InMobi interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
InMobi
4 rounds | 11 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, DBMS, OS, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date23 Jul 2020
Coding problem3
This round had 3 coding questions of Medium to Hard level of difficulty to be solved under 90 minutes.
1. Count all sub-arrays having sum divisible by k
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array ‘ARR’ and an integer ‘K’, your task is to find all the count of all sub-arrays whose sum is divisible by the given integer ‘K’.
Note:
If there exists no subarray in the given sequence whose sum is divisible by ‘K’ then simply return ‘0’.
Example:
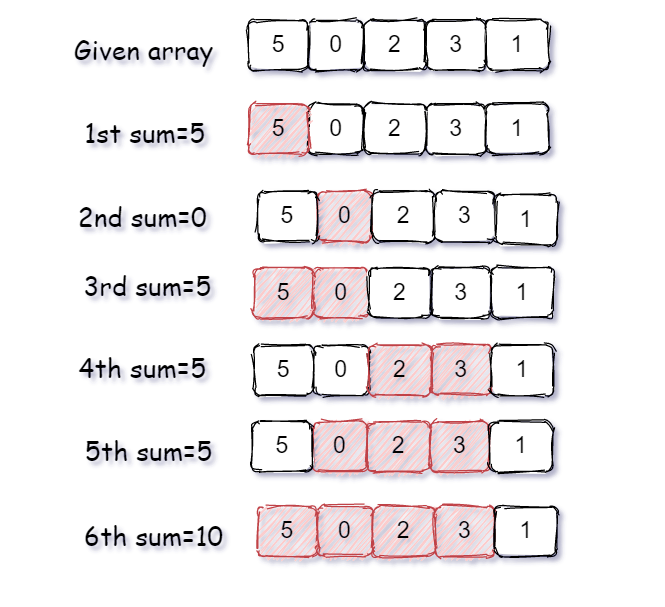
Suppose the given array is ‘ARR’ = { 5, 0, 2, 3, 1} and ‘K = 5’.
As we can see in below image, there are a total of 6 subarrays that have the total sum divisible by ‘K’
So we return the integer 6.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Naive Solution ) :
One by one calculate sum of all sub-arrays possible and check divisible by K.
TC : O(N^2)
SC : O(1)
Approach 2 (Efficient Solution) :
Observe : Let sum(i,j)=subarray sum from arr[i] to arr[j] (both inclusive) (arr[i]+arr[i+1]...+arr[j])
Now for sum(i,j) to be divisible by k , th following condition must hold :
sum(0,j)%k=sum(0,i-1)%k
Keeping the above points in mind , let's design an efficient algo for this problem :
Algorithm :
1) Make an auxiliary array of size k as Mod[k] . This array holds the count of each remainder we are getting after
dividing cumulative sum till any index in arr[].
2) Now start calculating cumulative sum and simultaneously take it’s mod with K, whichever remainder we get
increment count by 1 for remainder as index in Mod[] auxiliary array.
3) Sub-array by each pair of positions with same value of ( cumSum % k) constitute a continuous range whose sum is
divisible by K.
4) Now traverse Mod[] auxiliary array, for any Mod[i] > 1 we can choose any two pair of indices for sub-array by
(Mod[i]*(Mod[i] – 1))/2 number of ways .
5) Do the same for all remainders < k and sum up the result that will be the number all possible sub-arrays divisible
by K.
TC : O(N), where N = size of the array
SC : O(k)
2. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) First make a recursive function, say ‘solve’ taking the number of opening brackets ‘opening’, number of closing
brackets ‘closing’ output string ‘output’, and an array of strings ‘ans’ as arguments.
2) Make the base condition as if ‘opening’ = 0 and ‘closing’ = 0 then push the output string in the ‘ans’ and return.
3) If ‘opening’ is not equal to zero then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘opening’ by 1 and
inserting ‘(‘ into the ‘output’.
4) If ‘closing’ > ‘opening’ then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘closing’ by 1 and inserting ‘)’ into
the ‘output’.
TC : O(2 ^ N), where N is the given integer.
SC : O(N)
3. Minimum Connection Changes
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



In an internet cafe, there are 'N' computers numbered from 1 to ‘N’. These computers are connected by 'M' wires. Each wire connects two different computers. Information can be transmitted between two computers if there exists a path between the two computers by travelling through some ( possibly Zero ) intermediate computers. The cafe owner wants to remove some of the existing wires and then use those wires to connect some other pair of computers in such a manner that after the rearrangement, it is possible to transmit information between all the pairs of computers.
You are given the description of each of the 'M' wires, i.e., the two computers that the wire connects. Your task is to find the minimum number of wires that the cafe owner needs to remove and rearrange to satisfy the above conditions.
If there is no possible way to remove and rearrange wires to satisfy the above conditions, then return -1.
Problem approach
Approach (Using DSU) :
1) If N - 1 is greater than M, then we will return -1 as it will be impossible to make all the computers connected.
2) Let’s define a “parent” array of size N+1 to store the parent node of each node from 1 to N.
3) Create a DSU data structure and initialize it using makeSet( ), in which we will initialize the parent node of each node to itself.
4) Let’s define two functions findParent and unionSets, to find the parent node of a particular node and to merge two components of the graph, respectively.
5) Initialize the variable numberOfConnectedComponents as N to store the number of connected components in the graph as initially no two nodes are connected. Now whenever we will merge two sets, we will decrease our answer by 1.
6) Iterate through each the list of wires
6.1) Let computer1 and computer2 denote the two computers connected by this wire.
6.2) If findParent(computer1) is not equal to findParent(computer2), then decrease numberOfConnectedComponents by 1 and call unionSets(computer1,computer2). We are decreasing our answer by 1 as the two components to which computer1 and computer2 belong are already the same. So we do not need to connect them.
7) Return the final answer, i.e, numberOfConnectedComponents - 1.
TC : O(N+M), where N = no. of computers and M = no. of wires
SC : O(N)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration50 Minutes
Interview date23 Jul 2020
Coding problem2
This round had 2 Algorithmic questions wherein I was supposed to code both the problems after discussing their approaches and respective time and space complexities.
1. Number of rectangles in a grid
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary grid with M rows and N columns. You have to print the total number of rectangles which can be formed using the rows and columns of this grid. In simple words, print the number of unique rectangles in the grid.
For example:
Consider the grid shown below. The dark black boundary encloses a grid of dimension 3x4.

The green colour represents rectangles of dimension 1x1.
The brown colour represents the rectangles of dimension 1x2.
The blue colour represents the rectangles of dimension 2x2.
The red colour represents the rectangles of dimension 3x3.
The yellow colour represents the rectangles of dimension 3x1.
There can be many different other possibilities as well. You need to print the total number of all such rectangles.
Note:
Two rectangles are said to be unique if atleast one of their 4 sides is non-overlapping.
Problem approach
Approach :
If we look carefully at the given problem, we observe that to create a rectangle in a grid, we just need to select two horizontal and two vertical lines among all the lines present in the grid.
In a grid with N columns, we know that there are (N+1) vertical lines.
Also, in a grid with M rows, there are (N+1) horizontal lines (including the outer boundaries as well).
Our formula becomes → (M+1)C2 * (N+1)C2, where nCr is defined as the total number of unique ways to choose r objects from a set containing n different objects.
On simplification, this formula evaluates to → (M*(M+1)*N*(N+1))/4.
We can directly use this formula to get the total number of rectangles in a given grid with M rows and N columns.
TC : O(1)
SC : O(1)
2. Merge Intervals
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given N number of intervals, where each interval contains two integers denoting the start time and the end time for the interval.
The task is to merge all the overlapping intervals and return the list of merged intervals sorted by increasing order of their start time.
Two intervals [A,B] and [C,D] are said to be overlapping with each other if there is at least one integer that is covered by both of them.
For example:
For the given 5 intervals - [1, 4], [3, 5], [6, 8], [10, 12], [8, 9].
Since intervals [1, 4] and [3, 5] overlap with each other, we will merge them into a single interval as [1, 5].
Similarly, [6, 8] and [8, 9] overlap, merge them into [6,9].
Interval [10, 12] does not overlap with any interval.
Final List after merging overlapping intervals: [1, 5], [6, 9], [10, 12].
Problem approach
Approach :
1) We will first sort the intervals by non-decreasing order of their start time.
2) Then we will add the first interval to our resultant list.
3) Now, for each of the next intervals, we will check whether the current interval is overlapping with the last interval in
our resultant list.
4) If it is overlapping then we will update the finish time of the last interval in the list by the maximum of the finish time
of both overlapping intervals.
5) Otherwise, we will add the current interval to the list.
TC : O(N * log(N)), where N = number of intervals
SC : O(1)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date23 Jul 2020
Coding problem5
In this round, the interviewer asked me 2 coding questions in which I was expected to first explain my approach with proper complexity analysis and then write the corresponding pseudo codes. After these, I was asked some questions related to DBMS and MySQL.
1. Trapping Rain Water
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a long type array/list 'arr’ of size 'n’.
It represents an elevation map wherein 'arr[i]’ denotes the elevation of the 'ith' bar.
Print the total amount of rainwater that can be trapped in these elevations.
Note :
The width of each bar is the same and is equal to 1.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 6, ‘arr’ = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4].
Output: 10
Explanation: Refer to the image for better comprehension:

Note :
You don't need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Brute Force) :
1) Iterate over every elevation or element and find the maximum elevation on to the left and right of it. Say, the
maximum elevation on to the left of the current elevation or element that we are looking at is ‘maxLeftHeight’ and the
maximum elevation on to the right of it is ‘maxRightHeight’.
2) Take the minimum of ‘maxLeftHeight’ and ‘maxRightHeight’ and subtract it from the current elevation or element.
This will be the units of water that can be stored at this elevation.
3) Compute units of water that every elevation can store and sum them up to return the total units of water that can
be stored.
TC : O(N^2), where ‘N’ is the total number of elevations in the map.
SC : O(1)
Approach 2 (Efficient Approach) :
1) Create two lists or arrays, say, ‘leftMax’ and ‘rightMax’.
2) At every index in the ‘leftMax’ array store the information of the ‘leftMaxHeight’ for every elevation in the map.
3) Similarly, at every index in the ‘rightMax’ array store the information of the ‘rightMaxHeight' for every elevation in
the map.
4) Iterate over the elevation map and find the units of water that can be stored at this location by getting the left max
height and right max height from the initial arrays that we created.
TC : O(N), where ‘N’ is the total number of elevations in the map.
SC : O(N)
2. 0 1 Knapsack
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



A thief is robbing a store and can carry a maximal weight of W into his knapsack. There are N items and the ith item weighs wi and is of value vi. Considering the constraints of the maximum weight that a knapsack can carry, you have to find and return the maximum value that a thief can generate by stealing items.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) The idea is to create a 2-D array ‘result’ of size size (N + 1) * (W + 1).
2) Initially, all the elements of the ‘result’ matrix will be 0.
3) Now, the value result[i][j] denotes the maximum profit the thief can earn considering upto first 'i' items whose combined weight is less than or equal to 'j'.
4) The detailed algorithm to fill the ‘result’ matrix is as follows:
L1 : Run a loop from i = 1 to N to consider all the items.
L2 : Run a loop from j = 0 to W to consider all weights from 0 to maximum capacity W.
If the weight of the current item is more than j, we can not include it.
Thus, result[i][j] = result[i - 1][j].
Else, find the maximum profit obtained by either including the current item or excluding the current item.
i.e. result[i][j] = max(result[i - 1][j], values[i] + result[i - 1][j - weights[i]]).
5) Return result[N][W], the final profit that the thief can make.
TC : O(N*W), where N is the number of items and W is the maximum capacity of the knapsack.
SC : O(N*W)
3. DBMS Question
Explain the concept of ACID properties in DBMS?
Problem approach
ACID properties is the combination of Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability properties. These properties are very helpful in allowing a safe and secure way of sharing the data among multiple users.
1) Atomicity: This is based on the concept of “either all or nothing” which basically means that if any update occurs inside the database then that update should either be available to all the others beyond user and application program or it should not be available to anyone beyond the user and application program.
2) Consistency: This ensures that the consistency is maintained in the database before or after any transaction that takes place inside the database.
3) Isolation: As the name itself suggests, this property states that each transaction that occurs is in isolation with others i.e. a transaction which has started but not yet completed should be in isolation with others so that the other transaction does not get impacted with this transaction.
4) Durability: This property states that the data should always be in a durable state i.e. any data which is in the committed state should be available in the same state even if any failure or restart occurs in the system.
4. DBMS Question
Explain different levels of data abstraction in a DBMS.
Problem approach
The process of hiding irrelevant details from users is known as data abstraction. Data abstraction can be divided into 3 levels :
1) Physical Level : It is the lowest level and is managed by DBMS. This level consists of data storage descriptions and the details of this level are typically hidden from system admins, developers, and users.
2) Conceptual or Logical level : It is the level on which developers and system admins work and it determines what data is stored in the database and what is the relationship between the data points.
3) External or View level : It is the level that describes only part of the database and hides the details of the table schema and its physical storage from the users. The result of a query is an example of View level data abstraction. A view is a virtual table created by selecting fields from one or more tables present in the database.
5. SQL Question
What is Sharding in SQL?
Problem approach
The process of breaking up large tables into smaller chunks (called shards) that are spread across multiple servers is called Sharding.
The advantage of Sharding is that since the sharded database is generally much smaller than the original; queries, maintenance, and all other tasks are much faster.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date23 Jul 2020
Coding problem1
This was my last round and I hoped it to go good just like the other rounds. The interviewer was very straight to point and professional. The interview lasted for 30 minutes.
1. Basic HR Question
Why should we hire you ?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : The cross questioning can go intense some time, think before you speak.
Tip 2 : Be open minded and answer whatever you are thinking, in these rounds I feel it is important to have opinion.
Tip 3 : Context of questions can be switched, pay attention to the details. It is okay to ask questions in these round,
like what are the projects currently the company is investing, which team you are mentoring. How all is the work
environment etc.
Tip 4 : Since everybody in the interview panel is from tech background, here too you can expect some technical
questions. No coding in most of the cases but some discussions over the design can surely happen.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 13 problems
Interviewed by InMobi
2545 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by InMobi
1963 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes







