Ionic Software Services interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Development
Ionic Software Services
3 rounds | 15 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started coding in Java by taking a course from Coding Ninjas in my second year. Before that, I explored programming languages like Python, C++, and Java, which led me to choose Java. After completing the course, I started practicing on Coding Ninjas. Later, in my third year, I developed a mini-project. I have also undergone in-house training in Machine Learning.
Application story
I applied through Naukri.com, and my resume was shortlisted. After that, I had to go through two technical rounds. I received an email from Ionic Digital Labs a day before the first round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected in the last round because I couldn't provide an optimized solution to the coding question they asked. Additionally, they were looking for a candidate with training and project experience in web development. I was unable to clear the third round.
Preparation
Duration: 2 month
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1: Practice at least 250 questions.
Tip 2: Example: Do at least two projects.
Tip 3: Practice on CodeStudio.
Tip 4: Practice past years' questions.
Application process
Where: Naukri
Eligibility: 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Keep a maximum of three projects in the projects section but ensure that at least one of them is hosted/live and can be shown to the interviewer.
Tip 2: Do not include false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date6 Mar 2022
Coding problem5
In this round, the interviewer asked me four coding questions and a question based on OOPS.
1. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
The idea is to push all opening brackets onto the stack. Whenever you encounter a closing bracket, check if the top of the stack contains the corresponding opening bracket. If it does, pop the stack and continue the iteration. In the end, if the stack is empty, it means all brackets are balanced or well-formed. Otherwise, they are not balanced.
2. Spiral Matrix
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



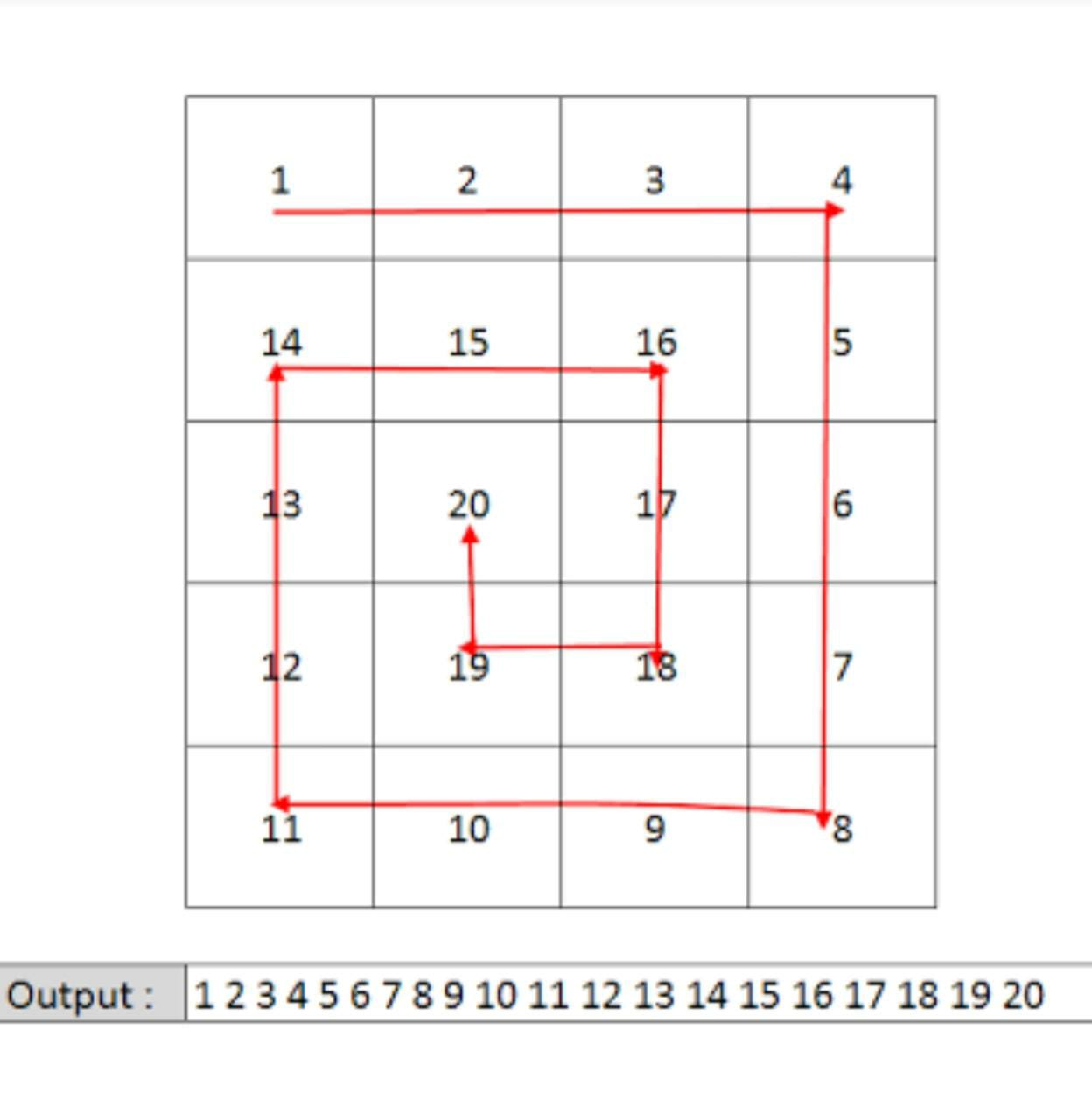
You are given a 2-D array 'MATRIX' of dimensions N x M, of integers. You need to return the spiral path of the matrix.
Example Of Spiral Path:
Problem approach
Draw the path that the spiral makes. We know that the path should turn clockwise whenever it would go out of bounds or into a previously visited cell.
Follow the given steps to solve the problem:
- Let the array have R rows and C columns.
- seen[r][c] denotes that the cell at the r-th row and c-th column has been visited. Our current position is (r, c), facing direction di, and we want to visit R × C total cells.
- As we move through the matrix, our candidate’s next position is (cr, cc).
- If the candidate position is within the bounds of the matrix and has not been visited, it becomes our next position. Otherwise, we perform a clockwise turn and choose the next position accordingly.
3. Course Schedule
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are a student of Netaji Subhas Institute of Technology. You have to take ‘N’ number of courses labelled from 1 to N to complete your B.Tech Degree.
Some courses may have prerequisites, for example, to take course 1 you have to first take course 2, which is expressed as a pair: [1, 2]. Now, your task is to find is it possible for you to finish all courses.
Note: There are no duplicate pairs in the prerequisites array.
For example-
If N = 2 and prerequisite = [[1, 2]]. Then, there are a total of 2 courses you need to take. To take course 1 you need to finish course 2. So, it is possible to complete all courses.
Problem approach
- Assuming that time T starts at 0, the task is to find the maximum number of lectures that are ongoing at any given instance of time. This will determine the minimum number of halls required to schedule all the lectures.
- To find the number of ongoing lectures at any instance of time, maintain a prefix_sum[] array that stores the count of lectures in progress at any given time t. For each lecture with a duration between [s,t], increment prefix_sum[s]++ and decrement prefix_sum[t + 1]--.
- Afterward, computing the cumulative sum of this prefix array will provide the count of lectures ongoing at any given time. The maximum value in this array represents the minimum number of halls required.
4. Bottom View Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a 'Binary Tree'.
Return the bottom view of the binary tree.
Note :
1. A node will be in the bottom-view if it is the bottom-most node at its horizontal distance from the root.
2. The horizontal distance of the root from itself is 0. The horizontal distance of the right child of the root node is 1 and the horizontal distance of the left child of the root node is -1.
3. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from root + 1, if node 'n' is the right child of its parent.
4. The horizontal distance of node 'n' from root = horizontal distance of its parent from the root - 1, if node 'n' is the left child of its parent.
5. If more than one node is at the same horizontal distance and is the bottom-most node for that horizontal distance, including the one which is more towards the right.
Example:
Input: Consider the given Binary Tree:
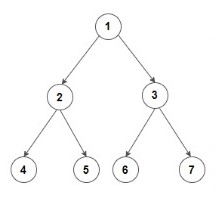
Output: 4 2 6 3 7
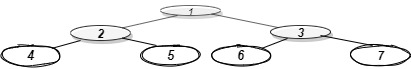
Explanation:
Below is the bottom view of the binary tree.
1 is the root node, so its horizontal distance = 0.
Since 2 lies to the left of 0, its horizontal distance = 0-1= -1
3 lies to the right of 0, its horizontal distance = 0+1 = 1
Similarly, horizontal distance of 4 = Horizontal distance of 2 - 1= -1-1=-2
Horizontal distance of 5 = Horizontal distance of 2 + 1= -1+1 = 0
Horizontal distance of 6 = 1-1 =0
Horizontal distance of 7 = 1+1 = 2
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -2 is 4.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of -1 is 2.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 0 is 5 and 6. However, 6 is more towards the right, so 6 is included.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 1 is 3.
The bottom-most node at a horizontal distance of 2 is 7.
Hence, the bottom view would be 4 2 6 3 7
Problem approach
- Store tree nodes in a queue for level-order traversal. Start with the horizontal distance (hd) of the root node as 0. Use a map to store key-value pairs sorted by key, and keep adding the left child to the queue with a horizontal distance of hd - 1 and the right child with hd + 1.
- Each time a new horizontal distance or an existing one is encountered, update the map with the node's data for that horizontal distance as the key. The first occurrence of a horizontal distance adds it to the map, while subsequent occurrences replace the existing value. This ensures that the bottom-most element for that horizontal distance is stored in the map. When viewed from below, only this element will be visible.
- Finally, traverse the keys of the map and print their respective values.
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 Mar 2023
Coding problem6
This was also a technical round. The interviewer asked me one coding problem and some questions based on my resume.
1. Convert binary tree to mirror tree
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree, convert this binary tree into its mirror tree.
A binary tree is a tree in which each parent node has at most two children.
Mirror of a Tree: Mirror of a Binary Tree T is another Binary Tree M(T) with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged.
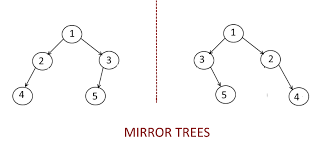
Note:
1. Make in-place changes, that is, modify the nodes given a binary tree to get the required mirror tree.
Problem approach
The idea is to traverse recursively and swap the right and left subtrees after traversing the subtrees.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
Call Mirror for left-subtree i.e., Mirror(left-subtree)
Call Mirror for right-subtree i.e., Mirror(right-subtree)
Swap left and right subtrees.
temp = left-subtree
left-subtree = right-subtree
right-subtree = temp
4. DBMS Question
What is the difference between DELETE, TRUNCATE, and DROP? (Learn)
5. ML Question
Difference between CNN and ANN. How do you use CNN in your project? (Learn)
6. Implementation: HashMap
Easy
30m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Design a data structure that stores a mapping of a key to a given value and supports the following operations in constant time.
1. INSERT(key, value): Inserts an integer value to the data structure against a string type key if not already present. If already present, it updates the value of the key with the new one. This function will not return anything.
2. DELETE(key): Removes the key from the data structure if present. It doesn't return anything.
3. SEARCH(key): It searches for the key in the data structure. In case it is present, return true. Otherwise, return false.
4. GET(key): It returns the integer value stored against the given key. If the key is not present, return -1.
5. GET_SIZE(): It returns an integer value denoting the size of the data structure.
6. IS_EMPTY(): It returns a boolean value, denoting whether the data structure is empty or not.
Note :
1. Key is always a string value.
2. Value can never be -1.
Operations Performed :
First(Denoted by integer value 1): Insertion to the Data Structure. It is done in a pair of (key, value).
Second(Denoted by integer value 2): Deletion of a key from the Data Structure.
Third(Denoted by integer value 3): Search a given key in the Data Structure.
Fourth(Denoted by integer value 4): Retrieve the value for a given key from the Data Structure.
Fifth(Denoted by integer value 5): Retrieve the size of the Data Structure.
Sixth(Denoted by integer value 6): Retrieve whether the Data Structure is empty or not.
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration30 minutes
Interview date21 Mar 2023
Coding problem4
In this round, the interviewer asked me about my projects, resume-related topics, puzzles, etc.
1. Puzzle
Two pipes, A and B, can fill a cistern in 37 minutes and 45 minutes, respectively. Both pipes are opened. The cistern will be filled in just half an hour if B is turned off after.
2. Puzzle
Egg dropping Puzzle:
The following is a description of an instance of the famous egg drop puzzle involving N = 2 eggs and a K = 36-floor building.
Suppose we wish to determine which floors in a 36-story building are safe to drop eggs from and which will cause the eggs to break upon landing. We make a few assumptions:
- An egg that survives a fall can be used again.
- A broken egg must be discarded.
- The effect of a fall is the same for all eggs.
- If an egg breaks when dropped from a certain floor, it would also break if dropped from any higher floor.
- If an egg survives a fall from a certain floor, it would also survive a fall from any lower floor.
- It is not ruled out that the first-floor window may break an egg, nor is it ruled out that the 36th-floor window may not.
If only one egg is available and we want to be certain of obtaining the correct result, the experiment can be conducted in only one way:
Drop the egg from the first floor; if it survives, drop it from the second floor, and continue upward until it breaks. In the worst case, this method may require 36 drops.
Now, suppose two eggs are available. What is the minimum number of egg drops required to guarantee determining the critical floor in all cases?
4. OOPs Question
Difference between java and cpp.(Learn)

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Trainee Software Engineer
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Ionic Software Services
819 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Development
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by PhonePe
12582 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Development
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amdocs
8227 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Development
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
1580 views
0 comments
0 upvotes








