Intuit interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Engineer
Intuit
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 Months
Topics: OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Data Structures,DBMS
Tip
Tip 1 : Prepare System Design
Tip 2 : Practice DSA Questions properly
Tip 3 : Practice OOPS and DBMS Concepts
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: B. Tech / Dual CSE, IT 2022 batch with Min. 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Your Resume should consist mainly of skills, projects, and achievements. Projects would play a crucial part in your interview and you should have at least one most relevant and good project that shows how strong your concepts are in development.
Tip 2 : The most important tip is that never lie on your resume If you have worked upon some technology for the project part only and don't know the proper depth you could write basics only in your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration90 Minutes
Interview date9 Mar 2022
Coding problem3
This round was conducted on HackerEarth. It had 3 DSA questions that needed to be completed in 90 minutes.
1. Time To Burn Tree
Hard
50m average time
50% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You have a binary tree of 'N' unique nodes and a Start node from where the tree will start to burn. Given that the Start node will always exist in the tree, your task is to print the time (in minutes) that it will take to burn the whole tree.
It is given that it takes 1 minute for the fire to travel from the burning node to its adjacent node and burn down the adjacent node.
For Example :
For the given binary tree: [1, 2, 3, -1, -1, 4, 5, -1, -1, -1, -1]
Start Node: 3
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
Output: 2
Explanation :
In the zeroth minute, Node 3 will start to burn.
After one minute, Nodes (1, 4, 5) that are adjacent to 3 will burn completely.
After two minutes, the only remaining Node 2 will be burnt and there will be no nodes remaining in the binary tree.
So, the whole tree will burn in 2 minutes.
Problem approach
Create a hashmap and find the node to parent mapping.
Make pointers that will point to the node having a value target.
Write a function that will call recursively to itself and returns the distance to all leaf nodes.
Return the maximum distance among them.
2. Distribute N candies among K people
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Sanyam has ‘N’ candies, he wants to distribute that into ‘K’ of his friends. He made his ‘K’ friends stand in line, in increasing order of his likeness. Not being so smart he gives 1 candy to the first friend, 2 to the second person, and so on till the kth person. In the next turn, the first person gets ‘K + 1’ candies, the second person gets ‘K + 2’ candies, and so on.
While distributing the candies, if at a turn, the number of candies to be given to a friend is less than the required candies, then that friend gets all the remaining candies and Sanyam stops the distribution.
Your task is to find the total number of candies every person has at the end.
Problem approach
find the largest number(say MAXI) whose sum upto natural numbers is less than N using Binary search. Since the last number will always be a multiple of K, we get the last number of complete turns. Subtract the summation till then from N. Distribute the remaining candies by traversing in the array.
3. Form the Biggest Number
Moderate
25m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array “A” of positive integers. Your task is to make the largest number possible formed by concatenating each of the array elements exactly once.
Example:
Let's say the given array is [ 9, 98, 7].
All the possible numbers formed by concatenating each of the array elements are 7989,7998,9879,9897,9987,9798. Among the six numbers, 9987 is the greatest number. Hence the answer is 9987.
Problem approach
Used a greedy algorithm to solve this is O(N) time complexity.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Mar 2022
Coding problem1
It was mainly focused on a DSA problem and later we had project discussion and some on-spot optimizations and design problem related to my project.
1. Rearrange Linked List
Moderate
22m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a singly Linked List in the form of 'L1' -> 'L2' -> 'L3' -> ... 'Ln'. Your task is to rearrange the nodes of this list to make it in the form of 'L1' -> 'Ln' -> 'L2' -> 'Ln-1' and so on. You are not allowed to alter the data of the nodes of the given linked list.
For example:
If the given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL.
Then rearrange it into 1 -> 5 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> NULL.
Problem approach
split linkedlist into two halves
find mid and split
and revese second half
merge these two halves
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date17 Mar 2022
Coding problem3
It was more focused on core concepts of CS, some questions on CN, OOPs were asked, we discussed my past internship experience, some of my projects, interestingly I was asked have you used any OOPs in any of your project, well I told them most of my projects are on Web Dev and I said I mostly prefer functional javascript and why is it so but then I explained some concepts like prototypical inheritance, event delegation in javascript, later I was given a DSA problem and at last I was asked to design Snake and Ladder game.
1. Distance between two nodes of a Tree
Moderate
25m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree and the value of two nodes, find the distance between the given two nodes of the Binary Tree.
Distance between two nodes is defined as the minimum number of edges in the path from one node to another.
Problem approach
The distance between two nodes can be obtained in terms of lowest common ancestor. Following is the formula.
Dist(n1, n2) = Dist(root, n1) + Dist(root, n2) - 2*Dist(root, lca)
'n1' and 'n2' are the two given keys
'root' is root of given Binary Tree.
'lca' is lowest common ancestor of n1 and n2
Dist(n1, n2) is the distance between n1 and n2.
2. Snake and Ladder
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Snake and Ladder Board with 'N' rows and 'N' columns with the numbers written from 1 to (N*N) starting from the bottom left of the board, and alternating direction each row.
For example
For a (6 x 6) board, the numbers are written as follows:
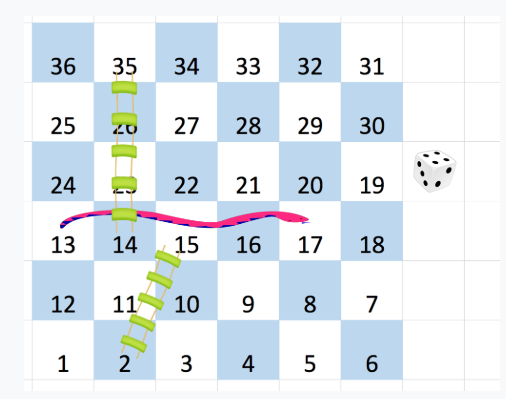
You start from square 1 of the board (which is always in the last row and first column). On each square say 'X', you can throw a dice which can have six outcomes and you have total control over the outcome of dice throw and you want to find out the minimum number of throws required to reach the last cell.
Some of the squares contain Snakes and Ladders, and these are possibilities of a throw at square 'X':
You choose a destination square 'S' with number 'X+1', 'X+2', 'X+3', 'X+4', 'X+5', or 'X+6', provided this number is <= N*N.
If 'S' has a snake or ladder, you move to the destination of that snake or ladder. Otherwise, you move to S.
A board square on row 'i' and column 'j' has a "Snake or Ladder" if board[i][j] != -1. The destination of that snake or ladder is board[i][j].
Note :
You can only take a snake or ladder at most once per move: if the destination to a snake or ladder is the start of another snake or ladder, you do not continue moving - you have to ignore the snake or ladder present on that square.
For example, if the board is:
-1 1 -1
-1 -1 9
-1 4 -1
Let's say on the first move your destination square is 2 [at row 2, column 1], then you finish your first move at 4 [at row 1, column 2] because you do not continue moving to 9 [at row 0, column 0] by taking the ladder from 4.
A square can also have a Snake or Ladder which will end at the same cell.
For example, if the board is:
-1 3 -1
-1 5 -1
-1 -1 9
Here we can see Snake/Ladder on square 5 [at row 1, column 1] will end on the same square 5.
3. OOPS Questions
What is method overloading?
What is the meaning of method overriding?
.How can data abstraction be accomplished?
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Be clear with the explanation
Tip 2 : if any question requires explanation use the resource that is provided for explaining
Tip 3 : study the most important questions.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Intuit
4308 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Intuit
3039 views
2 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Intuit
996 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Intuit
1205 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Optum
7922 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
5 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
10070 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
4394 views
1 comments
0 upvotes



