Incode interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
Incode
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I was advised by my seniors to practice DSA from the very start of B.Tech, but I did not take that seriously. Honestly speaking, I regretted not taking their advice, and in my third year, I started doing coding and had to increase my practice hours because I had started late. By the end of my third year, I was confident in both DSA and development, but even then, I kept revising the concepts.
Application story
This company visited my campus for placement. We just had to upload our resumes and fill out all the details in the form. First, they conducted the online assessment. Later, they called us for the interview rounds.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
The basic reason for my rejection was my not having very strong knowledge of core DSA fundamentals, and my problem-solving ability is also not very good.
Preparation
Duration: 8 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, OOPS, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Practice popular questions on Arrays, Binary Trees, and LinkedLists from CodeStudio's Interview Problems.
Tip 2: Make sure you are aware of calculating the time and space complexity for every problem you're coding.
Tip 3: Prepare through mock interviews to practice explaining your approach while solving problems in an actual interview.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Describe the best of your projects in as few words as possible. Don't forget to include buzzwords like REST APIs, DB Indexing, Benchmarking, etc., if you worked on the backend.
Tip 2: Don't include school achievements like Olympiads or being a Class Topper on your resume.
Tip 3: If you have work experience, present it in a way that markets yourself. Use terms like "Created/Owned the Project through the entire SDLC.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 mins
Interview date17 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Convert a binary tree to its sum tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree of integers, you are supposed to modify the given binary tree to a sum tree where each node value is replaced by the sum of the values of both left and right subtrees in the given tree. The value of leaf nodes is changed to zero.
Example:
Below is the example showing the input tree and its sum tree.
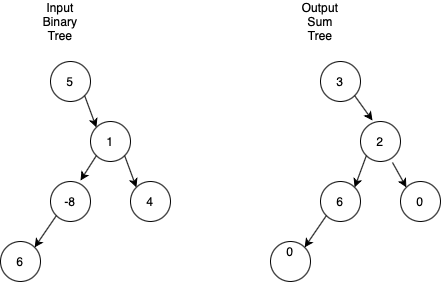
Problem approach
Do a traversal of the given tree. In the traversal, store the old value of the current node, recursively call for the left and right subtrees, and change the value of the current node to the sum of the values returned by the recursive calls. Finally, return the sum of the new value and the old value (which is the sum of the values in the subtree rooted at this node).
2. Remove BST keys outside the given range
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a Binary Search Tree (BST) and a range [min, max], remove all keys which are outside the given range. The modified tree should also be BST.
Problem approach
There are two possible cases for every node:
The node’s key is outside the given range. This case has two sub-cases: a) The node’s key is smaller than the minimum value. b) The node’s key is greater than the maximum value.
The node’s key is within the range.
We don’t need to do anything for case 2.
In case 1, we need to remove the node and change the root of the subtree rooted at this node. The idea is to fix the tree in a post-order fashion. When we visit a node, we ensure that its left and right subtrees are already fixed. In case
1.a), we simply remove the root and return the right subtree as the new root. In case
1.b), we remove the root and return the left subtree as the new root.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Zigzag Binary Tree Traversal
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a ‘Binary Tree’.
Return the level-order traversal of the Binary Tree.
Example:
Input: Consider the following Binary Tree:

Output:
Following is the level-order traversal of the given Binary Tree: [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 4]
Problem approach
We can use a queue just like we did in Level Order Traversal. However, in this case, we can also maintain a flag variable that keeps track of the alternate level to reverse the order of the corresponding level traversal. flag == true implies that we have to insert from left to right, and flag == false means we have to insert elements from right to left in our answer vector.
2. Quick Sort
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array of integers. You need to sort the array in ascending order using quick sort.
Quick sort is a divide and conquer algorithm in which we choose a pivot point and partition the array into two parts i.e, left and right. The left part contains the numbers smaller than the pivot element and the right part contains the numbers larger than the pivot element. Then we recursively sort the left and right parts of the array.
Example:
Let the array = [ 4, 2, 1, 5, 3 ]
Let pivot to be the rightmost number.
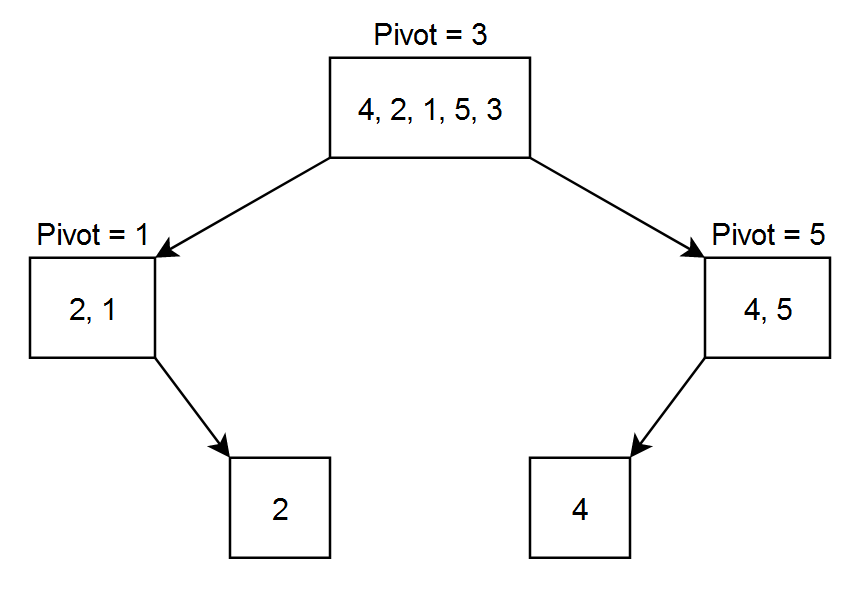
After the 1st level partitioning the array will be { 2, 1, 3, 4, 5 } as 3 was the pivot. After 2nd level partitioning the array will be { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 } as 1 was the pivot for the left part and 5 was the pivot for the right part. Now our array is sorted and there is no need to divide it again.
Problem approach
It is a straight forward sorting algorithm.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Apr 2023
Coding problem2
1. Rotate matrix by 90 degrees
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a square matrix of non-negative integers 'MATRIX'. Your task is to rotate that array by 90 degrees in an anti-clockwise direction using constant extra space.
For example:
For given 2D array :
[ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ] ]
After 90 degree rotation in anti clockwise direction, it will become:
[ [ 3, 6, 9 ],
[ 2, 5, 8 ],
[ 1, 4, 7 ] ]
2. Evaluation of postfix expression
Easy
15m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



An expression is called the postfix expression if the operator appears in the expression after the operands.
Example :
Infix expression: A + B * C - D
Postfix expression: A B + C D - *
Given a postfix expression, the task is to evaluate the expression. The answer could be very large, output your answer modulo (10^9+7). Also, use modular division when required.
Note:
1. Operators will only include the basic arithmetic operators like '*', '/', '+', and '-'.
2. The operand can contain multiple digits.
3. The operators and operands will have space as a separator between them.
4. There won’t be any brackets in the postfix expression.
Problem approach
An expression is called a postfix expression if the operator appears in the expression after the operands.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Incode
330 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Incode
397 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Incode
367 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Incode
327 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7923 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4395 views
1 comments
0 upvotes




