arrays/lists ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ of size ‘M’ and ‘N’. Ninja has to merge these sorted arrays/lists into ‘ARR1’ as one sorted array. You may have to assume that ‘ARR1’ has a size equal to ‘M’ + ‘N’ such that ‘ARR1’ has enough space to add all the elements of ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
For example:
‘ARR1’ = [3 6 9 0 0]
‘ARR2’ = [4 10]
After merging the ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
‘ARR1’ = [3 4 6 9 10]
Problem approach
I have used the merge logic that is used in merge sort algorithm.
2. Valid Parentheses
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You're given a string 'S' consisting of "{", "}", "(", ")", "[" and "]" .
Return true if the given string 'S' is balanced, else return false.
For example:
'S' = "{}()".
There is always an opening brace before a closing brace i.e. '{' before '}', '(' before ').
So the 'S' is Balanced.
Problem approach
I had used stack to solve this problem.
Iterated through the array with two condition
1. if its open braces than add that in stack
2. if its closed then validate that peek element in stack
3. if step 2 is false then break the loop and return false.
4. After the iteration if stack is empty then return true else return false
3. Reverse Integer
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a 32-bit signed integer ‘N’. So, the integer will lie in the range [-2^31, 2^31 - 1]. Your task is to return the reverse of the given integer. If reversing causes overflow, then return -1.
Note:
(1) Do not use data types with the capacity of more than 32-bit like ‘long int’ or ‘long long int’ in C++. The problem is meant to reverse the integer using a 32-bit data type only.
(2) You should assume that the environment does not allow storing signed or unsigned 64-bit integers.
Problem approach
Since its online I tried converting the integer to string and reversed that and it passed all the cases. For logical approach refer this article
02
Round
Easy
Assignment
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Dec 2020
Coding problem1
1. Backend Assignment
Build a file-based key-value data store that supports the basic CRD (create, read, and delete)operations. This data store is meant to be used as local storage for one single process on one laptop. The data store must be exposed as a library to clients that can instantiate a class and work with the data store.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : store the key value pair in specific format in file, so that while doing CRUD we can able to differentiate the pair stored in file
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date7 Jan 2021
Coding problem2
1. Deepest Left
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You are given a binary tree having ‘N’ number of nodes. Your task is to find the deepest leaf node in the given input tree.
Note:
The deepest leaf node is the leaf node which will be the left child of some node and will be at the maximum level in the tree.
If there are multiple deepest left leaf nodes, return the node with maximum value.
Note :
1. A binary tree is a tree in which each node can have at most two children.
2. The given tree will be non-empty i.e. the number of non-NULL nodes will always be greater than or equal to 1.
3. Multiple nodes in the tree can have the same values, all values in the tree will be positive.
Problem approach
Firstly I have two approaches in my mind one is through the recursion and other through BFS.
Since its straight forward problem I decided to solve this with BFS.
I have used BFS traversal logic and had track of leftmost node in each level once the traversal is completed then leftmostnode contains the result.
1. To do level order traversal in BFS we need to add a null in the queue once after adding the last element in the level
2. By using that null we can able to figure out whether we reached end of the level or not.
3. once we reach the null we need to pop that null and store the next element in leftMostNode.
4. when the traversal is done we can return the leftMostNode.
He is fine with the approach and asked me to code the same.
2. Sub Sort
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an integer array ‘ARR’. You have to find the length of the shortest contiguous subarray such that, if you sort this subarray in ascending order, then the whole array will be sorted in ascending order.
An array 'C' is a subarray of array 'D' if it can be obtained by deletion of several elements(possibly zero) from the beginning and the end from array 'D'.
Example:
Let’s say we have an array 'ARR' {10, 12, 20, 30, 25, 40, 32, 31, 35, 50, 60}. Then we have to find the subarray {30 , 25 , 40 , 32 , 31 , 35} and print its length = 5 as our output. Because, when we sort this subarray the whole array will be sorted.
Problem approach
I couldn’t thing the brute approach for the problem during my interview, but some how managed to get an idea of optimal solution.
The approach that I used was:
1. Have two variable which point start index and end index of array.
2. Now find the first element from start of the array which is less that the previous element. store this index in variable let's say 'startIndex'
3. Now find the first element from end of the array which greater than its next element. store the index in variable lets say 'endIndex'
4. Now find the 'max' and 'min' value in the subarray from startIndex to endIndex.
5. check if any value is greater than the min from 0 to startIndex in the array. if any then update startIndex with that index
6. check if any value is less than the max from endIndex to len(array) - 1 in the array. if any then update endIndex with that index
7. Return the startIndex and endIndex
04
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date13 Jan 2021
Coding problem3
1. Invert a Binary Tree
Moderate
45m average time
55% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are provided with a Binary Tree and one of its leaf nodes. You have to invert this binary tree. Inversion must be done by following all the below guidelines:
• The given leaf node becomes the root after the inversion.
• For a node (say, ‘x’)
○ If there exists the left child that is not yet taken then this child must become the right child of ‘x’.
○ If the left child is already taken then the right child is still on the right side of ‘x’.
• The parent of ‘x’ must be the left child of ‘x’.
For Example:

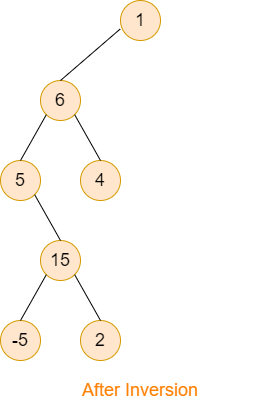
Consider the above binary tree (image- before inversion), if the given leaf node is ‘1’ then the binary tree after inversion becomes exactly the same as given in the image representing after inversion.
Note:
The given binary tree will only have distinct values of nodes.
Problem approach
I explained the approach of swaping the child two nodes while traversing each node. The interview was fine with that approach
2. Minimum cut puzzle
You have got someone working for you for five days and a gold bar to pay him. You must give them a piece of gold at the end of every day. What are the fewest number of cuts to the bar of gold that will allow you to pay him 1/5th each day?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : I used have a habit of learning puzzle when I get bored solving problems during my interview preparation. Luckily that habit helped me here.
3. SQL Questions
I was Asked to code some basic SQL queries. All them were really simple if you know the basics of SQL.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Do practice for SQL queries in hacker rank when you find that helps a lot.
05
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date25 May 2021
Coding problem1
This Round the HR checks whether you will be good fit for culture code that's followed by the company.
1. Basic HR Questions
Tell me about yourself.
How will you learn new coding language if asked to work on that?
Why do you want to join this company?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Try to answer the question by comparing some past situation that you had faced.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Freshworks
2201 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Freshworks
1021 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Freshworks
738 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Graduate Trainee
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Freshworks
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes


