Impetus Technology interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Impetus Technology
3 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I have recently completed my Engineering from Amity University Noida, specializing in Computer Science Engineering. In the second year, I started learning Java and DSA from Coding Ninjas. After learning DSA, I began working on projects. I was quite confident in my skills. I used to practice DSA questions daily on coding platforms and was very confident in my abilities.
Application story
I got this opportunity on campus. A form was rolled out for it, where we needed to fill in all the necessary details along with our resume.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I got rejected for this role. I was not confident in the interview. I knew all the answers perfectly, but there was a lack of confidence. From this incident, I learned that first, you need confidence, and then knowledge.
Preparation
Duration: 10 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS, DBMS, JAVA, OS
Tip
Tip 1: Practice at least 250 questions.
Tip 2: Prepare at least 2 good projects.
Tip 3: Have good communication skills.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Be honest with your resume.
Tip 2: Your resume should be crisp and short.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date23 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
It was proctored and It was in the afternoon.
1. Unique Paths
Moderate
25m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You are present at point ‘A’ which is the top-left cell of an M X N matrix, your destination is point ‘B’, which is the bottom-right cell of the same matrix. Your task is to find the total number of unique paths from point ‘A’ to point ‘B’.In other words, you will be given the dimensions of the matrix as integers ‘M’ and ‘N’, your task is to find the total number of unique paths from the cell MATRIX[0][0] to MATRIX['M' - 1]['N' - 1].
To traverse in the matrix, you can either move Right or Down at each step. For example in a given point MATRIX[i] [j], you can move to either MATRIX[i + 1][j] or MATRIX[i][j + 1].
Problem approach
Maintain a head and a tail pointer on the merged linked list.
Then choose the head of the merged linked list by comparing the first node of both linked lists.
For all subsequent nodes in both lists, you choose the smaller current node link it to the tail of the merged list, and move the current pointer of that list one step forward.
You keep doing this while there are some remaining elements in both lists.
If there are still some elements in only one of the lists, you link this remaining list to the tail of the merged list.
Initially, the merged linked list is NULL.
Compare the value of the first two nodes and make the node with the smaller value the head node of the merged linked list.
Since it’s the first and only node in the merged list, it will also be the tail.
Then move head1 one step forward.
2. Edit Distance
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'S' and 'T' of lengths 'N' and 'M' respectively. Find the "Edit Distance" between the strings.
Edit Distance of two strings is the minimum number of steps required to make one string equal to the other. In order to do so, you can perform the following three operations:
1. Delete a character
2. Replace a character with another one
3. Insert a character
Note:
Strings don't contain spaces in between.
Problem approach
The number of unique paths from a given cell (i,j) to the end cell is always fixed. So, we don't need to calculate and repeat the same process for a given cell multiple times. We can just store the result calculated for cell (i, j) and use that result in the future whenever required.
Thus, here we use a 2d array dp, where dp[i][j] denotes the number of unique paths from the cell (i, j) to the end cell (m-1, n-1). Once we get an answer for cell (i, j), we store the result in dp[i][j] and reuse it instead of recalculating it.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date26 Aug 2021
Coding problem3
1. N-th Node From The End
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. You have to find the N-th node from end.
For Example
If the given list is (1 -> -2 -> 0 -> 4) and N=2:
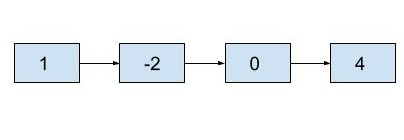
Then the 2nd node from the end is 0.
Problem approach
1. Initialize count = 0
2. Loop through the link list
a. If the count is equal to the passed index then return the current
node
b. Increment count
c. change current to point to next of the current.
2. Colour The Graph
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a graph with 'N' vertices numbered from '1' to 'N' and 'M' edges. You have to colour this graph in two different colours, say blue and red such that no two vertices connected by an edge are of the same colour.
Note :
The given graph may have connected components.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration35 minutes
Interview date30 Aug 2021
Coding problem4
1. Theory Questions
What is the difference between trees and graphs? Explain using proper coding explanation.
Problem approach
A graph can be connected or disconnected, can have cycles or loops, and does not necessarily have a root node. A tree is a type of graph that is connected, acyclic (meaning it has no cycles or loops), and has a single root node.
3. Inorder Traversal
Easy
32m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to return the In-Order traversal of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
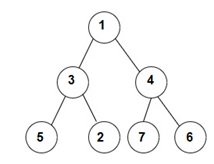
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
Problem approach
There are three solutions to this problem.
Iterative solution using stack: O(n) time and O(n) space;
Recursive solution: O(n) time and O(n) space (function call stack);
Morris traversal: O(n) time and O(1) space.
4. Maximum Subarray Sum
Moderate
35m average time
81% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'arr' of length 'n', consisting of integers.
A subarray is a contiguous segment of an array. In other words, a subarray can be formed by removing 0 or more integers from the beginning and 0 or more integers from the end of an array.
Find the sum of the subarray (including empty subarray) having maximum sum among all subarrays.
The sum of an empty subarray is 0.
Example :
Input: 'arr' = [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2, -10, 9, 1]
Output: 11
Explanation: The subarray yielding the maximum sum is [1, 2, 7, -4, 3, 2].
Problem approach
At each index i, we can either pick that element or not pick it.
If we pick the current element, then all future elements must also be picked since our array needs to be contiguous.
If we had picked any elements till now, we can either end further recursion at any time by returning the sum formed till now or we can choose the current element and recurse further. This denotes two choices either choosing the subarray formed from 1st picked element till now or expanding the subarray by choosing the current element respectively.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
937 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2661 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes





