Hike interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Hike
2 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS, Operating Systems
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Jun 2015
Coding problem2
Technical round with questions based on DSA were discussed.
1. Ninja and Two Sorted Arrays
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given two sorted integer arrays/lists ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ of size ‘M’ and ‘N’. Ninja has to merge these sorted arrays/lists into ‘ARR1’ as one sorted array. You may have to assume that ‘ARR1’ has a size equal to ‘M’ + ‘N’ such that ‘ARR1’ has enough space to add all the elements of ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
For example:
‘ARR1’ = [3 6 9 0 0]
‘ARR2’ = [4 10]
After merging the ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
‘ARR1’ = [3 4 6 9 10]
Problem approach
A simple approach would be to create a new arrays with size as sum of the sizes of both the arrays. Copy the elements of both the arrays in the new array and sort the array.
A space optimized approach also exists. While traversing the two sorted arrays parallelly, if we encounter the jth second array element is smaller than ith first array element, then jth element is to be included and replace some kth element in the first array.
Algorithm
1) Initialize i,j,k as 0,0,n-1 where n is size of arr1
2) Iterate through every element of arr1 and arr2 using two pointers i and j respectively
if arr1[i] is less than arr2[j]
increment i
else
swap the arr2[j] and arr1[k]
increment j and decrement k
3) Sort both arr1 and arr2
2. Reverse Alternate Nodes
Moderate
36m average time
51% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a perfect binary tree of 'N' nodes. Your task is to reverse alternate levels of the given binary tree. That is reverse level 2, level 4, level 6, and so on. The root is at level 1.
A perfect binary tree is a binary tree in which all the interior nodes have two children, and all leaves have the same depth or same level.
Example :
Given binary tree :
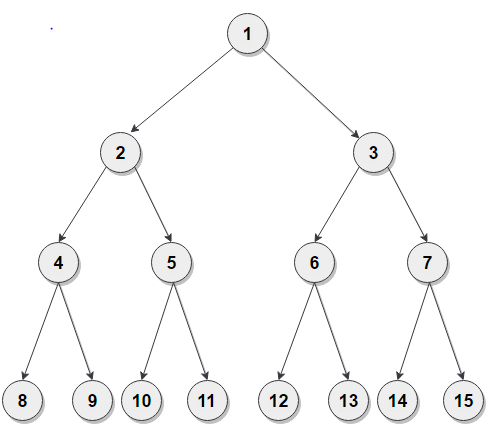
After the reversal of alternate nodes, the tree will be :
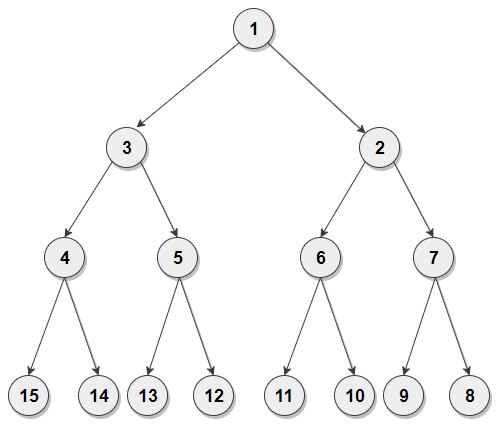
Problem approach
The brute force solution is to access nodes level by level and check if the current level is odd, then store nodes of this level in an array. Reverse the array and store elements back in the tree.
Another approach could be using a stack.
Traverse the tree in a depth-first fashion and for each level :
• If the level is odd, push the left and right child (if exists) in a stack.
• If the level is even, replace the value of the current node with the top of the stack.
Pseudocode:
reverseAlternate(Node root)
{
declare a queue q of node type
push the root node in q
define a node temp
initialise level as 1
declare a stack of int type
while (q is not empty) {
initialise a variable n to the current size of q
while (n != zero) {
fetch the front element of queue and assign it to variable temp
if (level % 2) {
if (left child of temp exists) {
push left child of temp in queue q
push key of left child in stack s
}
if (right child of temp exists) {
push right child of temp in queue q
push right of left child in stack s
}
}
else {
Replace the value of node (key of temp) with top of the stack
if (left child of temp exists) {
push left child of temp in queue q
}
if (right child of temp exists) {
push right child of temp in queue q
}
}
}
level++;
}
}
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date12 Jun 2015
Coding problem4
Technical round with questions based on OS, Java were discussed.
1. OS Question
Characteristics of distributed file systems
Problem approach
Remote data/file sharing: It allows a file to be transparently accessed by processes of any node of the system irrespective of the file’s location. Example: Any process ‘A’ can create the file and share it with other processes ‘B’ or ‘C’ and the same file can be accessed/modified process running in other nodes.
User mobility: Users in the distributed systems are allowed to work in any system at any time. So, users need not relocate secondary storage devices in distributed file systems.
Availability: Distributed file systems keep multiple copies of the same file in multiple places. Hence, the availability of the distributed file system is high and it maintains a better fault tolerance for the system.
Diskless workstations: Distributed file systems allow the use of diskless workstations to reduce noise and heat in the system. Also, diskless workstations are more economical than disk full workstations.
2. System Design Question
Design a file sharing mechanism between two users.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Design your structure and functions according to the requirements and try to convey your thoughts properly to the interviewer so that you do not mess up while implementing the idea .
3. Java Question
What is ConcurrentHashMap in Java?
Problem approach
The ConcurrentHashMap class of the Java collections framework provides a thread-safe map. That is, multiple threads can access the map at once without affecting the consistency of entries in a map.
It implements the ConcurrentMap interface.
4. Technical Question
How to analyze usage history of a application?
Problem approach
To access the App history tab, you first need to launch the Task Manager. We found it easiest to use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If you did not access this tool on Windows 10 before, it opens in the so-called compact view, providing a list of apps currently running on your device. Clicking or tapping More details opens the full version of the Task Manager.
Click or tap More details to open the full version of the Task Manager
By default, the full version of the Task Manager opens in the Processes tab. The next step is to go to the App history tab.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Hike
927 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hike
1063 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Hike
827 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Hike
285 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





