Impact Analytics interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Frontend Developer
Impact Analytics
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
When I joined college, I was unaware of Data Structures and Algorithms, which made my journey to getting an internship way more complicated. From that point, I started doing questions on Code Studio and other platforms.
Application story
This was an online contest in which all student around India can participate in it.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I have a good history of content preparation, and I do not have a decent rank on coding platforms.
Preparation
Duration: 8 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Practice from coding platforms, solve medium level problems.
Tip 2 : Brush up computer fundamentals from subjects like OS, DBMS and CN.
Tip 3 : Have a good project or good internship experience and have in-depth knowledge regarding what you have done.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume.
Tip 2: Do not put false things on resume
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 mins
Interview date9 Jun 2023
Coding problem2
1. All Paths From Source Lead To Destination
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



There is a directed graph consisting of ‘N’ nodes numbered from 0 to ‘N’-1. You are given a list ‘EDGES’ of size ‘M’, consisting of all the edges of this directed graph, and two nodes ‘SRC’ and ‘DEST’ of this graph. Determine whether or not all paths starting from node ‘SRC’ eventually end at node ‘DEST’, that is -:
1. At least one path exists from node ‘SRC’ to node ‘DEST’.
2. If there exists a path from the node ‘SRC’ to a node with no outgoing edges, then that node must be ‘DEST’.
3. There should be a finite number of paths from ‘SRC’ to ‘DEST’.
You should return True if all paths starting from node ‘SRC’ eventually end at node ‘DEST’, Otherwise, return False. See the example for more clarity.
Note :
1. The given graph may have self-loops and parallel edges.
Example :
Consider ‘N’ = 4, ‘EDGES’ = [[0, 1], [0, 3], [1, 2], [3, 2]], ‘SRC’ = 0 and ‘DEST’ = 2. The given directed graph is shown below.
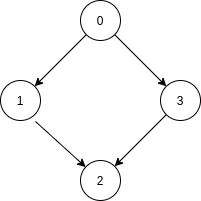
Here, all the paths that start from node 0 are -:
1. 0->1->2
2. 0->3->2
Both of these paths eventually end at node ‘2’ i.e node ‘DEST’. Thus we should return True.
Problem approach
The idea is to do Depth First Traversal of given directed graph.
Start the DFS traversal from source.
Keep storing the visited vertices in an array or HashMap say ‘path[]’.
If the destination vertex is reached, print contents of path[].
The important thing is to mark current vertices in the path[] as visited also so that the traversal doesn’t go in a cycle.
2. Design Question
I was given a wireframe of a dashboard and was asked to create a similar-looking dashboard using Angular and Node.js.
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Structure your code well.
Tip 2 : Be thorough with the whats and whys of the implementation.
Tip 3 : See that the project runs, and you can demo it.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 mins
Interview date9 Jun 2023
Coding problem2
1. Add Linked Lists
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given two numbers represented by linked lists. Your task is find the sum list and return the head of the sum list.
The sum list is a linked list representation of addition of two numbers.
Problem approach
PROGRAM:
class Solution
{
public:
//Function to add two numbers represented by linked list.
Node*reverse(struct Node*head){
Node*curr=head;
Node*prev=NULL;
Node*nxt;
while(curr!=NULL){
nxt=curr->next;
curr->next=prev;
prev=curr;
curr=nxt;
}
return prev;
}
public:
struct Node* addTwoLists(struct Node* first, struct Node* second)
{
// code here
first=reverse(first);
second=reverse(second);
int c=0;
int s=0;
Node*temp;
Node*cur;
Node*res=NULL;
while(first!=NULL||second!=NULL){
s=c+(first?first->data:0)+(second?second->data:0);
if(s>9){
c=1;
}
else{
c=0;
}
s=s%10;
temp=new Node(s);
if(res==NULL)res=temp;
else{
cur->next=temp;
}
cur=temp;
if(first)first=first->next;
if(second)second=second->next;
}
if(c!=0){
temp=new Node(c);
cur->next=temp;
cur=temp;
}
res=reverse(res);
return res;
}
};
2. Flatten A Linked List
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a linked list containing 'n' 'head' nodes, where every node in the linked list contains two pointers:
(1) ‘next’ which points to the next node in the list
(2) ‘child’ pointer to a linked list where the current node is the head.
Each of these child linked lists is in sorted order and connected by 'child' pointer.
Your task is to flatten this linked such that all nodes appear in a single layer or level in a 'sorted order'.
Example:
Input: Given linked list is:
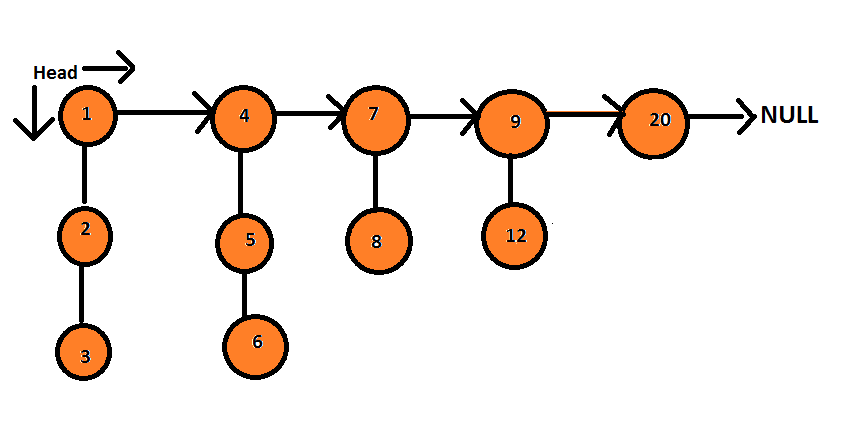
Output:
1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 → 6 → 7 → 8 → 9 → 12 → 20 → null.
Explanation:
The returned linked list should be in a sorted order. All the elements in this returned linked list are connected by 'child' pointers and 'next' pointers point to null.
Problem approach
PROGRAM:
Node*merge(Node*a,Node*b){//a=root b=root ka right wala
if(a==NULL)return b;
if(b==NULL)return a;
Node*res;
if(a->datadata)
{
res=a;
res->bottom=merge(a->bottom,b);
}
else{
res=b;
res->bottom=merge(a,b->bottom);
}
res->next=NULL;
return res;
}
Node *flatten(Node *root)
{
if(root==NULL || root->next==NULL)return root;
return merge(root,flatten(root->next));
}
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 mins
Interview date9 Jun 2023
Coding problem2
1. Maximum Sum
Moderate
35m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array “ARR” of N integers. You are required to perform an operation on the array each time until it becomes empty. The operation is to select an element from the array(let’s say at ith index i.e ARR[i]) and remove one occurrence of the selected element from the array and remove all the occurrences of (ARR[i]-1) and (ARR[i]+1) from the array(if present). Your task is to maximize the sum of selected elements from the array.
For example, let’s say the given array is [2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5].
The maximum possible sum for the given array would be 14. Because if we select one of the 3’s from the array, then one 3 and all occurrences of (3-1) and (3+1) i.e 2 and 4 will be deleted from the array. Now we left with {3,3,5} elements in the array. Then again we select 3 in the next two steps and in both steps 3 will be deleted also (3-1) and (3+1) doesn't exist in the array so nothing extra to delete in both steps. Now we left with only {5} and in the next step, we select the 5 and delete it. Then the array becomes empty. Thus the sum of selected elements will be 3+3+3+5 = 14.
Problem approach
Sort each row of the array and pick the maximum element from each to get the maximum sum.
2. Stack using queue
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Implement a Stack Data Structure specifically to store integer data using two Queues.
There should be two data members, both being Queues to store the data internally. You may use the inbuilt Queue.
Implement the following public functions :
1. Constructor:
It initializes the data members(queues) as required.
2. push(data) :
This function should take one argument of type integer. It pushes the element into the stack and returns nothing.
3. pop() :
It pops the element from the top of the stack and, in turn, returns the element being popped or deleted. In case the stack is empty, it returns -1.
4. top :
It returns the element being kept at the top of the stack. In case the stack is empty, it returns -1.
5. size() :
It returns the size of the stack at any given instance of time.
6. isEmpty() :
It returns a boolean value indicating whether the stack is empty or not.
Operations Performed on the Stack:
Query-1(Denoted by an integer 1): Pushes an integer data to the stack. (push function)
Query-2(Denoted by an integer 2): Pops the data kept at the top of the stack and returns it to the caller. (pop function)
Query-3(Denoted by an integer 3): Fetches and returns the data being kept at the top of the stack but doesn't remove it, unlike the pop function. (top function)
Query-4(Denoted by an integer 4): Returns the current size of the stack. (size function)
Query-5(Denoted by an integer 5): Returns a boolean value denoting whether the stack is empty or not. (isEmpty function)
Example
Operations:
1 5
1 10
2
3
4
Enqueue operation 1 5: We insert 5 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5]
Enqueue operation 1 10: We insert 10 at the back of the queue.
Queue: [5, 10]
Dequeue operation 2: We remove the element from the front of the queue, which is 5, and print it.
Output: 5
Queue: [10]
Peek operation 3: We return the element present at the front of the queue, which is 10, without removing it.
Output: 10
Queue: [10]
IsEmpty operation 4: We check if the queue is empty.
Output: False
Queue: [10]
Problem approach
Make sure that the newly entered element is always at the front of 'q1', so that the pop operation just dequeues from 'q1'. 'q2' is used to place every new element at the front of 'q1'.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Impact Analytics
2603 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Impact Analytics
806 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Impact Analytics
803 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Frontend Developer
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Impact Analytics
826 views
0 comments
0 upvotes


