IDEMIA interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Associate Software Engineer
IDEMIA
1 rounds | 17 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I began by strengthening my basics and consistently practicing through projects and mock interviews. Gradually, I gained confidence and improved problem-solving skills. Staying disciplined, learning from failures, and seeking guidance from peers helped me grow. This journey taught me persistence and adaptability, which eventually helped me crack the opportunity.
Application story
I came across the opportunity on LinkedIn and reached out for a referral from a known connection working in the organization. Their guidance on focusing on DSA and DBMS helped me prepare well. Proactively networking, seeking referrals, and preparing strategically played a key role in successfully moving through the process.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was not selected as the hiring process was put on hold due to a freeze. The feedback I received was positive regarding my performance, and the experience gave me valuable insights and confidence to prepare better for future opportunities.
Preparation
Duration: 2 months
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, DBMS, Operating Systems, System Design
Tip
Tip 1: Practise writing SQL queries. Do not focus only on theory.
Tip 2: Practise programming questions from various online coding platforms.
Tip 3: Have a good command over core computer science subjects.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: 6.5 CGPA, (Salary package: 4.5 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Keep at least two full-stack projects to showcase your end-to-end development skills.
Tip 2: Include your coding platform profiles, GitHub, and LinkedIn links in your resume to create a strong professional impression.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date23 Aug 2022
Coding problem17
The 90-minute online assessment was conducted on the Mettl platform in a secure and monitored environment. A timer was visible throughout, and no screen switching was allowed. There was no interviewer, but the system tracked activity and issued warning messages if any unusual behaviour was detected. The assessment consisted of 15 MCQs and 2 coding problems.
1. Puzzle
You have 8 balls, one of which is heavier. Using a weighing balance, find the heavier ball in minimum attempts.
Problem approach
Tip 1: Break problems into smaller steps.
2. Puzzle
A clock shows the time as 3:15. What is the angle between the hour and the minute hand?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Think logically, not just mathematically.
Tip 2: Draw diagrams or write notes.
3. Puzzle
Two trains are 120 km apart and move towards each other at speeds of 60 km/h and 40 km/h. A bird starts flying from one train to the other at 80 km/h until the trains meet. Find the total distance covered by the bird.
4. Puzzle
There are 100 doors initially closed. A person toggles doors in the following way: toggles every door in the first pass, every 2nd door in the second pass, every 3rd in the third pass, and so on till the 100th pass. Which doors remain open?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Break problems into smaller steps.
5. Puzzle
A man walks 1 km south, 1 km east, and 1 km north and comes back to the same point. How is this possible?
6. Operating System
Which scheduling algorithm may cause starvation?
Problem approach
SJF and Priority scheduling (non-preemptive).
7. Operating System
Consider 3 processes with burst times 10, 5, and 8. Calculate the average waiting time using FCFS scheduling.
Problem approach
Order P1(10), P2(5), P3(8). WT = [0, 10, 15], Avg = (0+10+15)/3 = 8.33 ms.
8. Operating System
Which of the following is not true about deadlock?
a) Mutual exclusion is a necessary condition
b) Hold and wait must exist
c) Circular wait must exist
d) Deadlock can always be resolved using FCFS
9. Operating System
In demand paging, what happens on a page fault?
10. Operating System
Which of the following is true about thrashing?
a) It increases CPU utilization
b) It occurs due to excessive paging
c) It reduces I/O time
d) It improves performance
11. DBMS
Consider a relation R(A,B,C,D) with functional dependencies:
A → B, B → C. What is the highest normal form?
Problem approach
3NF (since transitive dependency exists).
12. DBMS
Which of the following ensures atomicity in transactions?
a) Commit log
b) Checkpoint
c) Transaction log
d) Deadlock prevention
Problem approach
Transaction log
13. SQL
Given the SQL query:
SELECT name FROM Student WHERE marks > ALL (SELECT marks FROM Student WHERE dept = 'CSE');
What does it return?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Do practice for SQL queries.
Ans: Returns student(s) with marks greater than the highest marks in CSE.
14. DBMS
Which of the following indexing techniques is used in databases for faster access?
a) Hashing
b) B+ Tree
c) Both a & b
d) None
Problem approach
Tip 1: Ensure to cover indexing techniques in databases.
15. DBMS
In two-phase locking protocol, which problem can still occur?
a) Deadlock
b) Lost update
c) Dirty read
d) Non-repeatable read
Problem approach
Practice locking protocols.
16. Longest Subarray With Sum K
Easy
20m average time
75% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You are given an array 'a' of size 'n' and an integer 'k'.
Find the length of the longest subarray of 'a' whose sum is equal to 'k'.
Example :
Input: ‘n’ = 7 ‘k’ = 3
‘a’ = [1, 2, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Subarrays whose sum = ‘3’ are:
[1, 2], [3], [1, 1, 1] and [1, 1, 1]
Here, the length of the longest subarray is 3, which is our final answer.
Problem approach
1. Use a prefix-sum and a hashmap that maps prefix_sum → earliest_index. Initialize with {0: -1}.
2. Iterate i from 0 to n-1, update prefix_sum += arr[i].
3. Check if (prefix_sum - K) exists in the map. If yes, candidate length = i - map[prefix_sum - K]. Update max_len.
4. If prefix_sum is not already in the map, store map[prefix_sum] = i (store earliest index to maximize length).
5. After loop, return max_len (0 if no subarray found).
17. Is Height Balanced Binary Tree
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given the root node of a binary tree.
Return 'true' if it is a height balanced binary tree.
Note:
Height of a tree is the maximum number of nodes in a path from the node to the leaf node.
An empty tree is a height-balanced tree. A non-empty binary tree is a height-balanced binary tree if
1. The left subtree of a binary tree is already the height-balanced tree.
2. The right subtree of a binary tree is also the height-balanced tree.
3. The difference between heights of left subtree and right subtree must not more than ‘1’.
Example:
Input: Consider the binary tree given below:
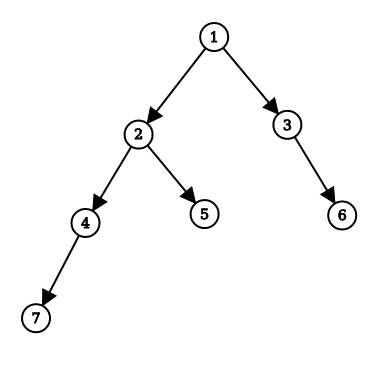
Output: 'true'
Explanation:
Consider subtree at Node ( 7 )
Left subtree height is ‘0’ and right subtree height is ‘0’, the absolute height difference is ‘0-0 = 0’ and ‘0’ is not more than ‘1’ so subtree at Node ( 7 ) is a height-balanced binary tree.
Same for subtrees at Nodes ( 5, 6 ).
Consider subtree at Node ( 4 )
Left subtree height is ‘1’ and right subtree height is ‘0’, the absolute height difference is ‘1-0 = 1’ and ‘1’ is not more than ‘1’ so subtree at Node ( 4 ) is a height-balanced binary tree.
Same for subtree at Node ( 3)
Consider subtree at Node ( 2 )
Left subtree height is ‘2’ and right subtree height is ‘1’, the absolute height difference is ‘2-1 = 1’ and ‘1’ is not more than ‘1’ so subtree at Node ( 2 ) is a height-balanced binary tree.
Consider subtree at Node ( 1 )
Left subtree height is ‘3’ and right subtree height is ‘2’, the absolute height difference is ‘3-2 = 1’ and ‘1’ is not more than ‘1’ so subtree at Node ( 1 ) is a height-balanced binary tree.
Because the root node ( 1 ) is a height-balanced binary tree, so the complete tree is height-balanced.
Problem approach
1. Define recursive helper height(node) that:
a. Returns 0 if node is None.
b. Calls left = height(node.left). If left == -1 return -1 (propagate unbalanced).
c. Calls right = height(node.right). If right == -1 return -1.
d. If abs(left - right) > 1 return -1 (unbalanced).
e. Else return max(left, right) + 1 (height).
2. Main check: tree is balanced iff height(root) != -1.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
2 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by IDEMIA
566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6544 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2729 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
3 rounds | 15 problems
Interviewed by Ernst & Young (EY)
2383 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Software Engineer
4 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by NCR Corporation
1503 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








