InMobi interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 2
InMobi
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 2 years of experience
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date22 Jul 2021
Coding problem2
This round started with a formal introduction where the interviewer and I discussed about my projects and prior work experience. After that, the interviewer gave me 2 coding problems wherein I was asked to first explain my approach along with proper complexity analysis and then write the pseudo code.
1. Search an element in a sorted and rotated array
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Aahad and Harshit always have fun by solving problems. Harshit took a sorted array consisting of distinct integers and rotated it clockwise by an unknown amount. For example, he took a sorted array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and if he rotates it by 2, then the array becomes: [4, 5, 1, 2, 3].
After rotating a sorted array, Aahad needs to answer Q queries asked by Harshit, each of them is described by one integer Q[i]. which Harshit wanted him to search in the array. For each query, if he found it, he had to shout the index of the number, otherwise, he had to shout -1.
For each query, you have to complete the given method where 'key' denotes Q[i]. If the key exists in the array, return the index of the 'key', otherwise, return -1.
Note:
Can you solve each query in O(logN) ?
Problem approach
This was a preety standard Binary Search Question and I had solved this question before on platforms like LeetCode and CodeStudio . I was asked this question to test my implementation skills and how well do I handle Edge Cases.
Approach :
1) The idea is to find the pivot point, divide the array in two sub-arrays and perform binary search.
2) The main idea for finding pivot is – for a sorted (in increasing order) and pivoted array, pivot element is the only element for which next element to it is smaller than it.
3) Using the above statement and binary search pivot can be found.
4) After the pivot is found out divide the array in two sub-arrays.
5) Now the individual sub–arrays are sorted so the element can be searched using Binary Search.
TC : O(Log(N))
SC : O(1)
2. Longest Palindromic Substring
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string ('STR') of length 'N'. Find the longest palindromic substring. If there is more than one palindromic substring with the maximum length, return the one with the smaller start index.
Note:
A substring is a contiguous segment of a string.
For example : The longest palindromic substring of "ababc" is "aba", since "aba" is a palindrome and it is the longest substring of length 3 which is a palindrome, there is another palindromic substring of length 3 is "bab" since "aba" starting index is less than "bab", so "aba" is the answer.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Create a 2-D dp boolean vector(with all false initially) where dp[i][j] states whether s[i...j] is a palindrome or not and initialise a variable ans=1 which will store the final answer.
2) Base Case : For every i from 0 to n-1 fill dp[i][i]=1 ( as a single character is always a palindrome ).
3) Now, run 2 loops first one from i=n-1 to i=0 (i.e., tarverse from the back of the string) and the second one from j=i+1 to n.
4) For every s[i]==s[j] , check if(j-i==1 i.e., if s[i] and s[ j] are two consecutive same letters) or if(dp[i+1][j-1]==1 or not i.e., if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is palindrome or not.
5) Because if the string s[i+1,....j-1] is a palindrome and s[i]==s[j] then s[i] and s[j] can be appended at the starting and the ending position of s[i+1,...j-1] and s[i...j] will then be a palindrome , so mark dp[i][j]=1 and update the answer as ans=max(ans , j-i+1).
6) Finally return the ans.
TC : O(N^2) where N=length of the string s
SC : O(N^2)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date22 Jul 2021
Coding problem2
Again a DSA specific round , where I was given two problems to solve ranging from Medium to Hard. Major topics discussed were Binary Trees and Dynamic Programming.
1. Pair Chain - Maximum Length
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given ‘N’ pairs of integers in which the first number is always smaller than the second number i.e in pair (a,b) -> a < b always. Now we define a pair chain as the continuous arrangement of pairs in which a pair (c,d) can follow another pair (a,b) only when b < c.
Find the length of the longest pair chain that can be formed using the given pairs.
Example:
Given Pairs = [3,4], [1,2], [2,3].
The length of the maximum chain will be 2. The longest chain is [1,2] -> [3,4].
Note:
1. You can select a pair only once.
2. You needn’t use up all the given pairs.
3. You can select pairs in any order.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Using DP ) :
Observe that , If a chain of length k ends at some pairs[i], and pairs[i][1] < pairs[j][0], we can extend this chain to a chain of length k+1
Steps :
1) Sort the pairs by the first coordinate, and let dp[i] be the length of the longest chain ending at pairs[i].
2) When i < j and pairs[i][1] < pairs[j][0], we can extend the chain, and so we have the candidate answer
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[i] + 1).
TC : O(N^2)
SC : O(N)
Approach 2 (Greedy based) :
We can greedily add to our chain.
Steps:
1) Choosing the next addition to be the one with the lowest second coordinate is at least better than a choice with a larger second coordinate.
2) Consider the pairs in increasing order of their second coordinate.
3) We'll try to add them to our chain. If we can, by the above argument we know that it is correct to do so.
TC : O(N*log(N))
SC : O(N)
2. Top view of Binary Tree
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree of 'n' nodes.
The Top view of the binary tree is the set of nodes visible when we see the tree from the top.
Find the top view of the given binary tree, from left to right.
Example :
Input: Let the binary tree be:
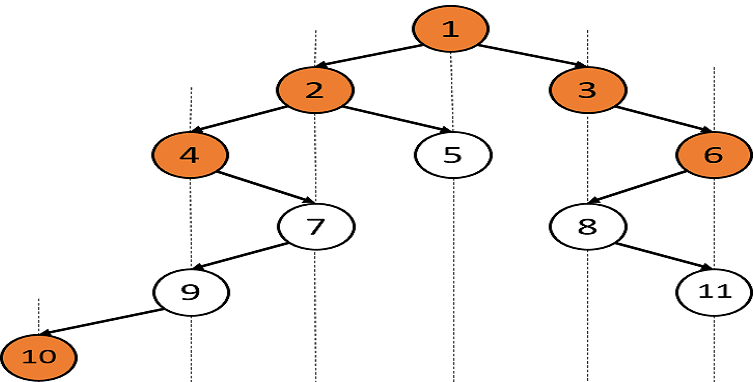
Output: [10, 4, 2, 1, 3, 6]
Explanation: Consider the vertical lines in the figure. The top view contains the topmost node from each vertical line.
Problem approach
Approach :
The approach is to use the preorder traversal of the tree to traverse the tree and check that we have visited the current vertical level and if visited then we can check for the smaller horizontal level node and store it. Else we can just update the vertical level as visited and store the node and horizontal level of the current node.
1) We have to create the map to check whether the horizontal level is visited or not as it will state the horizontal distance of the node from the root node. Where key will represent the horizontal distance and the value is the pair containing the value and level of each node.
2) We will traverse the tree using the preorder traversal.
3) Every time we check if the level of the current horizontal distance is less than the max level seen till now then we will update the value and the level for this horizontal distance.
4) We will pass level-1 for the left child and level+1 for the right child to get the vertical level.
5) Print the values present in the map.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date22 Jul 2021
Coding problem3
This round majorly focused on past projects and experiences from my Resume and some standard System Design + LLD questions + some basic OOPS questions which an SDE-2 is expected to know.
1. System Design Question
Design a URL Shortener
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Firstly, remember that the system design round is extremely open-ended and there’s no such thing as a standard answer. Even for the same question, you’ll have a totally different discussion with different interviewers.
Tip 2 : Before you jump into the solution always clarify all the assumptions you’re making at the beginning of the interview. Ask questions to identify the scope of the system. This will clear the initial doubt, and you will get to know what are specific detail the interviewer wants to consider in this service.
Some standard requirements for this problem would be :
1) Given a long URL, the service should generate a shorter and unique alias of it.
2) When the user hits a short link, the service should redirect to the original link.
3) Links will expire after a standard default time span.
4) The system should be highly available. This is really important to consider because if the service goes down, all the URL redirection will start failing.
5) URL redirection should happen in real-time with minimal latency.
6) Shortened links should not be predictable.
Tip 3 : Now knowing about the requirements, note down all the important factors to take into consideration while solving this problem. Most common factors include :
1) Traffic
2) URL Length
3) Data Capacity Modeling
4) URL Shortening Logic (Encoding basically) - Standard Hashing Techniques like Base62, MD5 should be known
5) Choice of Database - SQL vs NoSQL
Finally, for acing System Design Rounds I would suggest watching Gaurav Sen's System Design Videos on YouTube and for hands-on practice there is a Guided Path solely for System Design on CodeStudio which is very useful while preparing for these types of rounds.
2. OOPS Question
Explain SOLID principles in Object Oriented Design .
Problem approach
The SOLID principle is an acronym of the five principles which is given below :
1) Single Responsibility Principle (SRP)
2) Open/Closed Principle
3) Liskov’s Substitution Principle (LSP)
4) Interface Segregation Principle (ISP)
5) Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
Uses of SOLID design principles :
1) The SOLID principle helps in reducing tight coupling.
2) Tight coupling means a group of classes are highly dependent on one another which we should avoid in our code.
3) Opposite of tight coupling is loose coupling and our code is considered as a good code when it has loosely-coupled classes.
4) Loosely coupled classes minimize changes in your code, helps in making code more reusable, maintainable, flexible and stable.
Explaining the 5 SOLID principles one by one :
1) Single Responsibility Principle : This principle states that “a class should have only one reason to change” which means every class should have a single responsibility or single job or single purpose. Use layers in your application and break God classes into smaller classes or modules.
2) Open/Closed Principle : This principle states that “software entities (classes, modules, functions, etc.) should be open for extension, but closed for modification” which means you should be able to extend a class behavior, without modifying it. Using this principle separates the existing code from the modified code so it provides better stability, maintainability and minimizes changes as in your code.
3) Liskov’s Substitution Principle : According to this principle “Derived or child classes must be substitutable for their base or parent classes“. This principle ensures that any class that is the child of a parent class should be usable in place of its parent without any unexpected behavior.
4) Interface Segregation Principle : This principle is the first principle that applies to Interfaces instead of classes in SOLID and it is similar to the single responsibility principle. It states that “do not force any client to implement an interface which is irrelevant to them“. Here your main goal is to focus on avoiding fat interface and give preference to many small client-specific interfaces.
5) Dependency Inversion Principle : Two key points are here to keep in mind about this principle
a) High-level modules/classes should not depend on low-level modules/classes. Both should depend upon abstractions.
b) Abstractions should not depend upon details. Details should depend upon abstractions.
3. OOPS Question
What is Garbage collector in JAVA?
Problem approach
1) Garbage Collection in Java is a process by which the programs perform memory management automatically.
2) The Garbage Collector(GC) finds the unused objects and deletes them to reclaim the memory. I
3) In Java, dynamic memory allocation of objects is achieved using the new operator that uses some memory and the memory remains allocated until there are references for the use of the object.
4) When there are no references to an object, it is assumed to be no longer needed, and the memory, occupied by the object can be reclaimed.
5) There is no explicit need to destroy an object as Java handles the de-allocation automatically. The technique that accomplishes this is known as Garbage Collection. Programs that do not de-allocate memory can eventually crash when there is no memory left in the system to allocate. These programs are said to have memory
leaks.
Garbage collection in Java happens automatically during the lifetime of the program, eliminating the need to de-allocate memory and thereby avoiding memory leaks.
In C language, it is the programmer’s responsibility to de-allocate memory allocated dynamically using the free() function. This is where Java memory management leads.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
937 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3407 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2660 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 2
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Walmart
29739 views
8 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
6727 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
6 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
5224 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





