Josh Technology Group interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Josh Technology Group
8 rounds | 12 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
From my first year of B.Tech., I started learning DSA and practiced it consistently. With dedication and hard work, I kept improving my problem-solving skills and focused on building strong fundamentals. Over time, I also explored projects and applied my knowledge practically. All the continuous effort finally paid off when I successfully cracked Josh Technology Group.
Application story
I applied through the on-campus placement drive at my college. The process began with three elimination rounds conducted in the college labs under supervision — starting with a C++-based objective test, followed by two DSA rounds. Later, I was invited to the company’s office for another DSA round, followed by three technical interviews focused on problem-solving and DSA, and finally, the HR round.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was selected for this position after successfully clearing all the challenging rounds. They offered me a role as an SDE Intern along with a full-time position, which made all my hard work and consistent efforts truly worth it.
Preparation
Duration: 30 months
Topics: Data Structures, OOPS, Dynamic Programming, Segment Trees, Computer Networks
Tip
Tip 1: Be consistent in your preparation and practice.
Tip 2: Maintain daily problem-solving streaks on online coding platforms.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: NA, (Salary package: 15.47 LPA)
Resume tip
Tip 1: You don’t need to upload a resume since they use their own POD software to generate one automatically. Make sure to fill in all your details carefully while applying.
Tip 2: Avoid entering any fake marks, as they verify them with your college and will eliminate you before the first round if any discrepancies are found.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration50 minutes
Interview date21 Jun 2025
Coding problem0
Round 1 was an online objective test consisting of 35 multiple-choice questions to be completed in 50 minutes. The questions were based on C++ concepts, pointers, data structures, OOPs, and output-based problems. Negative marking was also applied.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration75 minutes
Interview date21 Jun 2025
Coding problem2
Round 2 included two DSA coding problems based on Linked List and Binary Tree, along with a few aptitude questions to test logical and analytical skills.
1. Equal Subtree Sums
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given a binary tree where each node contains an integer value. Your task is to count the number of nodes in the tree that satisfy a specific property: the sum of all node values in the node's left subtree must be equal to the node's own value, AND the sum of all node values in its right subtree must also be equal to the node's own value.
Definitions:
The sum of an empty subtree (i.e., if a child is null) is considered to be 0.
A leaf node has a left subtree sum of 0 and a right subtree sum of 0.
Problem approach
Start Recursion from Root: Begin a recursive function that returns the sum of the subtree rooted at the current node.
Base Case: If the node is NULL, return 0.
Recursive Call: Calculate the sum of the left and right subtrees recursively.
Compare Sums: Check if both left and right subtree sums are equal to the current node’s value.
Update Count: If the condition is satisfied, increment a reference counter.
Return Subtree Sum: Return the sum of left + right + current node’s value to the parent call.
2. Mirrored Difference Update
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You are given the head of a singly linked list with n nodes. Your task is to modify the values of the nodes in-place according to a specific "mirrored difference" rule.
The update rule is as follows:
The value of the 1st node should be updated to (Value of Last Node) - (Original Value of 1st Node).
The value of the 2nd node should be updated to (Value of 2nd to Last Node) - (Original Value of 2nd Node).
The value of the 3rd node should be updated to (Value of 3rd to Last Node) - (Original Value of 3rd Node).
...and so on.
This pattern continues until the pointers from the start and the end of the list meet or cross. If the list has an odd number of nodes, the middle node's value remains unchanged.
After modifying the list, your function should return its head.
Problem approach
Find the Middle Node: Use the slow and fast pointer technique to locate the middle of the linked list.
Reverse the Second Half: Reverse the second half of the linked list so that the last node comes first.
Two-Pointer Traversal: Initialize two pointers — one at the start of the first half, and one at the start of the reversed second half.
Update Values: For each pair of nodes, update the first half node’s value as:
first_pointer->val = second_pointer->val - first_pointer->val
Move Pointers Forward: Move both pointers to the next nodes until all nodes in the first half are updated.
Restore Order: Reverse the second half again to restore the original linked list order.
03
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration75 minutes
Interview date21 Jun 2025
Coding problem3
This test was conducted during the day and followed the previous rounds. It was purely DSA-based, consisting of three coding problems.
1. Asteroid Collision
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'asteroids' representing asteroids in a row.
For each element of the given array, its absolute value denotes the size of that asteroid, and its sign denotes the direction it moves in(+ve meaning right and -ve meaning left).
An asteroid with a weight of 0 denotes a massless asteroid that moves in the right direction.
All asteroids are moving at the same speed. Whenever two asteroids collide, the smaller asteroid gets destroyed.
If both asteroids are the same size, then both asteroids get destroyed. Two asteroids moving in the same direction never collide.
You are supposed to find the state of the asteroids after all collisions.
Example :
Input: ‘asteroids’ = [3,-2,4]
Output: [3, 4]
Explanation: The first asteroid will destroy the second asteroid. Hence, after the collision, the state of the asteroids will be [3,4].
Note:
You don’t need to print anything. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
I solved this with stack based approach as which is its famous approach. I was well aware with its solutions and directly solved it.
2. Second Largest in Tree Level
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You are given a binary tree where each node contains an integer value. Your task is to find the second largest unique value at each level of the tree.
You must return a list of these second-largest values, ordered from the root level to the deepest level.
Rules for determining the second largest value:
If a level has two or more unique node values (e.g., [5, 5, 3]), the second largest is the second highest distinct value (in this case, 3).
If a level has fewer than two unique node values (e.g., [10] or [20, 20, 20]), there is no second largest value. In such cases, you should use -1 as a placeholder for that level's result.
Problem approach
Initialize Two Arrays: Create two arrays — one to store the largest value at each level and another to store the second largest value.
Recursive Function for First Largest: Traverse the tree recursively level by level, and update the largest value for each level in the first array.
Recursive Function for Second Largest: Traverse the tree again, comparing each node’s value with the largest value of its level. Update the second largest array if the node’s value is less than the largest but greater than the current second largest.
Combine Results: After both traversals, the second array will contain the second largest value at each level.
Return or Print: Use this array as the final result for all levels.
3. Partition Linked List
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You are given the head of a singly linked list and an integer X. Your task is to partition the linked list around the value X such that:
All nodes with values less than X come first.
All nodes with values equal to X come next.
All nodes with values greater than X come at the end.
Crucially, the original relative order of the nodes within each of these three partitions must be preserved.
Your function should rearrange the nodes in-place (or by creating new lists and linking them) and return the head of the newly formed partitioned list.
Problem approach
Create Three Dummy Lists: Initialize three separate linked lists — less, equal, and greater.
Traverse Original List: Iterate through the original linked list and append each node to the appropriate list based on its value relative to X.
Connect Lists: Link the three lists in order: less → equal → greater.
Return Head: Return the head of the newly combined list as the final rearranged linked list.
04
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration45 minutes
Interview date2 Jul 2025
Coding problem1
This was first OA round at company and based on DSA. I was only able to solve one question due to some compiler issue, but still got selected.
1. Reverse List In K Groups
Hard
15m average time
85% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a linked list of 'n' nodes and an integer 'k', where 'k' is less than or equal to 'n'.
Your task is to reverse the order of each group of 'k' consecutive nodes, if 'n' is not divisible by 'k', then the last group of nodes should remain unchanged.
For example, if the linked list is 1->2->3->4->5, and 'k' is 3, we have to reverse the first three elements, and leave the last two elements unchanged. Thus, the final linked list being 3->2->1->4->5.
Implement a function that performs this reversal, and returns the head of the modified linked list.
Example:
Input: 'list' = [1, 2, 3, 4], 'k' = 2
Output: 2 1 4 3
Explanation:
We have to reverse the given list 'k' at a time, which is 2 in this case. So we reverse the first 2 elements then the next 2 elements, giving us 2->1->4->3.
Note:
All the node values will be distinct.
Problem approach
Unable to clear testcase due to some compiler issues.
05
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration90 minutes
Interview date2 Jul 2025
Coding problem2
Started around 11 AM, interviewer was 2.5 years experienced. Directly jumped into DSA problems after intro.
1. Count Univalue Subtrees
Moderate
30m average time
70% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree. Return the count of unival sub-trees in the given binary tree. In unival trees, all the nodes, below the root node, have the same value as the data of the root.
For example: for the binary tree, given in the following diagram, the number of unival trees is 5.
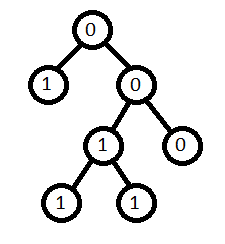
Problem approach
Define Recursive Function: Use a recursive function that returns a pair containing:
A boolean indicating whether the subtree rooted at the current node is a univalue subtree.
The count of univalue subtrees in the current subtree.
Base Case: If the node is NULL, return (true, 0) — an empty tree is considered univalue.
Recursive Calls: Recursively check the left and right subtrees, obtaining their boolean status and counts.
Check Current Node:
If both left and right subtrees are univalue and the node’s value matches its children (if they exist), then the current subtree is univalue.
Otherwise, it’s not.
Update Count:
Add the counts from left and right subtrees.
If the current subtree is univalue, increment the count by 1.
Return Pair: Return (isUnivalueSubtree, totalCount) to the parent call.
2. K-Balanced Linked List
Moderate
0/80
Asked in company

You are given a singly linked list and an integer K. A node in the list is considered "k-balanced" if the absolute difference between the sum of values of all nodes before it and the sum of values of all nodes after it is less than or equal to K.
| (Sum of values before the node) - (Sum of values after the node) | <= K
The sum of nodes before the head of the list is 0. The sum of nodes after the tail of the list is also 0.
Your task is to determine if every node in the linked list is k-balanced. If all nodes satisfy this condition, return true. If even one node fails the check, return false. An empty list or a list with a single node is considered balanced by definition.
Problem approach
Define Recursive Function:
Use a recursive function that returns a pair containing:
Boolean: Whether the current node satisfies the balance condition.
Integer: The sum of all nodes in the subtree rooted at this node.
Base Case:
If the node is NULL, return (true, 0) — an empty subtree is balanced with sum 0.
Recursive Calls:
Recursively calculate the left subtree and right subtree, obtaining their boolean status and sums.
Check Current Node Balance:
Compute the absolute difference between the sum of left subtree and sum of right subtree.
Check if this difference ≤ K.
Combine Results:
If the left and right subtrees are balanced and the current node satisfies the balance condition, the current subtree is balanced.
Otherwise, it’s not.
Compute Total Sum:
Sum = leftSum + rightSum + currentNodeValue
Return Pair:
Return (isBalanced, totalSum) to the parent node.
06
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration90 minutes
Interview date2 Jul 2025
Coding problem2
This was also DSA round, interviewer was 4 years experienced. After intro, directly jumped into DSA problems.
1. Size of Largest BST in Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'N' nodes, where the nodes have integer values. Your task is to return the size of the largest subtree of the binary tree which is also a BST.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example:
Given binary tree:
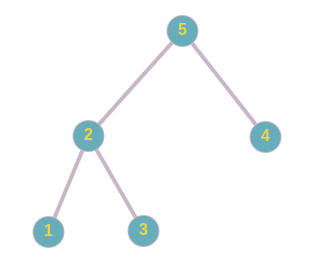
In the given binary tree, subtree rooted at 2 is a BST and its size is 3.
Problem approach
1. Use a helper class `treeNode` to store `isBst`, `size`, `mini`, and `maxi` for each subtree.
2. Recursively traverse the tree in a **post-order** manner.
3. For each node, check if left and right subtrees are BSTs and satisfy `left->maxi < node->data < right->mini`.
4. If yes, update the subtree size, min, max, and `maxSize`. Otherwise, mark it as not BST.
5. Return the updated `treeNode` info to the parent.
6. The final `maxSize` after recursion is the size of the largest BST.
2. Split Array Largest Sum
Hard
15m average time
85% success
0/120
Asked in companies


You’re given an array 'arr' of size 'n' and an integer 'k'.
Your task is to split 'arr' into 'k' sub-arrays such that the maximum sum achieved from the 'k' subarrays formed must be the minimum possible.
A subarray is a contiguous part of the array.
Return the minimum possible value of the maximum sum obtained after splitting the array into 'k' partitions.
Example:
Input: ‘arr’ = [1, 1, 2] and ‘k’ = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: If we want to make two subarrays, there are two possibilities: [[1], [1, 2]] and [[1, 1], [2]]. We can see that the maximum sum of any subarray is minimized in the second case. Hence, the answer is 2, which is the maximum sum of any subarray in [[1, 1], [2]].
Problem approach
1. Set `low = max(weights)` and `high = sum(weights)`.
2. Perform binary search: pick `mid = (low + high)/2` as candidate max weight.
3. Check if weights can be distributed among `K` students without exceeding `mid`.
4. If possible, try smaller `mid` (`high = mid - 1`); otherwise, try larger (`low = mid + 1`).
5. Return the smallest feasible `mid` as the answer.
07
Round
Hard
Face to Face
Duration150 minutes
Interview date2 Jul 2025
Coding problem2
This was also a pure DSA round, interviewer was 14 years experienced. This was a hard level DSA round and some discussion on projects too. Highly optimised approaches were required. Interviewer was helpful and gave many hints to solve problems.
1. Palindrome Partitioning ll
Hard
40m average time
60% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given a string 'str' of length 'n'.
Find the minimum number of partitions in the string so that no partition is empty and every partitioned substring is a palindrome.
Example :
Input: 'str' = "aaccb"
Output: 2
Explanation: We can make a valid partition like aa | cc | b.
Problem approach
Precompute Palindromes:
Create a 2D boolean array isPalindrome[i][j].
isPalindrome[i][j] = true if substring s[i..j] is a palindrome.
Fill this array using dynamic programming / tabulation.
Initialize Cuts Array:
Create an array minCuts[i] to store the minimum cuts needed for substring s[0..i].
Calculate Minimum Cuts:
For each i from 0 to n-1:
If s[0..i] is palindrome → minCuts[i] = 0.
Else, try all j < i and check if s[j+1..i] is palindrome:
minCuts[i] = min(minCuts[i], minCuts[j] + 1)
This gives the minimum cuts for s[0..i].
Return Result:
minCuts[n-1] gives the minimum number of cuts for the entire string.
2. Sorted Doubly Linked List to Balanced BST
Easy
0/40
Asked in company

You are given a special linked list that is sorted in ascending order. Each node in this list is a doubly linked list node, containing data, a next pointer to the next node, and a prev pointer to the previous node.
Your task is to convert this sorted doubly linked list into a height-balanced Binary Search Tree (BST).
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one. The BST property must also be maintained: for any given node, all values in its left subtree are less than the node's value, and all values in its right subtree are greater.
Your function should take the head of the doubly linked list and return the root of the newly constructed BST.
Problem approach
Case 1: Linked List with left and right pointers (O(n) time, O(1) space)
Find the Middle Node:
Use the slow and fast pointer technique on the linked list to find the middle node.
This node becomes the root of the BST.
Recursive Construction (In-Place):
Recursively apply the same method to the left half of the list → becomes left subtree.
Recursively apply the same method to the right half → becomes right subtree.
Link Subtrees:
Connect the left and right subtrees to the root.
Result:
BST is constructed in-place in O(n) time and O(1) extra space (ignoring recursion stack).
Case 2: Linked List without left and right pointers
The approach was explained recursively:
Find the middle node of the linked list to act as root.
Recursively construct the left and right subtrees from the two halves of the list.
No extra data structures were used; recursion handled the construction.
No code was required for this follow-up; only the recursive strategy was explained.
08
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration25 minutes
Interview date2 Jul 2025
Coding problem0
In the HR round, the interviewer highlighted that they were impressed with my DSA skills. They asked about my daily routine, how I would resolve conflicts with teammates, and my understanding of the company culture. The HR also explained the bond conditions and other policies of the company.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
6 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
5571 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
5 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
3257 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1130 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
7 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1123 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3714 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
2667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2336 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





