Google interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Google
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
Initially grappling with the syntax of languages like Python and Java, I gradually embraced the logic and problem-solving aspects of programming. Each milestone brought a sense of accomplishment as I delved into data structures, algorithms, and web development. Collaborating on projects with peers honed my teamwork and communication skills. Facing bugs and errors became opportunities for learning, fostering resilience. By the end of the initial phase of my coding journey, I had transformed from a novice into a more confident programmer, eager to explore the vast realms of software development that lay ahead.
Application story
This is a Google Engineering Graduate opportunity for which I applied offline. Initially, I had to complete a coding assessment test. Once that was cleared, the interview process began.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I could not secure the position due to my inability to comprehend and accurately respond to all the challenges presented during the selection process.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Regularly participate in coding challenges on platforms like CodeStudio to enhance your problem-solving skills and gain exposure to diverse coding scenarios.
Tip 2: Engage in collaborative coding projects that focus on real-world applications. This demonstrates practical coding abilities and enhances your teamwork and project management skills, making you more appealing to potential employers.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Highlight quantifiable achievements and results on your resume, showcasing the impact of your contributions in previous roles, such as increased efficiency, cost savings, or successful project outcomes.
Tip 2: Tailor your resume for each job application by emphasizing relevant skills and experiences that align with the specific requirements of the position. This customization enhances your chances of standing out to recruiters and matching the role's needs.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jul 2024
Coding problem2
1. Count with K different characters
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'str' of lowercase alphabets and an integer 'k' .
Your task is to return the count all the possible substrings that have exactly 'k' distinct characters.
For example:
'str' = abcad and 'k' = 2.
We can see that the substrings {ab, bc, ca, ad} are the only substrings with 2 distinct characters.
Therefore, the answer will be 4.
Problem approach
I first used brute force and I got TLE. So, I optimized the code using sliding windows and map and it passed all test cases.
2. Buildings Projection
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja Land can be represented as a N * N grid in the XY plane. Each cell of this grid can have a building of some height.
You are given a matrix ‘GRID[][]’ of size ‘N’ * ‘N’, where ‘GRID[i][j]’ gives the height of the building at cell (i, j) in XY plane. Note, building at any cell (i, j) is represented as a cuboid that is an axis aligned with the axis ‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’ and has the dimension 1 * 1 * GRID[i][j] along X, Y, Z-axis respectively.
Ninja views the projection of these buildings onto the XY, YZ, and ZX planes. A projection is like a shadow, that maps a 3-dimensional figure to a 2-dimensional plane. We are viewing the "shadow" when looking from the top, the side, and the front, in XY, YZ, ZX plane respectively.
Your task is to find and return the total area of all three projections. See the example for more clarity.
Note:
‘GRID[i][j]’ = 0, if there is no building at cell (i, j).
Example:
Consider the following 2*2 ‘GRID[][]’:
[1, 2]
[3, 4]
Its projection in XY, YZ, XZ plane is shown below -:
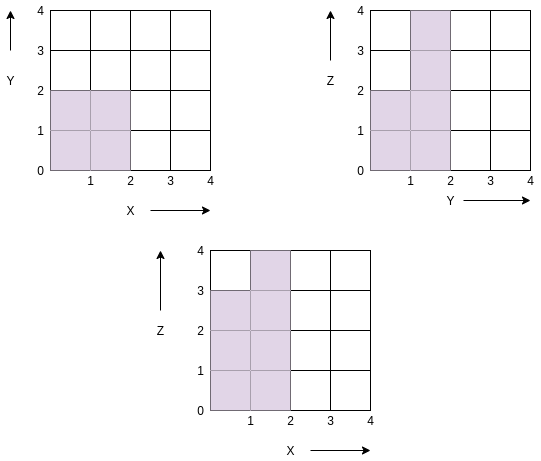
Area covered in XY plane is 4, Area covered in YZ plane is 6, Area covered in ZX plane is 7, Thus the total area is 4 + 6 + 7 = 17.
Problem approach
I solved using a nested loop that had O(n^2) time complexity. After the interview, I was able to come up with a greedy approach with O(n) time complexity.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date18 Jul 2024
Coding problem2
1. Closest Cost
Moderate
34m average time
67% success
0/80
Asked in company

Ninja is given the task to create a perfect gift for the king. He has ‘N’ wraps to choose from which he can choose to wrap the gifts. He also has ‘M’ gifts from which he can choose the gifts for the king. To choose the gifts, he sets some rules:
1) He must select exactly one wrapper to wrap all the chosen gifts.
2) He can select one or more gifts or no gifts at all.
3) He has 2 copies of the same gift. So, he can take 0 or 1 or 2 copies of each gift.
He also has a number ‘X’. He decided to spend in such a way that the total cost is as close as ‘X’. If there are multiple answers, print the minimum one.
For example:
Let’s say you have two wrappers with cost [1, 2] and three gifts with cost [3, 4, 5] and ‘X’ = 7. In the first case, you select wrapper number ‘2’ and gift number ‘1’ and ‘3’, so your total cost will be 2 + 3 + 5 = 10. While in the second case, you select wrapper number ‘1’ and gift number ‘2’, so your total cost will be 1 + 4 = 5. So out of both the cases, second case is closer to ‘X’ as abs(7 - 5) = 2 and abs(7 - 10) = 3.
Problem approach
I was it to figure out that this problem could be solved using a priority queue but I wasn't sure how. After trying different methods the interviewer give me a tip on how to use the priority queue method for this and I was able to grasp the logic for solving the problem.
2. Check If Path Exists
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a directed and unweighted graph of 'V' vertices and 'E' edges. All edges are given in a 2-dimensional array of ‘Edges’ in which ‘Edges[i][0]’ and ‘Edges[i][1]’ contain an edge. Your task is to check if there exists a path from the vertex 'source' to 'destination'.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration45 minutes
Interview date19 Jul 2024
Coding problem2
This was my last round. Those who are selected here goes to next round.
1. DFS Traversal
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an undirected and disconnected graph G(V, E), containing 'V' vertices and 'E' edges, the information about edges is given using 'GRAPH' matrix, where i-th edge is between GRAPH[i][0] and GRAPH[i][1]. print its DFS traversal.
V is the number of vertices present in graph G and vertices are numbered from 0 to V-1.
E is the number of edges present in graph G.
Note :
The Graph may not be connected i.e there may exist multiple components in a graph.
2. Remove Boxes
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given several boxes with different colours represented by different positive numbers. For moving the boxes you can remove them in multiple iterations until there are no boxes left. Now, every time you can choose some continuous boxes with the same color (i.e., composed of 'k' boxes, 'k' >= 1), remove them and get 'k' * 'k' points for removing them.
Your task for the problem is to find and return the maximum points you can get by removing those boxes.
For Example:
Input: boxes = [1, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 3, 1]
Output: 23
Explanation:
[1, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4, 3, 1]
----> [1, 3, 3, 4, 3, 1] (Remove 3 boxes with number 2, 3*3=9 points)
----> [1, 3, 3, 3, 1] (Remove one box with number 4, 1*1=1 points)
----> [1, 1] (Remove 3 boxes with number 3, 3*3=9 points)
----> [] (2*2=4 points)

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
Which SQL clause is used to specify the conditions in a query?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Google
3541 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by Google
1998 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Google
4291 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Google
1932 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
113897 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
57279 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
34687 views
6 comments
0 upvotes






