Jio Platforms Limited interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Specialist Programmer
Jio Platforms Limited
3 rounds | 7 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
- aThe main objective of these evaluations to maximize profitability and efficiency for companies. I have analytical and technical skills in addition to problem-solving techniques and excellent communication skills. I am set up new designs and models that can automate various industrial processes for manufacturing business organizations. I also participate in maintaining complex data and accessibility in Cloud-based data platforms.
- Practice data structures and optimise complexity.
Application story
1- Applied by off-campus
2- Selected in interview on the basis of grades in acedemics performance
3- Practice coding and logical complexities during interview period
4- Attend for HR interview and salary discussion
TIPS : Coding rounds are focused on Problem Solving with Data Structures & Algorithms. These questions tend to be tricky and provide valuable insight into the candidate’s analytical ability.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
- My success from selection is due to practice on Amcat and hacker- rank
- Attend mock interviews
- Success on the basis of practice and communication
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming
Tip
Tip 1 : Participate in live contests on websites like Codechef, Codeforces etc as much as possible.
Tip 2 : Practice previous interview questions from LeetCode, GeeksForGeeks.
Tip 3 : Revise Computer Science subjects like DBMS, OOPS thoroughly.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: No criteria
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Add projects and Internships if you have done any and add only those things which you really know.
Tip 2 : Do not put false things on resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date4 Jan 2023
Coding problem2
- Morning time
- Environment was good.
- No
- Interviewer was good
1. Next greater number
Moderate
15m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a string S which represents a number. You have to find the smallest number strictly greater than the given number which contains the same set of digits as of the original number i.e the frequency of each digit from 0 to 9 should be exactly the same as in the original number.
For example:
If the given string is 56789, then the next greater number is 56798. Note that although 56790 is also greater than the given number it contains 1 '0' which is not in the original number and also it does not contain the digit '8'.
Note:
The given string is non-empty.
If the answer does not exist, then return -1.
The given number does not contain any leading zeros.
Problem approach
s1- I have done this question earlier so just use already built algorithm which traverses the number from the back.
2. Circular Queue
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You will be given ‘Q’ queries. You need to implement a circular queue according to those queries. Each query will belong to one of these two types:
1 ‘X’: Enqueue element ‘X’ into the end of the nth queue. Returns true if the element is enqueued, otherwise false.
2: Dequeue the element at the front of the nth queue. Returns -1 if the queue is empty, otherwise, returns the dequeued element.
Note:
Enqueue means adding an element to the end of the queue, while Dequeue means removing the element from the front of the queue.
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date10 Feb 2023
Coding problem4
- Morning time
- Environment was good.
- No
- Interviewer was good
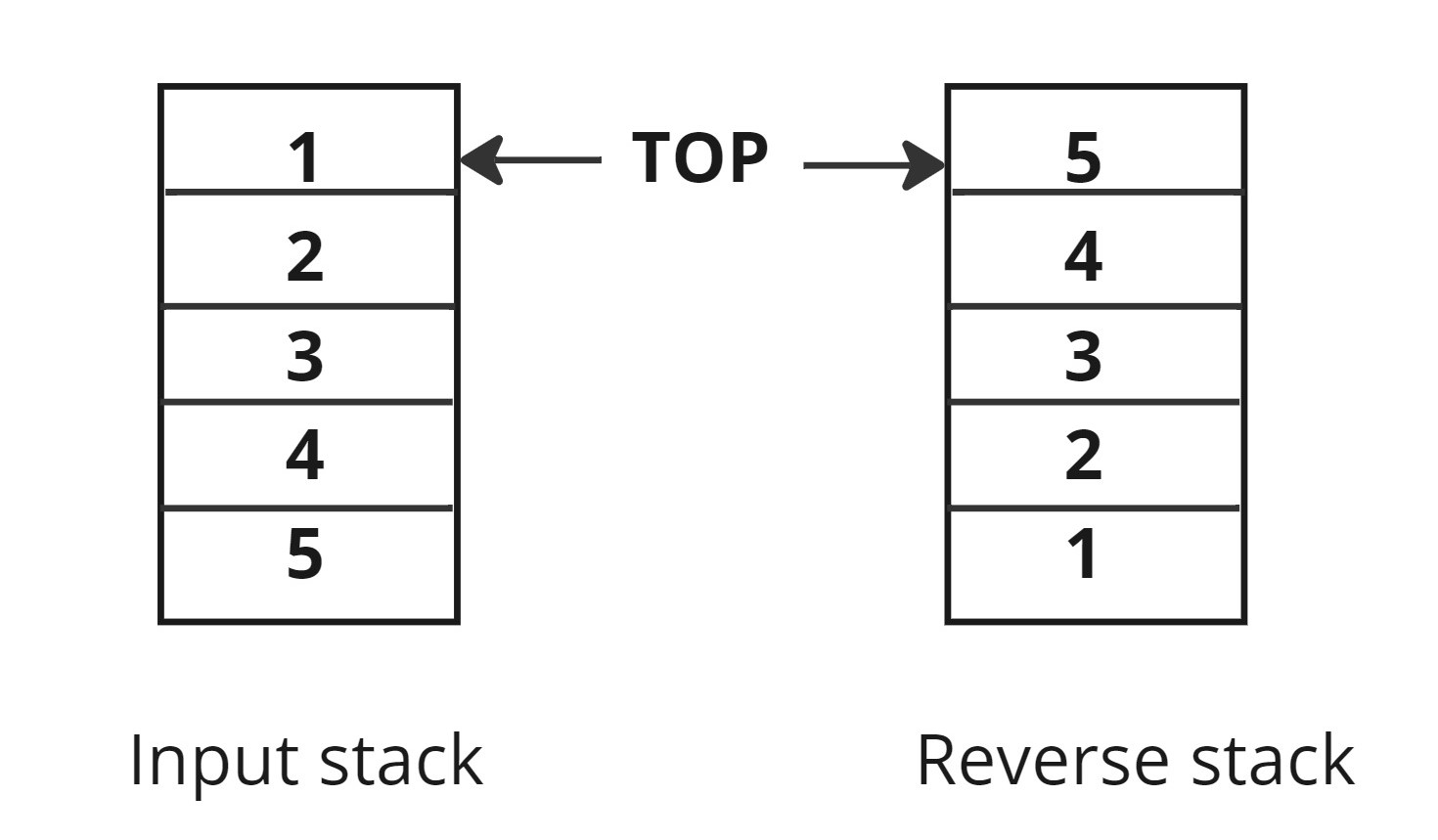
1. Reverse Stack Using Recursion
Easy
21m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Reverse a given stack of 'N' integers using recursion. You are required to make changes in the input parameter itself.
Note: You are not allowed to use any extra space other than the internal stack space used due to recursion.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Problem approach
s1- I told him proper algorithm with code on paper to the interviewer. He asked me to dry run the algorithm which I did by taking an example of stack.
2. Anagram Pairs
Moderate
30m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings 'str1' and 'str1'.
You have to tell whether these strings form an anagram pair or not.
The strings form an anagram pair if the letters of one string can be rearranged to form another string.
Pre-requisites:
Anagrams are defined as words or names that can be formed by rearranging the letters of another word. Such as "spar" can be formed by rearranging letters of "rasp". Hence, "spar" and "rasp" are anagrams.
Other examples include:
'triangle' and 'integral'
'listen' and 'silent'
Note:
Since it is a binary problem, there is no partial marking. Marks will only be awarded if you get all the test cases correct.
Problem approach
I simply used hashing to solve this problem by checking the frequency of characters in both strings.
3. Rod cutting problem
Moderate
40m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a rod of length ‘N’ units. The rod can be cut into different sizes and each size has a cost associated with it. Determine the maximum cost obtained by cutting the rod and selling its pieces.
Note:
1. The sizes will range from 1 to ‘N’ and will be integers.
2. The sum of the pieces cut should be equal to ‘N’.
3. Consider 1-based indexing.
Problem approach
Method 1 : A naive solution to this problem is to generate all configurations of different pieces and find the highest-priced configuration. This solution is exponential in terms of time complexity. Let us see how this problem possesses both important properties of a Dynamic Programming (DP) Problem and can efficiently be solved using Dynamic Programming.
4. Coin Change(Finite Supply)
Hard
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an array of integers ‘coins’ denoting the denomination of coins and another array of integers ‘freq’ denoting the number of coins of each denomination.
You have to find the number of ways to make the sum ‘V’ by selecting some(or all) coins from the array.
The answer can be very large. So, return the answer modulo 1000000007.
For Example :
‘N’ = 3, ‘coins’ = {1, 2, 3}, ‘freq’ = {1, 1, 3}, ‘V’ = 6
For the given example, we can make six by using the following coins:
{1, 2, 3}
{3. 3}
Hence, the answer is 2.
Problem approach
s1- We have 2 choices for a coin of a particular denomination, either i) to include, or ii) to exclude.
If we are at coins[n-1], we can take as many instances of that coin ( unbounded inclusion ) i.e count(coins, n, sum – coins[n-1] ); then we move to coins[n-2].
s2- After moving to coins[n-2], we can’t move back and can’t make choices for coins[n-1] i.e count(coins, n-1, sum).
s3- Finally, as we have to find the total number of ways, so we will add these 2 possible choices, i.e count(coins, n, sum – coins[n-1] ) + count(coins, n-1, sum );
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration50 minutes
Interview date16 Feb 2023
Coding problem1
- Morning time
- Environment was good.
- No
- Interviewer was good
1. Basic HR Questions
Describe a time when you experienced conflict with a coworker. How did you handle it?
How does this job compare to others you might be interviewing for?
What interests you about this role?
What critical feedback do you most often receive?
Problem approach
Tip 1: Practice well
Tip 2: Speak in front of mirror

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
1203 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
1105 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
1182 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Specialist Programmer
2 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Jio Platforms Limited
647 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




