Groww interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Groww
2 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, DBMS, OOPS, Operating System, Graph, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice questions are a must to clear coding tests. As in for this job, only those candidates shortlisted for the interview round who solved all the questions in the coding round. So you should be prepared for this type of worst-case scenario.
Tip 2 : focus on core subjects too.
Tip 3 : Do atleast 1 project.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 6.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Have put your coding experience.
Tip 3 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Feb 2022
Coding problem2
1. Buy and Sell Stock
Hard
0/120
Asked in companies



You are Harshad Mehta’s friend. He told you the price of a particular stock for the next ‘n’ days.
You are given an array ‘prices’ which such that ‘prices[i]’ denotes the price of the stock on the ith day.
You don't want to do more than 2 transactions. Find the maximum profit that you can earn from these transactions.
Note
1. Buying a stock and then selling it is called one transaction.
2. You are not allowed to do multiple transactions at the same time. This means you have to sell the stock before buying it again.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 7, ‘prices’ = [3, 3, 5, 0, 3, 1, 4].
Output: 6
Explanation:
The maximum profit can be earned by:
Transaction 1: Buying the stock on day 4 (price 0) and then selling it on day 5 (price 3).
Transaction 2: Buying the stock on day 6 (price 1) and then selling it on day 6 (price 4).
Total profit earned will be (3 - 0) + ( 4 - 1) = 6.
Problem approach
int maxProfit(vector& prices)
{
int n=prices.size();
int profit,mi=INT_MAX;
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i {
mi=min(mi,prices[i]);
profit=prices[i]-mi;
ans=max(profit,ans);
}
return ans;
}
2. Find the minimum cost to reach destination using a train
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There are ‘N’ stations on the route of a train. The train goes from station 0 to ‘N’ - 1. The ticket cost for all pairs of stations (i, j) is given where ‘j’ is greater than ‘i’. Your task is to find the minimum cost to reach the Nth station.
Note:
Cost of entries where j < i will be represented as INT_MAX VALUE which is 10000 in the price matrix.
Example:
If ‘N’ = 3
'PRICE[3][3]' = {{0, 15, 80,},
{INF, 0, 40},
{INF, INF, 0}};
First, go from 1st station to 2nd at 15 costs, then go from 2nd to 3rd at 40. 15 + 40 = 55 is the total cost.It is cheaper than going directly from station 1 to station 3 as it would have cost 80.
The output will be 55.
Problem approach
I solved this problem using dynamic programming.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date16 Feb 2022
Coding problem3
1. Missing and repeating numbers
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array of size ‘N’. The elements of the array are in the range from 1 to ‘N’.
Ideally, the array should contain elements from 1 to ‘N’. But due to some miscalculations, there is a number R in the range [1, N] which appears in the array twice and another number M in the range [1, N] which is missing from the array.
Your task is to find the missing number (M) and the repeating number (R).
For example:
Consider an array of size six. The elements of the array are { 6, 4, 3, 5, 5, 1 }.
The array should contain elements from one to six. Here, 2 is not present and 5 is occurring twice. Thus, 2 is the missing number (M) and 5 is the repeating number (R).
Follow Up
Can you do this in linear time and constant additional space?
Problem approach
Step 1: First take an ans array and intialize with 0.
Step 2: Run a loop over the given array for storing the frequency of element in ans array.
Step 3: Run a loop over the ans array and if count 0 i.e missing and >1 repeating
2. Nodes In Complete Binary Tree
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given the root of a complete binary tree, you need to calculate the number of nodes in the given complete binary tree.
A complete binary tree is a tree in which all the levels are completely filled except the last level. Nodes in the last level are as left as possible.
For Example:
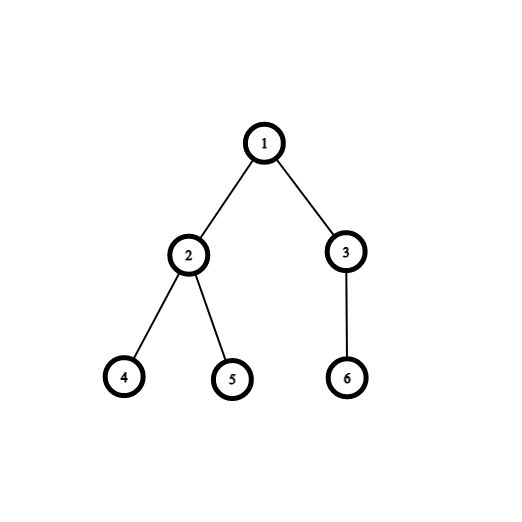
In the above complete binary tree, all the levels are filled except for the last. In the last level, all the nodes in the last level are as far left as possible.
Problem approach
I solved using DFS approach to get the steps from source to destination.
3. DBMS Questions
What is Candidate key, Unique Key and Composite Key . He also asked about the term "indexing" and normalization type and their explanation.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Groww
1609 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Groww
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Groww
3581 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Groww
1532 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





