Hewlett Packard Enterprise interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Hewlett Packard Enterprise
3 rounds | 10 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OS, DBMS, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration70 Minutes
Interview date5 Jun 2019
Coding problem2
This round had 40 MCQ's followed by 2 questions of DS and Algo. The coding questions were of Easy to Medium level of difficulty.
1. Terms Of AP
Easy
10m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ayush is given a number ‘X’. He has been told that he has to find the first ‘X’ terms of the series 3 * ‘N’ + 2, which are not multiples of 4. Help Ayush to find it as he has not been able to answer.
Example: Given an ‘X’ = 4. The output array/list which must be passed to Ayush will be [ 5, 11, 14, 17 ].
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Declare a temporary array/list variable ‘ANS’ in which we store our answer.
2) Declare a temporary variable ‘GOT’ that will store the total number of elements we obtained until now, which are acceptable.
3) Declare a temporary variable ‘CURRENT’ that will store the current number of series 3 * ‘N’ + 2 and initialize with the first number of series 5.
4) Run a loop while ‘GOT’ is not equal to ‘X’:
4.1) If ‘CURRENT’ is not divisible by 4, we will append the value at the end of ‘ANS’ and increment the value of ‘GOT’ by 1.
4.2) Increment the value of ‘CURRENT’ by three as the next value of the series.
5) Finally, return ‘ANS’.
TC : O(N), where N=number of elements in the series.
SC : O(N)
2. Mirror image of triangle
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies


Ninja’s younger sister got a project to print the pattern for the given number of rows, say ‘N’. She finds it difficult to write such a pattern for every ‘N’.
Ninja decided to help his sister and decided to write a code for this but wasn't able to write the code for the same. Ninja wants help to write a code and asks you for help. Help Ninja.
Example:
Pattern for N = 2
0
101
21012
Problem approach
Approach :
1) First, initialize two integer variables, say ‘number1’ and ‘number2’ to print the digits in the pattern and initialize both the variables with value = 1;
2) Make an iteration with iterator pointer ‘i’ to print the number of rows which will iterate from 0 to ‘N’.
3) Make a nested iteration to generate the spaces in the pattern with an iterator pointer ‘j’ which will iterate from ‘N’ - 1 to ‘i’ and print the spaces.
4) Make an iteration to print the digits inside the pattern with an iterator pointer ’k’ from 1 to ‘number1’and print the value = (‘k’ - ‘number2’).
5) Increment ‘number1’ with value 2.
6) Increment ‘number2’ with value 1.
7) Leave a line after that.
TC : O(N^2), where N=given integer.
SC : O(1)
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date5 Jun 2019
Coding problem7
This was a mixed round where I was asked to code Merge Sort and later I was asked some important concepts from Computer Networks and Operating Systems/Linux.
1. Merge Sort
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of numbers ‘ARR’. Your task is to return a sorted sequence of ‘ARR’ in non-descending order with help of the merge sort algorithm.
Example :
Merge Sort Algorithm -
Merge sort is a Divide and Conquer based Algorithm. It divides the input array into two-parts, until the size of the input array is not ‘1’. In the return part, it will merge two sorted arrays a return a whole merged sorted array.
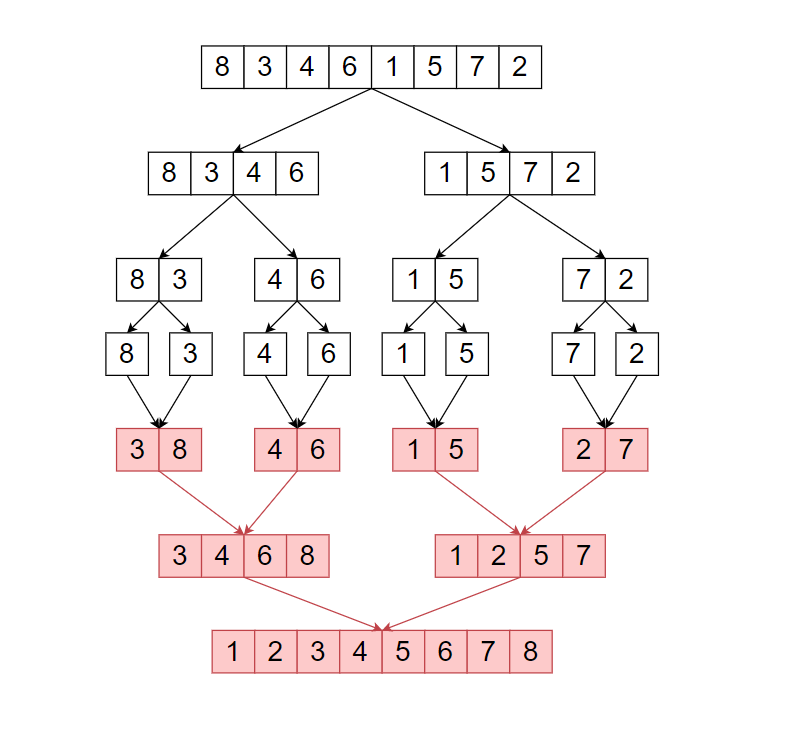
The above illustrates shows how merge sort works.
Note :
It is compulsory to use the ‘Merge Sort’ algorithm.
Problem approach
Merge Sort : The basic idea is that we divide the given ‘ARR’ into two-part call them ‘leftHalves’ and ‘rightHalves’ and call the same function again with both the parts. In the end, we will get sorted ‘leftHaves’ and sorted ‘righthalves’ which we merge both of them and return a merged sorted ‘ARR’.
Pseudo Code :
// Merge function.
void merge(vector < int > & arr, int left, int mid, int right) {
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
vector < int > leftarr(n1);
vector < int > rightarr(n2);
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) {
leftarr[i] = arr[left + i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n2; i++) {
rightarr[i] = arr[mid + 1 + i];
}
int i = 0;
// Initial index of second subarray.
int j = 0;
// Initial index of merged subarray.
int k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (leftarr[i] <= rightarr[j]) {
arr[k] = leftarr[i];
i++;
}
else {
arr[k] = rightarr[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of leftarr if there are any.
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = leftarr[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// Copy the remaining elements of rightarr[], if there are any.
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = rightarr[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
void mergeSortHelper(vector < int > & arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSortHelper(arr, left, mid);
mergeSortHelper(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
void mergeSort(vector < int > & arr, int n) {
mergeSortHelper(arr, 0, n - 1);
}
TC : O(N*log(N)), where N=size of ARR.
SC : O(N)
2. Technical Question
Add two numbers using 1) Inline functions and 2) Macros.
Problem approach
1) Using Inline functions :
inline int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int main()
{
int c=add(5,3);
cout< return 0;
}
2) Using Macros :
#define add(a, b) a+b
int main()
{
int c=add(5,3);
cout< return 0;
}
3. Networking Question
Difference b/w TCP and UDP
Problem approach
TCP (Transmission control protocol) :
1) TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. Connection-orientation means that the communicating devices should establish a connection before transmitting data and should close the connection after transmitting the data.
2) TCP is reliable as it guarantees the delivery of data to the destination router.
3) TCP is comparatively slower than UDP.
4) Retransmission of lost packets is possible in TCP, but not in UDP.
5) TCP doesn’t support Broadcasting.
UDP (User datagram protocol) :
1) UDP is the Datagram oriented protocol. This is because there is no overhead for opening a connection, maintaining a connection, and terminating a connection. UDP is efficient for broadcast and multicast type of network transmission.
2) The delivery of data to the destination cannot be guaranteed in UDP.
3) UDP is faster, simpler, and more efficient than TCP.
4) There is no retransmission of lost packets in the User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
5) UDP supports Broadcasting.
4. Networking Question
What happens when you enter Google.com on the web browser.
Problem approach
1) The browser extracts the domain name from the URL.
2) The browser queries DNS for the IP address of the URL. Generally, the browser will have cached domains previously visited, and the operating system will have cached queries from any number of applications. If neither the browser nor the OS have a cached copy of the IP address, then a request is sent off to the system's configured DNS server. The client machine knows the IP address for the DNS server, so no lookup is necessary.
3) The request sent to the DNS server is almost always smaller than the maximum packet size, and is thus sent off as a single packet. In addition to the content of the request, the packet includes the IP address it is destined for in its header. Except in the simplest of cases (network hubs), as the packet reaches each piece of network equipment between the client and server, that equipment uses a routing table to figure out what node it is connected to that is most likely to be part of the fastest route to the destination. The process of determining which path is the best choice differs between equipment and can be very complicated.
4) The data is either lost (in which case the request fails or is reiterated), or makes it to its destination, the DNS server.
5) If that DNS server has the address for that domain, it will return it. Otherwise, it will forward the query along to DNS server it is configured to defer to. This happens recursively until the request is fulfilled or it reaches an authoritative name server and can go no further.
6) Assuming the DNS request is successful, the client machine now has an IP address that uniquely identifies a machine on the Internet. The web browser then assembles an HTTP request, which consists of a header and optional content. The header includes things like the specific path being requested from the web server, the HTTP version, any relevant browser cookies, etc.
7) This HTTP request is sent off to the web server host as some number of packets, each of which is routed in the same was as the earlier DNS query. (The packets have sequence numbers that allow them to be reassembled in order even if they take different paths.) Once the request arrives at the webserver, it generates a response (this may be a static page, served as-is, or a more dynamic response, generated in any number of ways.) The web server software sends the generated page back to the client.
This is what happens when we type Google.com on our browser.
5. OS Question
What are the different types of semaphores ?
Problem approach
Answer :
There are two main types of semaphores i.e. counting semaphores and binary semaphores.
1) Counting Semaphores :
These are integer value semaphores and have an unrestricted value domain. These semaphores are used to coordinate the resource access, where the semaphore count is the number of available resources. If the resources are added, semaphore count automatically incremented and if the resources are removed, the count is decremented.
2) Binary Semaphores :
The binary semaphores are like counting semaphores but their value is restricted to 0 and 1. The wait operation only works when the semaphore is 1 and the signal operation succeeds when semaphore is 0. It is sometimes easier to implement binary semaphores than counting semaphores.
6. OS Question
Explain demand paging
Problem approach
Demand paging is a method that loads pages into memory on demand. This method is mostly used in virtual memory. In this, a page is only brought into memory when a location on that particular page is referenced during execution. The following steps are generally followed:
1) Attempt to access the page.
2) If the page is valid (in memory) then continue processing instructions as normal.
3) If a page is invalid then a page-fault trap occurs.
4) Check if the memory reference is a valid reference to a location on secondary memory. If not, the process is terminated (illegal memory access). Otherwise, we have to page in the required page.
5) Schedule disk operation to read the desired page into main memory.
6) Restart the instruction that was interrupted by the operating system trap.
7. OS Question
Explain Piping in Unix/Linux
Problem approach
1) A pipe is a form of redirection (transfer of standard output to some other destination) that is used in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems to send the output of one command/program/process to another command/program/process for further processing.
2) The Unix/Linux systems allow stdout of a command to be connected to stdin of another command. We can make it do so by using the pipe character ‘|’.
3) Pipe is also used to combine two or more commands, and in this, the output of one command acts as input to another command, and this command’s output may act as input to the next command and so on.
4) It can also be visualized as a temporary connection between two or more commands/ programs/ processes. The command line programs that do the further processing are referred to as filters.
Examples :
1) Listing all files and directories and give it as input to more command.
$ ls -l | more
2) Use sort and uniq command to sort a file and print unique values.
$ sort record.txt | uniq
3) Use head and tail to print lines in a particular range in a file.
$ cat sample2.txt | head -7 | tail -5
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date5 Jun 2019
Coding problem1
This is a cultural fitment testing round .HR was very frank and asked standard questions. Then we discussed about my role.
1. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you ?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round, like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 11 problems
Interviewed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
1176 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 11 problems
Interviewed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
1773 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
2184 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






