Hike interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Hike
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
It all started in my second year of college when I began studying data structures and algorithms. I always knew that these subjects were essential for interviews. Initially, I found them very challenging, but I kept practising. I started by studying data structures and their implementations, repeating the process multiple times. Once I gained confidence, I moved on to studying algorithms and their implementations. At that point, I hadn't started using coding practice platforms yet. After covering the major algorithms, I began practising on these platforms. From then on, I religiously practised until my interview day, and as a result, I found the interview very easy. That is all about my journey. Thank you.
Application story
I was offered this opportunity from college through pool placement. Multiple colleges took part in it.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected as I am good in DSA and my computer science fundamentals are up to the mark. Also, I am good at explaining my solutions.
Preparation
Duration: 12 months
Topics: Binary Search Patterns, Trees, Graphs, Union-find, Tries, Bit manipulations, DP
Tip
Tip 1: Start with data structures.
Tip 2: Cover algorithm patterns based on all data structures.
Tip 3: Practice on coding platforms.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: GPA - 7 or above, Degree: Computer Science Engineering
Resume tip
Tip 1:Keep all the projects.
Tip 2:Mention all the achievements.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date6 Mar 2023
Coding problem3
1. Search Insert Position
Easy
10m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a sorted array 'arr' of distinct values and a target value 'm'. You need to search for the index of the target value in the array.
Note:
1. If the value is present in the array, return its index.
2. If the value is absent, determine the index where it would be inserted in the array while maintaining the sorted order.
3. The given array has distinct integers.
4. The given array may be empty.
Example:
Input: arr = [1, 2, 4, 7], m = 6
Output: 3
Explanation: If the given array 'arr' is: [1, 2, 4, 7] and m = 6. We insert m = 6 in the array and get 'arr' as: [1, 2, 4, 6, 7]. The position of 6 is 3 (according to 0-based indexing)
Problem approach
The problem was based on simple logic.
2. Validate Binary Tree Nodes
Problem approach
Set the upper bound as the maximum integer, and the lower bound as the minimum integer in the run-time environment.
Start DFS traversal from the root node, and check whether each level follows BST rules or not.
Update the lower bound and upper bound before going down to the next level.
Once we find the violation, reject and early return False.
Otherwise, accept and return True if all tree nodes follow the BST rule.
3. Pattern Matching
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a pattern in the form of a string and a collection of words. Your task is to determine if the pattern string and the collection of words have the same order.
Note :
The strings are non-empty.
The strings only contain lowercase English letters.
Problem approach
Used pattern matching algorithm to solve that.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date8 Feb 2023
Coding problem2
1. Maximum Width In Binary Tree
Moderate
38m average time
50% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the maximum width of the given Binary Tree. The maximum width of the tree is the maximum width among all the levels of the given tree.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the leftmost and the rightmost, non-null nodes in the level, where the null nodes in between the leftmost and rightmost are excluded into length calculation.
For example :
For the given binary tree
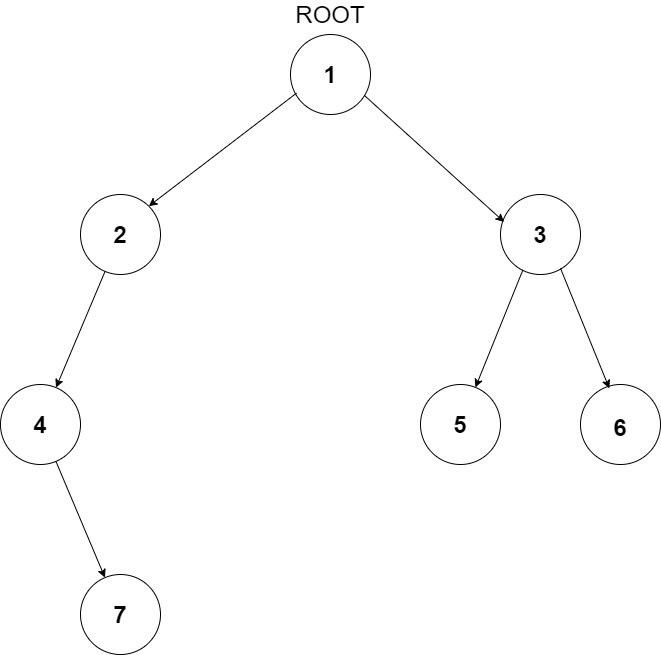
The maximum width will be at the third level with the length of 3, i.e. {4, 5, 6}.
Problem approach
Standard tree traversal with critical thinking was enough.
2. Sibling Nodes
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of ‘N’ nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to print all nodes that don’t have a sibling node.
Note:
1. Node ‘U’ is said to be a sibling of node ‘V’ if and only if both ‘U’ and ‘V’ have the same parent.
2. Root 1 is a sibling node.
Problem approach
Standard tree traversal with critical thinking was enough.
03
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date14 Mar 2023
Coding problem2
1. Making The Largest Island
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an 'n' x 'n' binary matrix 'grid'.
You are allowed to change at most one '0' to be '1'. Your task is to find the size of the largest island in the grid after applying this operation.
Note:
An island is a 4-directionally (North, South, East, West) connected group of 1s.
Example:
Input: 'grid' = [[1,0],
[0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation:
We can change the 0 at (0,1) to 1 and get an island of size 3.
Problem approach
The problem was straightforward.
2. Find Number Of Islands
Moderate
34m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 2-dimensional array/list having N rows and M columns, which is filled with ones(1) and zeroes(0). 1 signifies land, and 0 signifies water.
A cell is said to be connected to another cell, if one cell lies immediately next to the other cell, in any of the eight directions (two vertical, two horizontal, and four diagonals).
A group of connected cells having value 1 is called an island. Your task is to find the number of such islands present in the matrix.
Problem approach
The problem was straightforward.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Hike
2107 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Hike
1026 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Hike
1051 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Hike
1645 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15556 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15417 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10180 views
2 comments
0 upvotes


