Grab interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
Grab
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I was advised by my seniors to practice DSA from the very starting of B.Tech but I did not took that seriously. Honestly speaking, I regretted not taking their advice and in third year I started doing coding and I had to increase practice hours because I started late. But by the end of Third year, I was confident in both DSA and development but even then, I kept on revising the concepts.
Application story
This company visited to my campus for the placement. We just had to upload our resume and fill in all the details in the form. First, they took the online assessment. Later, they called us for the interview rounds.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
The basic reason for my rejection was my not-that-strong knowledge of core DSA fundamentals and my problem-solving ability is also not that good.
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, Machine Learning and AI
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice popular questions from Arrays, Binary Trees, and LinkedList from CodeStudio's Interview Problems
Tip 2 : Make sure you are aware of calculating the time and space complexity for every problem you're coding.
Tip 3 : Prepare through Mock Interviews to practice explaining your approach while solving in an actual interview.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Describe the best of your projects in minimum words. Don't forget to add buzzwords like REST APIs/ DB Indexing/ Benchmarking etc if you worked on the backend.
Tip 2 : Don't add school achievements like Class Topper in your resume.
Tip 3 : If you've some work experience, put it in a way you're marketing yourself. Add terms like 'Created/Owned the Project through the entire SDLC.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date25 Jan 2023
Coding problem2
One coding question, some general talk & questions on puzzle
1. Diameter of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
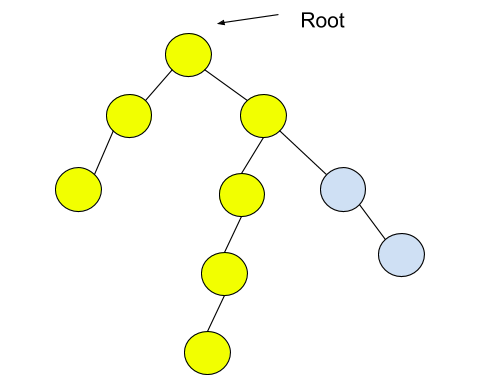
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
Problem approach
int height(TreeNode* root,int *x)
{
int lh=0;
int rh=0;
int ld=0;
int rd=0;
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
ld=height(root->left,&lh);
rd=height(root->right,&rh);
*x=max(lh,rh)+1;
return max(lh+rh+1,max(ld,rd));
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
int x=0;
return height(root,&x)-1;
}
2. Puzzle Question
Make a fair coin from a biased coin.
You are given a function foo() that represents a biased coin. When foo() is called, it returns 0 with 60% probability, and 1 with 40% probability. Write a new function that returns 0 and 1 with a 50% probability each. Your function should use only foo(), no other library method.
Problem approach
We know foo() returns 0 with 60% probability. How can we ensure that 0 and 1 are returned with a 50% probability?
The solution is similar to this post. If we can somehow get two cases with equal probability, then we are done. We call foo() two times. Both calls will return 0 with a 60% probability. So the two pairs (0, 1) and (1, 0) will be generated with equal probability from two calls of foo(). Let us see how.
(0, 1): The probability to get 0 followed by 1 from two calls of foo() = 0.6 * 0.4 = 0.24
(1, 0): The probability to get 1 followed by 0 from two calls of foo() = 0.4 * 0.6 = 0.24
So the two cases appear with equal probability. The idea is to return consider only the above two cases, return 0 in one case, return 1 in other case. For other cases [(0, 0) and (1, 1)], recur until you end up in any of the above two cases.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date27 Jan 2023
Coding problem2
1. Check Permutation
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given two strings 'STR1' and 'STR2'. You have to check whether the two strings are anagram to each other or not.
Note:
Two strings are said to be anagram if they contain the same characters, irrespective of the order of the characters.
Example :
If 'STR1' = “listen” and 'STR2' = “silent” then the output will be 1.
Both the strings contain the same set of characters.
Problem approach
bool isAnagram(string s, string t) {
int a[256]={0};
for(int i=0;i {
a[s[i]]++;
}
for(int i=0;i {
a[t[i]]--;
}
for(int i=0;i<256;i++)
if(a[i]!=0)
return false;
return true;
}
2. Find Peak Element
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n'. Find the index(0-based) of a peak element in the array. If there are multiple peak numbers, return the index of any peak number.
Peak element is defined as that element that is greater than both of its neighbors. If 'arr[i]' is the peak element, 'arr[i - 1]' < 'arr[i]' and 'arr[i + 1]' < 'arr[i]'.
Assume 'arr[-1]' and 'arr[n]' as negative infinity.
Note:
1. There are no 2 adjacent elements having same value (as mentioned in the constraints).
2. Do not print anything, just return the index of the peak element (0 - indexed).
3. 'True'/'False' will be printed depending on whether your answer is correct or not.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [1, 8, 1, 5, 3]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are two possible answers. Both 8 and 5 are peak elements, so the correct answers are their positions, 1 and 3.
Problem approach
int findPeakElement(vector& nums) {
int max=-2147483648;
int pos=0;
for(int i=0;imax)
{
max=nums[i];
pos=i;
}
}
return pos;
}
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date29 Jan 2023
Coding problem2
1. Median of two sorted arrays
Hard
25m average time
65% success
0/120
Asked in companies



Given two sorted arrays 'a' and 'b' of size 'n' and 'm' respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays.
Median is defined as the middle value of a sorted list of numbers. In case the length of list is even, median is the average of the two middle elements.
The expected time complexity is O(min(logn, logm)), where 'n' and 'm' are the sizes of arrays 'a' and 'b', respectively, and the expected space complexity is O(1).
Example:
Input: 'a' = [2, 4, 6] and 'b' = [1, 3, 5]
Output: 3.5
Explanation: The array after merging 'a' and 'b' will be { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }. Here two medians are 3 and 4. So the median will be the average of 3 and 4, which is 3.5.
Problem approach
The given arrays are sorted, so merge the sorted arrays in an efficient way and keep the count of elements inserted in the output array or printed form. So when the elements in the output array are half the original size of the given array print the element as a median element. There are two cases:
Case 1: m+n is odd, the median is at (m+n)/2 th index in the array obtained after merging both the arrays.
Case 2: m+n is even, the median will be the average of elements at index ((m+n)/2 – 1) and (m+n)/2 in the array obtained after merging both the arrays
2. Matrix Chain Multiplication
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given ‘N’ 2-D matrices and an array/list “ARR” of length ‘N + 1’ where the first ‘N’ integers denote the number of rows in the Matrices and the last element denotes the number of columns of the last matrix. For each matrix, the number of columns is equal to the number of rows of the next matrix. You are supposed to find the minimum number of multiplication operations that need to be performed to multiply all the given matrices.
Note :
You don’t have to multiply the matrices, you only have to find the minimum number of multiplication operations.
For Example :
ARR = {2, 4, 3, 2}
Here, we have three matrices with dimensions {2X4, 4X3, 3X2} which can be multiplied in the following ways:
a. If the order of multiplication is (2X4, 4X3)(3X2), then the total number of multiplication operations that need to be performed are: (2*4*3) + (2*3*2) = 36
b. If the order of multiplication is (2X4)(4X3, 3X2), then the total number of multiplication operations that need to be performed are (2*4*2) + (4*3*2) = 40
Problem approach
Create a recursive function that takes i and j as parameters that determines the range of a group.
Iterate from k = i to j to partition the given range into two groups.
Call the recursive function for these groups.
Return the minimum value among all the partitions as the required minimum number of multiplications to multiply all the matrices of this group.
The minimum value returned for the range 0 to N-1 is the required answer.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Grab
1001 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
1 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Grab
915 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Grab
1073 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Grab
897 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7923 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4395 views
1 comments
0 upvotes




