Hike interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Hike
5 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Coding Test - Pen and paper
Duration90 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem2
This test has 2 sections :
Section 1 ( Technical objective questions)
– 25 mcq’s mainly focusing on c , c++ , os , data structures , algorithms
Section 2 ( 2 Coding questions )
– Code was supposed to be written on paper.
1. Next Greater Number
Moderate
15m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string S which represents a number. You have to find the smallest number strictly greater than the given number which contains the same set of digits as of the original number i.e the frequency of each digit from 0 to 9 should be exactly the same as in the original number.
For example:
If the given string is 56789, then the next greater number is 56798. Note that although 56790 is also greater than the given number it contains 1 '0' which is not in the original number and also it does not contain the digit '8'.
Note:
The given string is non-empty.
If the answer does not exist, then return -1.
The given number does not contain any leading zeros.
Problem approach
Observations:
1. If all digits are sorted in descending order, then output is always “Not Possible”.
2. If all digits are sorted in ascending order, then we need to swap last two digits.
3. For other cases, we need to process the number from rightmost side to find the smallest of all greater numbers.
Steps:
1. Traverse the given number from rightmost digit, keep traversing till you find a digit which is smaller than the previously traversed digit. If no such digit is found, then output is “Not Possible”.
2. Now search the right side of above found digit ‘d’ for the smallest digit greater than ‘d’.
3. Swap the above found two digits.
4. Now sort all digits from position next to ‘d’ to the end of number. The number that we get after sorting is the required output.
2. Reverse Words In A String
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'str' of length 'N'.
Your task is to reverse the original string word by word.
There can be multiple spaces between two words and there can be leading or trailing spaces but in the output reversed string you need to put a single space between two words, and your reversed string should not contain leading or trailing spaces.
Example :
If the given input string is "Welcome to Coding Ninjas", then you should return "Ninjas Coding to Welcome" as the reversed string has only a single space between two words and there is no leading or trailing space.
Problem approach
Steps :
1. Reverse the individual words of the given string one by one.
2. Then, reverse the whole string from start to end to get the desired output.
Time Complexity : O(n)
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem1
First round of interview was based on basic data structures. Concepts related to binary search tree , uses and comparing complexity were asked. He also asked about Hashing , Collisions.
1. K Largest Element
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an unsorted array containing ‘N’ integers. You need to find ‘K’ largest elements from the given array. Also, you need to return the elements in non-decreasing order.
Problem approach
To solve the question using a max heap, make a max heap of all the elements of the list. Run a loop for k-1 times and remove the top element of the heap. After running the loop, the element at top will be the kth largest element, return that. Time Complexity : O(n + klogn)
The question can also be solved using a min heap.
Approach:
1. Create a min heap class with a capacity of k
2. When the heap reaches capacity eject the minimum number.
3. Loop over the array and add each number to the heap.
4. At the end, the largest k number of elements will be left in the heap, the smallest of them being at the top of the heap, which is the kth largest number
The time complexity for this solution is O(N logK).
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem2
The interview started with a programming question. Then he asked me a puzzle. There was a small discussion about my projects then .Then he started asking questions about operating system. The interviewer wanted to test my understanding about semaphores and asked some tricky and confusing questions .
1. Level Order Traversal
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the level order traversal of the given tree.
For example:
For the given binary tree
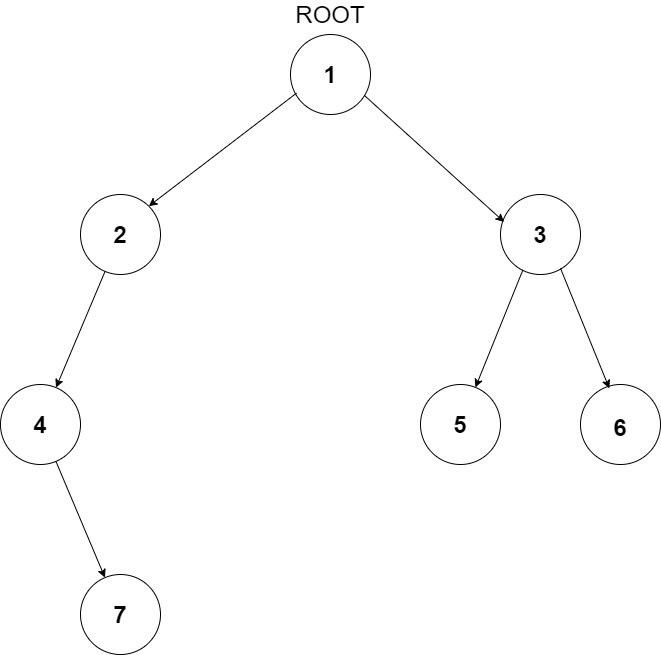
The level order traversal will be {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}.
Problem approach
A queue can be used to do level order traversal of the tree. For each node, first visit the node and then push its children nodes in the FIFO queue.
printLevelorder(tree)
1) Create an empty queue q
2) temp_node = root /*start from root*/
3) Loop while temp_node is not NULL
a) print temp_node->data.
b) Enqueue temp_node’s children
(first left then right children) to q
c) Dequeue a node from q.
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree
Space Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree
2. OS Question
Producer Consumer problem using Semaphores
Problem approach
Initialization of semaphores –
mutex = 1
Full = 0 // Initially, all slots are empty. Thus full slots are 0
Empty = n // All slots are empty initially
Solution for Producer –
do{
//produce an item
wait(empty);
wait(mutex);
//place in buffer
signal(mutex);
signal(full);
}while(true)
When producer produces an item then the value of “empty” is reduced by 1 because one slot will be filled now. The value of mutex is also reduced to prevent consumer to access the buffer. Now, the producer has placed the item and thus the value of “full” is increased by 1. The value of mutex is also increased by 1 because the task of producer has been completed and consumer can access the buffer.
Solution for Consumer –
do{
wait(full);
wait(mutex);
// remove item from buffer
signal(mutex);
signal(empty);
// consumes item
}while(true)
As the consumer is removing an item from buffer, therefore the value of “full” is reduced by 1 and the value is mutex is also reduced so that the producer cannot access the buffer at this moment. Now, the consumer has consumed the item, thus increasing the value of “empty” by 1. The value of mutex is also increased so that producer can access the buffer now.
04
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem1
Technical Interview round with questions based on DSA.
1. Find Peak Element
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n'. Find the index(0-based) of a peak element in the array. If there are multiple peak numbers, return the index of any peak number.
Peak element is defined as that element that is greater than both of its neighbors. If 'arr[i]' is the peak element, 'arr[i - 1]' < 'arr[i]' and 'arr[i + 1]' < 'arr[i]'.
Assume 'arr[-1]' and 'arr[n]' as negative infinity.
Note:
1. There are no 2 adjacent elements having same value (as mentioned in the constraints).
2. Do not print anything, just return the index of the peak element (0 - indexed).
3. 'True'/'False' will be printed depending on whether your answer is correct or not.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [1, 8, 1, 5, 3]
Output: 3
Explanation: There are two possible answers. Both 8 and 5 are peak elements, so the correct answers are their positions, 1 and 3.
Problem approach
The brute force solution would be to do a linear search and find the element.
Time Complexity : O(n)
The brute force solution can be optimized using Binary Search. The idea is to find the bitonic point k which is the index of the maximum element of a given sequence. If the element to be searched is greater than the maximum element return -1, else search the element in both halves.
Steps :
1. Find the bitonic point in the given array, i.e the maximum element in the given bitonic array using binary search.
2. If the element to be searched is equal to the element at the bitonic point then print the index of the bitonic point.
3. If the element to be searched is greater than the element at a bitonic point then the element does not exist in the array.
4. If the element to be searched is less than the element at a bitonic point then search for the element in both halves of the array using binary search.
05
Round
Easy
Telephonic
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 May 2015
Coding problem2
This round was a telephonic interview with the CTO of the company. The he started with a small discussion about my projects and research paper .He then moved on to data structures and asked me how to choose a relevant data structure for a given problem. I gave him advantages of every data structure and certain problems where specific data structures could be useful .Then he gave a question and asked me for what data structure should be used keeping time complexity in mind. He asked me a few HR questions in the end .
1. DBMS Question
What is an index? What kind of data structure is an index?
Problem approach
An index is a data structure (most commonly a B- tree) that stores the values for a specific column in a table. An index is created on a column of a table. So, the key points to remember are that an index consists of column values from one table, and that those values are stored in a data structure. The index is a data structure – remember that.
B- trees are the most commonly used data structures for indexes. The reason B- trees are the most popular data structure for indexes is due to the fact that they are time efficient – because look-ups, deletions, and insertions can all be done in logarithmic time. And, another major reason B- trees are more commonly used is because the data that is stored inside the B- tree can be sorted. The RDBMS typically determines which data structure is actually used for an index.
2. Average Marks
Easy
5m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given the name of a student in the form of a character ‘firstLetterOfName’ and 3 integers ‘M1’, ‘M2’, ‘M3’ representing the marks of the student in 3 subjects. You have to print the ‘firstLetterOfName’ of the student and the average marks obtained by the student.
Note: You need to print the integer part of the average only and neglect the decimal part.
For Example :
If ‘firstLetterOfName’ = ‘K’, ‘M1’ = 10, ‘M2’ = 6 and ‘M3’ = 9, then the average marks would be around 7.67. Hence, the output should be as follows:
K 7
Problem approach
I gave a solution by indexing marks with a linked list of students creating an array of link lists.
He then modified the question by adding marks in floating points were also allowed .
I gave him a solution using map (c++) based on a key value pair of marks and list of students but he asked to optimize the time complexity
I then gave a modification of my first solution and added concept of buckets and binary search .

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Hike
927 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hike
1063 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Hike
827 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hike
285 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





