HSBC interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Trainee Software Engineer
HSBC
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 - Practice At least 250 Questions of DS algo
Tip 2 - Do at least 2 application based projects
Application process
Where: Other
Eligibility: 6.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Tip 3 : Project should clear.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration120 minutes
Interview date19 Nov 2021
Coding problem3
It was an aptitude and coding test. Also it consists of technical questions MCQS
1. Merge Two Sorted Arrays
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given two sorted integer arrays/lists ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ of size ‘M’ and ‘N’. Ninja has to merge these sorted arrays/lists into ‘ARR1’ as one sorted array. You may have to assume that ‘ARR1’ has a size equal to ‘M’ + ‘N’ such that ‘ARR1’ has enough space to add all the elements of ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
For example:
‘ARR1’ = [3 6 9 0 0]
‘ARR2’ = [4 10]
After merging the ‘ARR1’ and ‘ARR2’ in ‘ARR1’.
‘ARR1’ = [3 4 6 9 10]
Problem approach
The idea is to begin from the last element of ar2[] and search it in ar1[]. If there is a greater element in ar1[], then we move the last element of ar1[] to ar2[]. To keep ar1[] and ar2[] sorted, we need to place the last element of ar2[] at the correct place in ar1[]. We can use Insertion Sort type of insertion for this.
2. Anagram Pairs
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'str1' and 'str1'.
You have to tell whether these strings form an anagram pair or not.
The strings form an anagram pair if the letters of one string can be rearranged to form another string.
Pre-requisites:
Anagrams are defined as words or names that can be formed by rearranging the letters of another word. Such as "spar" can be formed by rearranging letters of "rasp". Hence, "spar" and "rasp" are anagrams.
Other examples include:
'triangle' and 'integral'
'listen' and 'silent'
Note:
Since it is a binary problem, there is no partial marking. Marks will only be awarded if you get all the test cases correct.
Problem approach
This method assumes that the set of possible characters in both strings is small. In the following implementation, it is assumed that the characters are stored using 8 bit and there can be 256 possible characters.
Create count arrays of size 256 for both strings. Initialize all values in count arrays as 0.
Iterate through every character of both strings and increment the count of character in the corresponding count arrays.
Compare count arrays. If both count arrays are same, then return true.
3. Bottom View of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
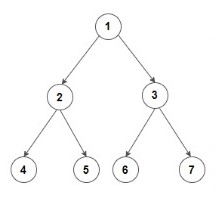
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
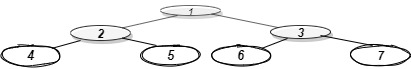
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
The following are steps to print the Bottom View of the Binary Tree.
We put tree nodes in a queue for the level order traversal.
Start with the horizontal distance(hd) 0 of the root node, and keep on adding a left child to the queue along with the horizontal distance as hd-1 and the right child as hd+1.
Also, use a TreeMap which stores key-value pairs sorted on key.
Every time, we encounter a new horizontal distance or an existing horizontal distance put the node data for the horizontal distance as the key. For the first time it will add to the map, next time it will replace the value. This will make sure that the bottom-most element for that horizontal distance is present on the map and if you see the tree from beneath that you will see that element.
02
Round
Easy
Assignment
Duration30 minutes
Interview date15 Nov 2021
Coding problem0
Scenario-based , decision making, situation-based analysis and behavioural questions. questions were asked and students had to choose the most appropriate options accordingly.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Nov 2021
Coding problem2
This was the technical round.
1. Painter's Partition Problem
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array/list of length ‘n’, where the array/list represents the boards and each element of the given array/list represents the length of each board. Some ‘k’ numbers of painters are available to paint these boards. Consider that each unit of a board takes 1 unit of time to paint.
You are supposed to return the area of the minimum time to get this job done of painting all the ‘n’ boards under a constraint that any painter will only paint the continuous sections of boards.
Example :
Input: arr = [2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3], k = 2
Output: 11
Explanation:
First painter can paint boards 1 to 3 in 8 units of time and the second painter can paint boards 4-6 in 11 units of time. Thus both painters will paint all the boards in max(8,11) = 11 units of time. It can be shown that all the boards can't be painted in less than 11 units of time.
2. Interleaving Two Strings
Moderate
45m average time
50% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given three strings 'A', 'B' and 'C'. Check whether 'C' is formed by an interleaving of 'A' and 'B'.
'C' is said to be interleaving 'A' and 'B', if the length of 'C' is equal to the sum of the length of 'A' and length of 'B', all the characters of 'A' and 'B' are present in 'C' and the order of all these characters remains the same in all three strings.
For Example:
If A = “aab”, 'B' = “abc”, 'C' = “aaabbc”
Here 'C' is an interleaving string of 'A' and 'B'. because 'C' contains all the characters of 'A' and 'B' and the order of all these characters is also the same in all three strings.
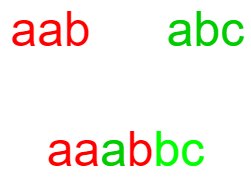
If 'A' = “abc”, 'B' = “def”, 'C' = “abcdefg”
Here 'C' is not an interleaving string of 'A' and 'B'. 'B'ecause neither A nor 'B' contains the character ‘g’.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Trainee Software Engineer
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by HSBC
2766 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Trainee Software Engineer
3 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by HSBC
2080 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Trainee Software Engineer
4 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by HSBC
6646 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by HSBC
1453 views
0 comments
0 upvotes


