Jio Platforms Limited interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Specialist Programmer
Jio Platforms Limited
2 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I revise coding and logical abilities during interview period. Give aptitude and coding test and clear all approaches. I have good hands-on data structures and algorithms. I practice Aptitude and reasoning.
Practice data structures and optimize complexity. Attend HR interview (give mock interviews first)
Application story
Started with applied by on-campus. Selected in interview on the basis of acedemics
Practice coding and logical complexities during interview period. Give mock test before 2 days of interview. Go for HR interview.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
We were given different dates and had three hours to solve three problems.
They have their own platform, and I began the test in the afternoon.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 - Practice Atleast 250 Questions
Tip 2 - Ex- Do atleast 2 projects
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have some projects on resume
Tip 2 : well formatted resume
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration30 minutes
Interview date8 Feb 2023
Coding problem4
My interview was scheduled at 4 p.m.
Before beginning the interview, I was asked to show my college ID card to the interviewer, who was a Senior Developer.
1. Kth Smallest and Largest Element of Array
Easy
15m average time
70% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array ‘Arr’ consisting of ‘N’ distinct integers and a positive integer ‘K’. Find out Kth smallest and Kth largest element of the array. It is guaranteed that K is not greater than the size of the array.
Example:
Let ‘N’ = 4, ‘Arr’ be [1, 2, 5, 4] and ‘K’ = 3.
then the elements of this array in ascending order is [1, 2, 4, 5]. Clearly, the 3rd smallest and largest element of this array is 4 and 2 respectively.
Problem approach
s1 - Create a max-heap using the STL priority_queue.
s2 - Insert all elements of the array A into the max-heap.
s3 - Keep only the k smallest elements in the heap by popping the largest elements until the heap has k elements.
s4 - The top element of the heap is the kth smallest element in the array.
2. DBMS Questions
Difference between SQL and NoSQL databases.
What is virtual memory
what is the difference between DROP, DELETE and TRUNCATE?
Problem approach
Tip 1:Be confident
Tip 2:Read the major interview topics of DBMS.
Tip 3:Simply say NO if you do not know the answer.
3. Conceptual Questions
Explain the lifecycle of process.
Tell About OS, CPU and Deadlock
Problem approach
Tip 1 : Just Do some interview questions on OS
4. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
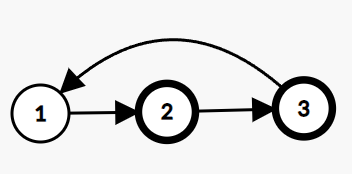
Problem approach
Tell 2 approaches-
s1- one with the hashmap-
Individually traverse the list, adding node addresses to a Hash Table.
If NULL is reached at any point, return false.
Return true if the next current node points to any of the previously stored nodes in Hash.
another with Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm:
Two pointers are used to traverse a linked list.
Move one pointer (slow p) one step and another pointer (fast p) two steps.
There is a loop if these pointers meet at the same node. If no pointers meet, the linked list does not have a loop.
02
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date7 Feb 2023
Coding problem3
My interview was scheduled at 6 p.m.
Before beginning the interview, I was asked to show my college ID card to the interviewer, who was a Senior Developer.
1. Minimum Characters For Palindrome
Hard
20m average time
70% success
0/120
Asked in companies



Given a string STR of length N. The task is to return the count of minimum characters to be added at front to make the string a palindrome.
For example, for the given string “deed”, the string is already a palindrome, thus, minimum characters needed are 0.
Similarly, for the given string “aabaaca”, the minimum characters needed are 2 i.e. ‘a’ and ‘c’ which makes the string “acaabaaca” palindrome.
Problem approach
s1- So, this is a graph problem. We shall create the edge s[i] - s[n-i-1] for each index I if s[i]!= s[n-i-1].
s2- Following that, we obtain k graph components.
Now we'll find the sizes of all those components and add them up to ans variable as ans+= sz() - 1; the result will be saved in ans variable.
2. Maximum Score
Hard
0/120
Asked in companies


Ninja is playing a board game in which two lists of distinct numbers ‘A’ and ‘B’ arranged in a non-descending order are given. The game has certain rules and the player has to pick some numbers from the given list and the score is the sum of unique picked numbers. The rules are:
1. Choose any list ‘A’ or ‘B’.
2. Traverse from left to right.
3. After picking a number, if the picked number is present in both the arrays, you are allowed to traverse to the other array.
You are given arrays,’A’ and ‘B’ of size ‘N’ and ‘M’ respectively. Your task is to find the maximum score Ninja can achieve.
Since the answer can be very large, print answer % (10^9 + 7).
For Example
If the given array are ‘A’ = [1,3,5,7,9] and ‘B’ = [3,5,100]”.The maximum score can be achieved is 109[1+3+5+100].
Problem approach
s1 - Choose any list ‘A’ or ‘B’.
s2 . Traverse from left to right.
s3 . After picking a number, if the picked number is present in both the arrays, you are allowed to traverse to the other array.
3. Count Subarrays with Given XOR
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an array of integers ‘ARR’ and an integer ‘X’, you are supposed to find the number of subarrays of 'ARR' which have bitwise XOR of the elements equal to 'X'.
Note:
An array ‘B’ is a subarray of an array ‘A’ if ‘B’ that can be obtained by deletion of, several elements(possibly none) from the start of ‘A’ and several elements(possibly none) from the end of ‘A’.
Problem approach
s1- Let us refer to the XOR of all items in the range [i+1, j] as A, [0, I as B, and [0, j] as C. When we XOR B with C, the overlapping elements from B and C in [0, I zero out, and we receive XOR of all elements in the range [i+1, j], i.e. A. We have B = A XOR C because A = B XOR C.
s2- Now, if we know the value of C and take the value of A as m, we may calculate the count of A as the number of B that satisfy this connection. We basically get the count of all subarrays with XOR-sum m for each C.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
1133 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
1048 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Specialist Programmer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
878 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
725 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





