Gojek interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Android Engineer
Gojek
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 1 Month
Topics: Data structures, Algorithms, OOPS, Android, OS
Tip
Tip 1 : Clear all the topics related to Android with deep details about every topics.
Tip 2 : Practice DSA and algorithms from GFG, CodeStudio daily.
Tip 3 : Dry run code before running the code.
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA , Previous Android Development Experience Required
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep it to the point don't add anything for the sake of making it large.
Tip 2 : Put atleast 2 good projects if you are a fresher.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date4 May 2021
Coding problem2
1. Beautiful String
Easy
18m average time
70% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given a binary string ‘STR’ containing either ‘0’ or ‘1’. A binary string is called beautiful if it contains alternating 0s and 1s.
For Example:‘0101’, ‘1010’, ‘101’, ‘010’ are beautiful strings.
He wants to make ‘STR’ beautiful by performing some operations on it. In one operation, Ninja can convert ‘0’ into ‘1’ or vice versa.
Your task is to determine the minimum number of operations Ninja should perform to make ‘STR’ beautiful.
For Example :
Minimum operations to make ‘STR’ ‘0010’ beautiful is ‘1’. In one operation, we can convert ‘0’ at index ‘0’ (0-based indexing) to ‘1’. The ‘STR’ now becomes ‘1010’ which is a beautiful string.
2. Reverse Blocks
Hard
56m average time
30% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers and an integer array 'B' of size 'N'. Each element in the array 'B' represents a block size. Modify the linked list by reversing the nodes in each block whose sizes are given by the array 'B'.
Note:
1. If you encounter a situation when 'B[i]' is greater than the number of remaining nodes in the list, then simply reverse the remaining nodes as a block and ignore all the block sizes from 'B[i]'.
2. All block sizes are contiguous i.e. suppose that block 'B[i]' ends at a node cur, then the block 'B[i+1]' starts from the node just after the node cur.
Example
Linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
Array B: 3 3 5
Output: 3->2->1->5->4
We reverse the first block of size 3 and then move to block 2. Now, since the number of nodes remaining in the list (2) is less than the block size (3), we reverse the remaining nodes (4 and 5) as a block and ignore all the block sizes that follow.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date5 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
1. Maximum Sum Rectangle
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



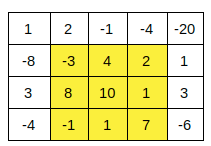
You are given a matrix ‘ARR’ with ‘N’ rows and ‘M’ columns. Your task is to find the maximum sum rectangle in the matrix.
Maximum sum rectangle is a rectangle with the maximum value for the sum of integers present within its boundary, considering all the rectangles that can be formed from the elements of that matrix.
For Example
Consider following matrix:
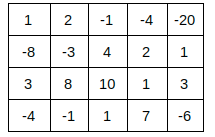
The rectangle (1,1) to (3,3) is the rectangle with the maximum sum, i.e. 29.
2. Technical Questions
Difference between constraint and relative layout Kotlin co routines.
Why kotlin over java.
Fragment life cycle with a live app explanation.
How to import 3d models in an app Broadcast receivers and services.
Project questions

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Gojek
1343 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes







