InfoEdge India Private Limitied interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
InfoEdge India Private Limitied
4 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
My journey started with building a strong foundation in the basics. In the beginning, I focused heavily on understanding core concepts—data structures, algorithms, operating systems, databases, and basic system design—rather than rushing toward advanced topics. There were phases where progress felt slow, but consistently revisiting fundamentals helped me gain clarity and confidence over time.
Alongside theory, I made it a point to apply what I learned through projects and hands-on practice. Building real applications, debugging my own mistakes, and improving existing code taught me far more than just solving problems mechanically. I also spent a lot of time reflecting on why a solution works, not just how to write it.
Preparation wasn’t always linear. There were rejections, self-doubt, and moments where I questioned whether I was on the right path. Instead of getting discouraged, I treated each setback as feedback—identifying gaps in my knowledge and working on them deliberately. Consistency mattered more than intensity; even small daily efforts added up over time.
What truly helped me crack this interview was discipline, patience, and a mindset focused on learning rather than just clearing an interview. I stopped comparing my journey with others and focused on improving a little every day. To anyone starting out: trust the process, stay curious, and don’t underestimate the power of strong fundamentals. With persistence and honest effort, results will eventually follow.
Application story
I applied for this opportunity through the on-campus placement process at my college. After submitting my resume on the campus portal, I was shortlisted for the initial screening based on my profile. The recruitment process was well-structured and communicated clearly at each stage. I received timely updates regarding the next steps, which helped me prepare accordingly. The entire process, from application to interview, was smooth and professionally conducted, making it a valuable and positive experience overall.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I believe I was selected because of my strong grasp of fundamentals, clear problem-solving approach, and ability to communicate my thoughts logically. I focused on understanding concepts deeply rather than memorizing solutions, which helped me handle questions calmly and confidently.
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures and Algorithms, OOPS, Computer Networks, DBMS, OS, System Design
Tip
Tip 1: Focus on strengthening your fundamentals (DSA, OS, DBMS, OOPs) before moving to advanced topics.
Tip 2: Practice coding problems regularly and analyse multiple approaches instead of memorizing solutions.
Tip 3: Build and work on real-world projects to apply concepts, improve problem-solving.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7 CGPA, (Stipend: 60k per month)
Resume tip
Tip 1: Keep your resume concise and highlight strong fundamentals, relevant projects, and measurable impact rather than listing everything.
Tip 2: Be honest about your skills and experiences, and ensure you can confidently explain anything mentioned on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date20 Sep 2024
Coding problem2
It was an online assessment consisting of a coding problem and some computer fundamentals.
1. Operating System
- Why do we need virtual memory when physical memory (RAM) already exists? How does virtual memory allow a process to use more memory than the available physical RAM? What are the advantages and disadvantages of virtual memory? (Learn)
- What is the role of paging in virtual memory management? (Learn)
- Can you explain how logical (virtual) address is converted into a physical address? (Learn)
- What is a page fault, and how does the operating system handle it step by step? (Learn)
- What is demand paging, and how is it different from loading all pages at once? (Learn)
- What are page replacement algorithms? Can you name a few and explain when they are used? (Learn)
- What is thrashing, and under what conditions does it occur? (Learn)
2. Single Source Shortest Path
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given an undirected graph with 'N' nodes and 'M' edges. The weight of each edge in the graph is one unit.
Given a source vertex 'src', you must return an array 'answer' of length 'N', where 'answer[i]' is the shortest path length between the source vertex 'src' and 'i'th vertex.
Note:
All the nodes are zero-based.
Example:
Input:
N=5, M=5, edges=[(0, 1), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)], src=1
Output: 1 0 2 2 1
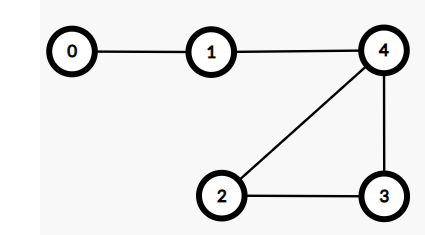
Explanation: The path from vertices are:-
(1->0) = 1 -> 0, path length is 1.
(1->1) = 1 -> 1, path length is 0.
(1->2) = 1 -> 4 -> 2, the path length is 2.
(1->3) = 1 -> 4 -> 3, path length is 2.
(1->4) = 1 -> 4, the path length is 1.
Hence we return [1, 0, 2, 2, 1]
Problem approach
Step 1: I first analysed the problem and identified that it was a graph-based problem involving minimum cost / shortest path between nodes.
Step 2: Since the graph had non-negative edge weights, I decided to use Dijkstra’s Algorithm, as it is optimal for finding the shortest path in such scenarios.
Step 3: I represented the graph using an adjacency list to efficiently store the nodes and edges, considering the input size constraints.
Step 4: I initialized a distance array with infinite values for all nodes except the source node, which was set to 0.
Step 5: I used a min-heap (priority queue) to always pick the node with the minimum current distance.
Step 6: For each extracted node, I relaxed all its adjacent edges by updating their distances if a shorter path was found.
Step 7: This process was repeated until all reachable nodes were processed and the minimum distances from the source were finalized.
Step 8: Finally, I returned the distance array, assigning -1 to nodes that were not reachable from the source.
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date29 Sep 2024
Coding problem2
1. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
Step 1: I started with a brute-force recursive approach to check all possible subsequences, but it was inefficient.
Step 2: The interviewer suggested optimizing, so I introduced DP by storing results of subproblems in an array.
Step 3: I explained the optimized DP solution with O(n²) time complexity, which the interviewer was satisfied with.
2. Kth largest element in the unsorted array
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array consisting of 'N' distinct positive integers and a number 'K'. Your task is to find the kth largest element in the array.
Example:
Consider the array {2,1,5,6,3,8} and 'K' = 3, the sorted array will be {8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1}, and the 3rd largest element will be 5.
Note:
1) Kth largest element in an array is the kth element of the array when sorted in non-increasing order.
2) All the elements of the array are pairwise distinct.
Problem approach
Step 1: Initially, I thought of sorting the array and picking the k-th largest element.
Step 2: The interviewer asked for a better solution, so I used a min-heap of size k.
Step 3: By maintaining the heap efficiently, I achieved an optimized solution with better time complexity, which was accepted.
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration75 minutes
Interview date29 Sep 2024
Coding problem2
This round involved a mix of Operating Systems, DBMS, OOPs, and Computer Networks.
1. Operating System
Problem approach
Tip 1: Read Operating System Concepts by Galvin thoroughly to build strong conceptual clarity.
Tip 2: Focus on understanding real-world use cases of OS concepts like synchronization and memory management.
2. DBMS
- What is normalization? Explain different normal forms. (Learn)
- What is denormalization? When is it used? (Learn)
- What is a primary key, foreign key, and unique key? (Learn)
- Explain ACID properties in databases. (Learn)
- What is indexing? How does it improve query performance? (Learn)
- What is a deadlock? How can it be prevented? (Learn)
Problem approach
Follow DBMS notes from any channel or a book.
04
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration75 minutes
Interview date29 Sep 2024
Coding problem1
The round was conducted during normal college hours and did not extend into late night. The environment was structured and discussion-oriented, allowing open communication and logical thinking. The discussion involved understanding requirements first, followed by designing the system step by step with clarifying questions. The interviewer was patient and interactive, guiding the discussion and encouraging reasoning behind design choices.
1. System Design
Design a scalable URL Shortening Service (similar to bit.ly).
The problem involved discussing functional and non-functional requirements, high-level architecture, database schema, scalability considerations, and handling high traffic efficiently.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1011 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15556 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15417 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10180 views
2 comments
0 upvotes






