Gameskraft interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Gameskraft
4 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started preparing DSA from scratch to advanced and maintained consistency for four months straight. Meanwhile, I also prepared Web Development and Database, ensuring I had a well-rounded skill set.
Application story
It was an on-campus opportunity, and I applied through a Google Form. All the students who were eligible for the process had to apply using the same Google Form.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I think I got rejected because I was only able to explain my approach to the coding question in last round but could not provide the full code as I ran out of time.
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, OS, OOPS, Web Development, Algorithms
Tip
Tip 1: Prepare DSA well, as it forms the foundation of most interview rounds.
Tip 2: Database knowledge is equally important, so make sure to revise and practice it thoroughly.
Tip 3: Be confident during the interviews, as confidence leaves a strong impression on the interviewer.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7 CGPA, (Salary package: 32 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Make sure to build some really good projects that showcase your skills effectively.
Tip 2: Never put any wrong or false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Hard
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date1 Aug 2024
Coding problem3
It was in evening. Environment was good.
1. Longest Normal-Character Substring
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

Given a string comprising of lowercase characters and type of each of the characters (a-z) where each alphabet can be of type normal and special. We were asked to find the longest substring comprising of at most k normal characters. The string can be of length 10^5.
Problem approach
Use sliding window: Maintain a window over the string that expands and shrinks based on the count of normal characters.
Track normal characters: Keep a count of normal characters in the current window.
Expand the window: Move the right end of the window forward, including one character at a time.
Shrink when needed: If normal characters exceed k, move the left end forward until the window is valid again.
Update maximum length: After each adjustment, check if the current window is the longest valid substring so far.
Continue till end: Repeat expanding and shrinking until the entire string is processed.
Result: The maximum length recorded is the answer.
2. Weighted Job Scheduling
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given 'N' jobs with their start time 'Start', end time 'End' and profit 'Profit'. You need to tell the maximum profit you can obtain by performing these jobs such that no two jobs overlap.
Note:
The start time of one job can be equal to the end time of another.
Problem approach
Understand the problem: Maximize profit by selecting non-overlapping jobs.
Sort jobs by end time to make it easier to find compatible jobs.
Use a DP array where each entry stores maximum profit including that job.
Find last non-conflicting job for each current job using binary search.
Apply recurrence: Maximum profit = max(current job + profit till last non-conflict, profit till previous job).
Fill DP for all jobs to accumulate maximum profit step by step.
Return the last DP value as the maximum achievable profit.
3. Connecting Cities With Minimum Cost
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There are ‘N’ cities numbered from 1 to ‘N’ and ‘M’ roads. Each road connectss two different cities and described as a two-way road using three integers (‘U’, ‘V’, ‘W’) which represents the cost ‘W’ to connect city ‘U’ and city ‘V’ together.
Now, you are supposed to find the minimum cost so that for every pair of cities, there exists a path of connections (possibly of length 1) that connects those two cities together. The cost is the sum of the connection costs used. If the task is impossible, return -1.
Problem approach
The problem is asking for the minimum cost to connect all cities, which is equivalent to finding a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of the graph.
First, we treat each city as a node and each road with a repair cost as a weighted edge.
We sort all edges by their repair cost in ascending order, so we can always pick the cheapest available connection first.
We then use Kruskal’s algorithm (or Prim’s) to add edges one by one, making sure no cycles are formed while connecting the cities.
To check for cycles efficiently, we can use a Union-Find (Disjoint Set) data structure.
We keep adding the smallest cost edge that connects two disconnected components until all cities are connected.
Finally, the sum of the selected edges’ costs gives the minimum total cost to repair roads and connect all cities.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date1 Aug 2024
Coding problem2
Interviewer was very kind. He asked one DSA questions then follow up and asked me to dry run my solution on his test cases.
1. Container With Most Water
Moderate
15m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array arr[] of non-negative integers, where each element arr[i] represents the height of the vertical lines, find the maximum amount of water that can be contained between any two lines, together with the x-axis.
Problem approach
Two-Pointer Approach – Initialize two pointers, one at the start and one at the end of the array.
Calculate Area – At each step, calculate the area as min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left) and keep track of the maximum area seen so far.
Move Pointers Strategically – Move the pointer pointing to the smaller height, because moving the larger height cannot increase the area.
Repeat Until Pointers Meet – Continue moving pointers and updating the maximum area until the two pointers meet.
Return Result – The maximum area tracked is the answer.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration80 minutes
Interview date22 Aug 2024
Coding problem4
It was in afternoon. Interviewer was already prepared with questions. He asked lots of follow up questions.
1. Insert Into A Binary Search Tree
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Insert a given Node in Binary Search Tree.
Problem approach
To insert a node in a Binary Search Tree (BST), start at the root and compare the new value with the current node’s value. If it is smaller, move to the left subtree; if larger, move to the right subtree. Repeat this process recursively (or iteratively) until you find a null position where the new node can be inserted. Once inserted, the BST property is maintained: left child < parent < right child.
2. Level Order Traversal
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the level order traversal of the given tree.
For example:
For the given binary tree
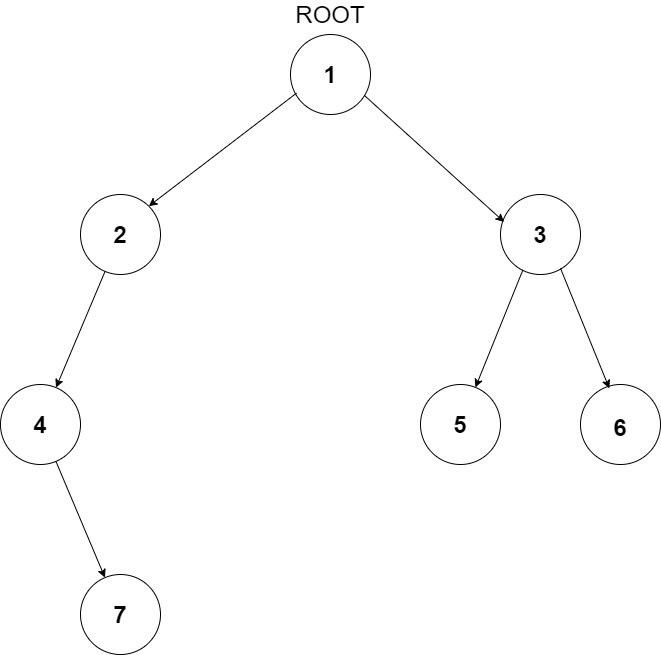
The level order traversal will be {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}.
Problem approach
Level order traversal visits nodes of a tree level by level from top to bottom. We typically use a queue to keep track of nodes at the current level. Start by enqueuing the root, then repeatedly dequeue a node, process it, and enqueue its left and right children if they exist. Continue this process until the queue is empty, which ensures all levels are visited in order.
3. LCA of Two Nodes In A BST
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary search tree of integers with N nodes. You are also given references to two nodes 'P' and 'Q' from this BST.
Your task is to find the lowest common ancestor(LCA) of these two given nodes.
The lowest common ancestor for two nodes P and Q is defined as the lowest node that has both P and Q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself)
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
For example:
'P' = 1, 'Q' = 3
tree = 2 1 4 -1 -1 3 -1 -1 -1,
The BST corresponding will be-
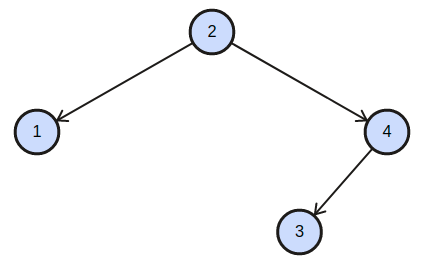
Here, we can clearly see that LCA of node 1 and node 3 is 2.
Problem approach
Start at the root and compare the values of the two target nodes (p and q) with the root.
If both values are smaller than root, move to the left subtree; if both are larger, move to the right subtree.
When one value is on the left and the other is on the right (or one equals the root), the current root is the LCA.
4. SQL
- Find the second highest salary from the Employee table. What if there are duplicates? (Practice)
- Find the Nth highest salary (generalization). Use window functions instead of subqueries. (Learn)
04
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration70 minutes
Interview date30 Aug 2024
Coding problem1
Interviewer was prepared with the problem. Several questions were asked from internship experience as well.
1. Maximum Freshness in Harvest Windows
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You have a row of fruit baskets represented as an array freshness[], where each element is the freshness score of the fruit in that basket. You have a basket size k, and you want to pick k consecutive baskets at a time. Your task is to find the maximum freshness score in each window of k baskets.
Problem approach
Treat the array freshness[] as a row of baskets and the window of size k as the current selection of baskets.
Use a deque to keep track of indices of baskets that could be the maximum freshness in the current window.
Iterate through each basket from left to right. For each basket, remove indices from the front of the deque if they are out of the current window.
Remove indices from the back of the deque if their freshness is less than the current basket, because they can never be the maximum while this basket is in the window.
Add the current basket’s index to the deque. The basket at the front of the deque is the maximum freshness for the current window.
Continue this process for all baskets, recording the maximum freshness for each window of size k.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Gameskraft
2710 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Gameskraft
5894 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Gameskraft
1768 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Gameskraft
1017 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes







