HestaBit interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Trainee Software Engineer
HestaBit
4 rounds | 18 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
HestaBit is a leading managed web and mobile app development service company. The team ranks as the number one development team for web and mobile-based projects in the UK. The company visited our college for the profile of Trainee Software Engineer. Around 100 students participated in the drive, but no one was selected.
Application story
The company came to our college for the profile of Trainee Software Engineer. It conducted 4 rounds: Aptitude Test, Machine Coding Test, Technical Interview 1, and Technical Interview 2. Around 100 students participated in the drive, but no one was selected.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected for this role in the last round of interviews. My interview went well, but I don't know why I got rejected. No one from our college was selected for the drive. It seems like the position they were hiring for may have closed earlier than expected.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Operating System, Data Structures, Databases, Frontend Technologies, Cloud (Either Google or Amazon)
Tip
Tip 1: Prepare the operating system in detail. Be ready for cross-questioning.
Tip 2: Practice complex coding questions.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 60% throughout with no backlogs
Resume tip
Tip 1: Mention Java projects in your resume if you have any.
Tip 2: Do not include false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Jan 2022
Coding problem5
This round was conducted online on Hestabit's platform. This test included MCQs of aptitude and operating system. It was 60 minutes long test, which had 40 questions.
1. Puzzle
A jogger running at 9 kmph alongside a railway track 240 metres ahead of the engine of a 120 metres long train running at 45 kmph in the same direction. In how much time will the train pass the jogger?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice aptitude questions.
Tip 2: Keep pen and paper aside.
2. Puzzle
A tank is filled by three pipes with uniform flow. The first two pipes operating simultaneously fill the tank at the same time during which the tank is filled by the third pipe alone. The second pipe fills the tank 5 hours faster than the first pipe and 4 hours slower than the third pipe. The time required by the first pipe is:
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice aptitude questions
Tip 2: Keep pen and paper aside.
3. Puzzle
If Rs. 10 is allowed as a true discount on a bill of Rs. 110 due at the end of a certain time, then the discount allowed on the same sum due at the end of double the time is:
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice aptitude questions
Tip 2: Keep pen and paper aside.
4. Puzzle
A wheel that has 6 cogs is meshed with a larger wheel of 14 cogs. When the smaller wheel has made 21 revolutions, then the number of revolutions made by the larger wheel is:
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice aptitude questions
Tip 2: Keep pen and paper aside.
5. Puzzle
A boat having a length of 3 m and a breadth of 2 m is floating on a lake. The boat sinks by 1 cm when a man gets on it. The mass of the man is:
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice aptitude questions.
Tip 2: Keep pen and paper aside.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Jan 2022
Coding problem2
This round was conducted on Hestabit's platform. It had 2 medium-level coding questions which needed to be answered in 60 minutes. Those who answered both questions correctly were moved to the next round.
1. Minimum Operations
Easy
20m average time
82% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' of 'N' positive integers. You need to find the minimum number of operations needed to make all elements of the array equal. You can perform addition, multiplication, subtraction or division with any element on an array element.
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication or Division on any element of the array will be considered as a single operation.
Example:
If the given array is [1,2,3] then the answer would be 2. One of the ways to make all the elements of the given array equal is by adding 1 to the array element with value 1 and subtracting 1 from the array element with value 3. So that final array would become [2,2,2].
Problem approach
Step 1: Let m be the length of word1 and n be the length of word2.
Step 2: Create a 2D array, dp, of size (m+1) x (n+1).
Step 3: Initialize the first row of dp with values from 0 to n (representing the number of operations required to convert an empty string to word2).
Step 4: Initialize the first column of dp with values from 0 to m (representing the number of operations required to convert word1 to an empty string).
Step 5: Iterate over the rows of dp from 1 to m:
a) Iterate over the columns of dp from 1 to n:
b) If the characters at word1[i-1] and word2[j-1] are equal, set dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] (no operation required).
c) Otherwise, set dp[i][j] = 1 + min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]) (take the minimum of the three adjacent cells and add 1).
Step 6: Return dp[m][n], which represents the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
2. Remove Duplicates From an Unsorted Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a linked list of N nodes. Your task is to remove the duplicate nodes from the linked list such that every element in the linked list occurs only once i.e. in case an element occurs more than once, only keep its first occurrence in the list.
For example :
Assuming the linked list is 3 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3 -> NULL.
Number ‘2’ and ‘3’ occurs more than once. Hence we remove the duplicates and keep only their first occurrence. So, our list becomes : 3 -> 2 -> 4 -> NULL.
Problem approach
Step 1: Create a dummy node and set its next pointer to the head of the linked list. This dummy node will handle cases where the head itself needs to be deleted.
Step 2: Initialize two pointers, prev and current, to the dummy node.
Step 3: Traverse the linked list while the current node and its next node are None:
a) If the current node's value is equal to its next node's value, enter a loop to find the last node with the same value:
b) Increment the next node until its value is not equal to the current node's value.
c) Set the next node of the current node to the next node of the last node with the same value.
d) If the current node's value is not equal to its next node's value, move the previous and current pointers to their next nodes.
Step 4: Return the next node of the dummy node, which will be the head of the modified and sorted linked list.
03
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date20 Jan 2022
Coding problem7
This round was conducted on the Zoom platform. Three interviewers took the interview. The interview was 50-55 minutes long. There was a lot of cross-questioning by the interviewers.
1. OS Question
What is Round Robin Scheduling Algorithm? Explain it with an example. (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Study Round Robin scheduling algorithm in detail
Tip 2: Answer confidently
3. Cloud Computing Question
Do you have knowledge of any cloud? What do you know?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Have a brief knowledge of any cloud, whether it is Amazon or Google Cloud
Tip 2: Hear the question carefully
4. DBMS Question
What are the different types of JOINS available in SQL? (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Study JOINS in SQL
Tip 2: Answer confidently
Tip 3: Explain the answer with examples
5. SQL Question
Write an SQL query to remove duplicate rows. (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice SQL queries.
Tip 2: Don't take much time to write a query.
6. Python question
What is a lambda function in Python? Write the syntax of the lambda function. (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Grab knowledge of any one programming language
Tip 2: Hear the question carefully
7. Star Pattern
Easy
10m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Print the following pattern
Pattern for N = 4

The dots represent spaces.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice pattern-related questions
Tip 2: Don't take much time to write logic
04
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date28 Jan 2022
Coding problem4
This round was conducted on Zoom. It was 90% technical, while 10% HR interview. It was 50 minutes long. The interviewers seemed experienced.
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
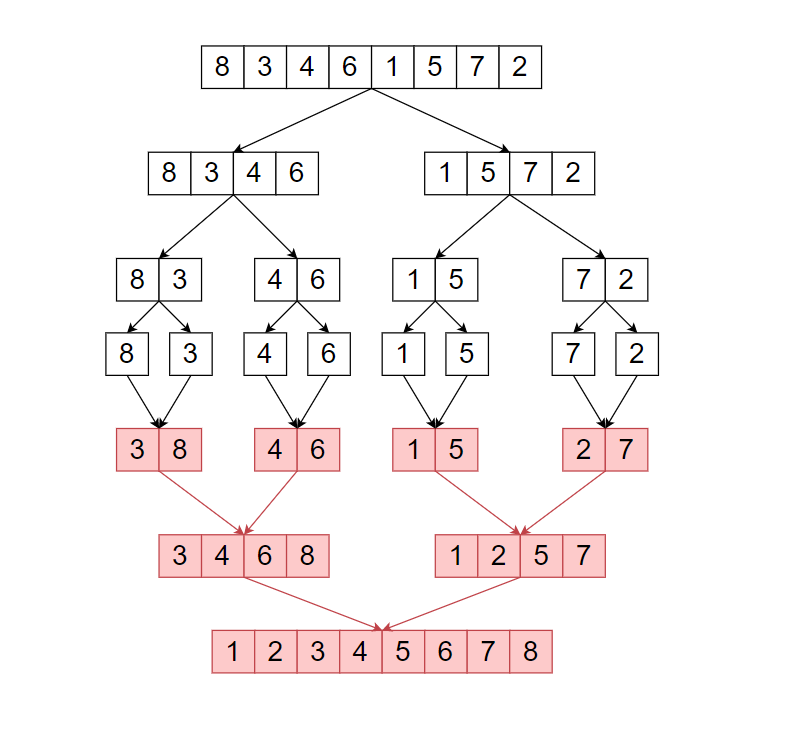
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
Step 1: If the length of the input array arr is less than or equal to 1, return the array as it is already sorted.
Step 2: Divide the array arr into two halves: left and right.
Step 3: Set the midpoint mid as the floor of (length of arr divided by 2).
Step 4: Set left as the subarray from index 0 to mid (exclusive).
Step 5: Set right as the subarray from index mid to the end of the array.
Step 6: Recursively sort the left and right subarrays by calling the merge sort function on each half.
Step 7: Set left as merge_sort(left).
Step 8: Set right as merge_sort(right).
Step 9: Merge the sorted left and right subarrays into a new sorted array merged.
Step 10: Initialize three pointers: i for left, j for right, and k for merged. Set them to 0.
Step 11: Compare the elements at indices i and j in left and right, respectively.
a) If left[i] is less than or equal to right[j], set merged[k] as left[i] and increment i and k by 1.
b) If left[i] is greater than right[j], set merged[k] as right[j] and increment j and k by 1.
c) Repeat this process until either i reaches the end of left or j reaches the end of right.
Step 12: Copy the remaining elements from the non-empty subarray (left or right) to merged.
Step 13: Return the merged array as the final sorted array.
2. SQL question
What is RAID in SQL? (Learn)
Problem approach
Tip 1: Study RAID in SQL
Tip 2: Answer confidently

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1012 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








