Gartner interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Gartner
3 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I began my coding journey through coding platforms. This involved actively participating in numerous interviews, each contributing to valuable learning experiences. I meticulously analyzed the feedback from each interview, identifying areas for improvement. Armed with this insight, I diligently worked on honing those aspects before confidently rejoining the interview circuit. This iterative approach not only enhanced my coding skills but also ensured continuous evolution and adaptation based on feedback and experiences encountered during the interview process.
Application story
After coming across a job opening on LinkedIn, I submitted my application through the Gartner Careers portal. Following a wait of 15 days, I received notification that my resume had been shortlisted for an online test.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
This job required hands-on experience in Data structure and I was not well-versed with these skills.
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, AWS, SQL, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Craft your resume precisely so that everything listed becomes second nature to you. Your ability to talk about and elaborate on any skill mentioned in your resume should be instantaneous.
Tip 2: Before an interview, quickly familiarize yourself with the details of your current project. Anticipate questions about the intricacies of your specific contributions and be ready for potential follow-up queries that arise based on your responses.
Tip 3: Engage in hands-on coding practice on various platforms. This sharpens your problem-solving skills and trains you to think dynamically when presented with challenges. Don't shy away from asking the interviewer questions that pop into your mind during the process – it demonstrates your active engagement and genuine curiosity.
Application process
Where: Linkedin
Eligibility: No Criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1: Ensure clarity and conciseness in your resume; aim for an ideal length of 1-2 pages.
Tip 2: Emphasize your role, delineate responsibilities, and spotlight the skills applied to accomplish tasks in each position.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date12 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
1. Valid Parentheses
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You're given a string 'S' consisting of "{", "}", "(", ")", "[" and "]" .
Return true if the given string 'S' is balanced, else return false.
For example:
'S' = "{}()".
There is always an opening brace before a closing brace i.e. '{' before '}', '(' before ').
So the 'S' is Balanced.
Problem approach
1. Implement stack, push opening brackets in stack and pop closing brackets of same type ( & ), [ & ] , { & }
2. If stack at end is empty, it's valid else invalid
2. Set Matrix Zeros
Easy
30m average time
65% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an N x M integer matrix. Your task is to modify this matrix in place so that if any cell contains the value 0, then all cells in the same row and column as that cell should also be set to 0.
Requirements:
- If a cell in the matrix has the value 0, set all other cells in that cell's row and column to 0.
- You should perform this modification in place (without using additional matrices).
You must do it in place.
For Example:
If the given grid is this:
[7, 19, 3]
[4, 21, 0]
Then the modified grid will be:
[7, 19, 0]
[0, 0, 0]
Problem approach
Step 1: Identify Zero Positions
Traverse the matrix and mark the rows and columns where zeros are present. You can use additional data structures to store this information.
Step 2: Set Zeros
Iterate through the matrix again.
For each cell, if its corresponding row or column was marked in Step 1, set the cell value to zero.
Step 3: Optimized Solution without Extra Space
Instead of using extra space, you can use the first row and the first column to store information about whether the corresponding row or column should be zeroed.
Use separate variables to track whether the first row and the first column should be zeroed.
Detailed Steps:
Initialize Flags:
Initialize two flags, zeroFirstRow and zeroFirstColumn, to track whether the first row and first column should be zeroed.
Scan First Row and Column:
Scan the first row and first column separately.
If you find any zero in the first row, set zeroFirstRow to true.
If you find any zero in the first column, set zeroFirstColumn to true.
Mark Zero Positions:
Iterate through the rest of the matrix.
If a zero is found at position (i, j), set matrix[i][0] = 0 and matrix[0][j] = 0 to mark that the corresponding row and column should be zeroed.
Set Zeros Based on Marks:
Iterate through the matrix again (excluding the first row and first column).
If matrix[i][0] == 0 or matrix[0][j] == 0, set matrix[i][j] = 0.
Zero First Row and Column if Necessary:
If zeroFirstRow is true, set all elements in the first row to zero.
If zeroFirstColumn is true, set all elements in the first column to zero.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date26 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
1. Rod cutting problem
Moderate
40m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a rod of length ‘N’ units. The rod can be cut into different sizes and each size has a cost associated with it. Determine the maximum cost obtained by cutting the rod and selling its pieces.
Note:
1. The sizes will range from 1 to ‘N’ and will be integers.
2. The sum of the pieces cut should be equal to ‘N’.
3. Consider 1-based indexing.
Problem approach
USE DP Approch
2. Longest Palindromic Substring
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'str' of length 'N'.
Your task is to return the longest palindromic substring. If there are multiple strings, return any.
A substring is a contiguous segment of a string.
For example :
str = "ababc"
The longest palindromic substring of "ababc" is "aba", since "aba" is a palindrome and it is the longest substring of length 3 which is a palindrome.
There is another palindromic substring of length 3 is "bab". Since starting index of "aba" is less than "bab", so "aba" is the answer.
Problem approach
Eg
str = "ababc"
The longest palindromic substring of "ababc" is "aba", since "aba" is a palindrome and it is the longest substring of length 3 which is a palindrome.
There is another palindromic substring of length 3 is "bab". Since the starting index of "aba" is less than "bab", so "aba" is the answer.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date31 Aug 2021
Coding problem4
1. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a string 'S' of length 'L', return the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Example:
Suppose given input is "abacb", then the length of the longest substring without repeating characters will be 3 ("acb").
2. Theory Questions
Problem approach
Thrashing:
Thrashing refers to the state in computing where excessive paging or swapping of data between the main memory and secondary storage occurs, severely degrading system performance. This situation arises when the system lacks sufficient physical memory to support its workload, leading to a constant, inefficient swapping of pages between the main memory and the disk.
Multithreaded Programming:
Multithreaded programming involves the simultaneous execution of multiple threads within a program. This approach aims to enhance performance and responsiveness by allowing different threads to execute independently. Threads share the same resources, such as memory space, but run concurrently, enabling parallelism. This can lead to improved overall system efficiency. Multithreaded programming is beneficial for tasks like parallel computation, managing asynchronous operations, and optimizing resource utilization in systems with multiple processors or cores.
3. OS Questions
Problem approach
Virtual Memory:
Virtual memory is a memory management technique used by operating systems to provide an illusion to the users that each process has its dedicated memory. It extends the available physical memory by using a combination of RAM (Random Access Memory) and disk space. In virtual memory systems, each process is given a contiguous block of virtual memory, which may exceed the actual physical memory available. The operating system then uses a mechanism called paging or segmentation to swap data between the physical memory and the disk, allowing processes to execute even if the entire program or data set cannot fit into the physical RAM.
Buffer:
A buffer is a temporary storage area in computer memory used to hold data while it's being transferred from one place to another. Buffers are employed to address differences in data transfer rates between two devices or processes. For example, in input/output operations, a buffer is often used to hold data temporarily as it's transferred between a slower peripheral (like a hard disk) and a faster component (such as RAM). Buffers help smooth out these differences and improve overall system performance by reducing the impact of speed mismatches between the producing and consuming elements in a computing system.
4. Boundary Traversal of Binary Tree
Hard
20m average time
85% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree having 'n' nodes.
The boundary nodes of a binary tree include the nodes from the left and right boundaries and the leaf nodes, each node considered once.
Figure out the boundary nodes of this binary tree in an Anti-Clockwise direction starting from the root node.
Example :
Input: Consider the binary tree A as shown in the figure:
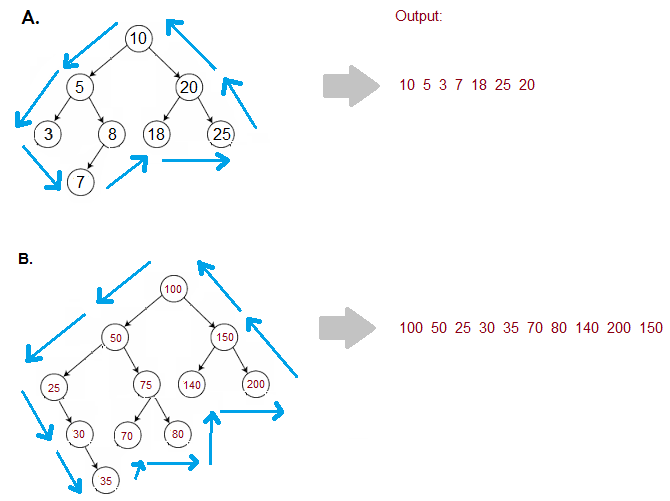
Output: [10, 5, 3, 7, 18, 25, 20]
Explanation: As shown in the figure
The nodes on the left boundary are [10, 5, 3]
The nodes on the right boundary are [10, 20, 25]
The leaf nodes are [3, 7, 18, 25].
Please note that nodes 3 and 25 appear in two places but are considered once.
Problem approach
Use recursion method

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Gartner
918 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Gartner
750 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Gartner
1092 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Gartner
1289 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
6315 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
2179 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





