Josh Technology Group interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Josh Technology Group
5 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Arrays, Searching, Sorting, Trees, LinkedList, Arrays, Dynamic Programming, Graphs
Tip
Tip 1 : Don't use STL in OA or in Interview rounds
Tip 2 : Use commented code in OA (some OA rounds are checked by humans not machines).
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Keep only those projects which you know extremely well.
Tip 2 : Keep 1 page resume only
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration50 minutes
Interview date28 May 2021
Coding problem0
We had 40 mcqs and 10 output based questions, there was negative marking with mcqs one and not with the output based.
02
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date29 May 2021
Coding problem1
In this round we had 2 coding questions, and 1 long C++ output based question.
1. Diameter Of Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Binary Tree.
Return the length of the diameter of the tree.
Note :
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two end nodes in a tree.
The number of edges between two nodes represents the length of the path between them.
Example :
Input: Consider the given binary tree:
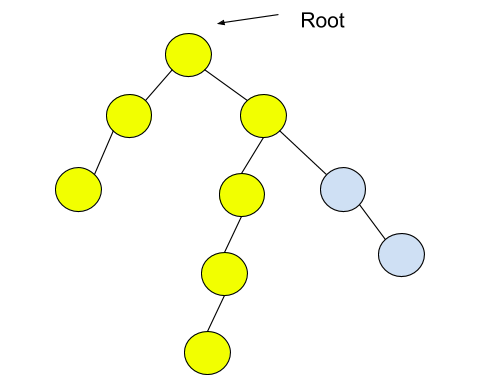
Output: 6
Explanation:
Nodes in the diameter are highlighted. The length of the diameter, i.e., the path length, is 6.
03
Round
Hard
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date1 Jun 2021
Coding problem2
This round consisted of 3 coding questions, 2 of linked list (hard) and 1 of tree (medium)
1. Count Pairs
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a cartesian plane, having ‘N’ points in the form of the array ‘PointX’ and ‘PointY’ where ‘PointX[i]’ and ‘PointY[i]’ represent the ‘X’ coordinates and ‘Y’ coordinates of the i’th point, respectively. You have to find the number of pairs satisfying the following conditions:
1. The points in the pair are distinct.
2. Euclidean distance and the Manhattan distance between the points of the pair should be equal.
Note :
1. Pair (‘P’, ‘Q’) is the same as pair (‘Q’, ‘P’).
2. Euclidean distance is given by: (( ‘X2’ - ‘X1’) ^ 2 + (‘Y2’ - ‘Y1’) ^ 2) ^ 0.5.
3. Manhattan distance is given by: |’X2’ - ‘X1’| + |’Y2’ - ‘Y1’|, where points are (‘X1’, ‘Y1’) and (‘X2’, ‘Y2’).
For example :
Let points be: (1, 2), (2, 3), (1, 3)
The Euclidean distance between points (1, 2) and (1, 3) is: 1
The Manhattan distance between points (1, 2) and (1, 3) is: 1
The Euclidean distance between points (2, 3) and (1, 3) is: 1
The Manhattan distance between points (2, 3) and (1, 3) is: 1
So the pairs can be: [(1, 2), (1, 3)] and [(2, 3), (1, 3)].
So the number of pairs is 2.
2. Sort A “K” Sorted Doubly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You’re given a doubly-linked list with N nodes, where each node deviates at max K position from its position in the sorted list. Your task is to sort this given doubly linked list.
For example :
Let us consider K is 3, an element at position 4 in the sorted doubly linked list, can be at positions 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 in the given linked list because the absolute difference of all these indices with 4 is at most 3.
Note :
All elements are distinct.
A doubly linked list is a type of linked list that is bidirectional, that is, it can be traversed in both directions, forward and backward.
04
Round
Hard
Face to Face
Duration120 minutes
Interview date10 Jun 2021
Coding problem2
Interviewer was extremely humble, after introduction he asked 2 medium level questions one from LinkedList and one from Trees.
1. Merge Two Sorted Linked Lists
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two sorted linked lists. You have to merge them to produce a combined sorted linked list. You need to return the head of the final linked list.
Note:
The given linked lists may or may not be null.
For example:
If the first list is: 1 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL and the second list is: 2 -> 3 -> 5 -> NULL
The final list would be: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 5 -> NULL
2. Binary Tree Pruning
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree where the value of each node is either 0 or 1. Your task is to return the same Binary Tree but all of its subtrees that don't contain a 1 have been removed.
Note :
A subtree of a node X is X, plus every node that is a descendant of X.
For Example :
Look at the below example to see a Binary Tree pruning.
Input: [1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
Output: [1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
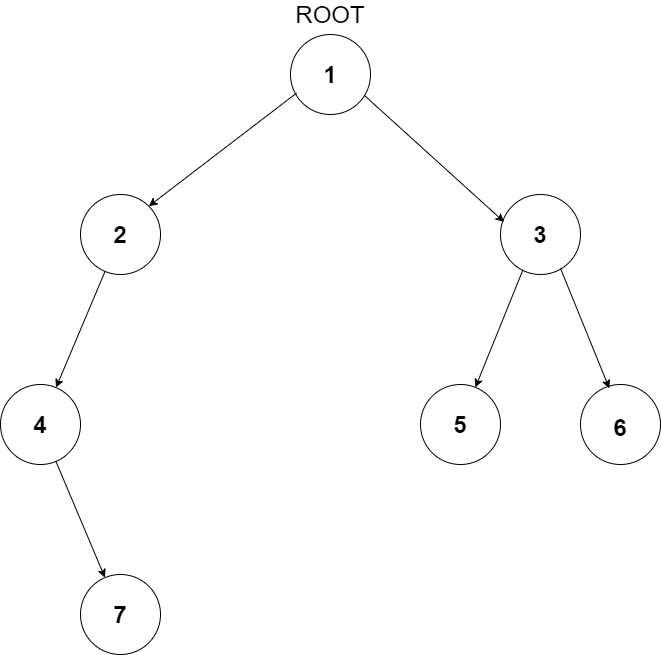
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
05
Round
Hard
Face to Face
Duration180 minutes
Interview date17 Jun 2021
Coding problem1
This round is the final technical round, the interviewer asked me 3 questions.
1. Missing and repeating numbers
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array of size ‘N’. The elements of the array are in the range from 1 to ‘N’.
Ideally, the array should contain elements from 1 to ‘N’. But due to some miscalculations, there is a number R in the range [1, N] which appears in the array twice and another number M in the range [1, N] which is missing from the array.
Your task is to find the missing number (M) and the repeating number (R).
For example:
Consider an array of size six. The elements of the array are { 6, 4, 3, 5, 5, 1 }.
The array should contain elements from one to six. Here, 2 is not present and 5 is occurring twice. Thus, 2 is the missing number (M) and 5 is the repeating number (R).
Follow Up
Can you do this in linear time and constant additional space?
Problem approach
I used simple binary solution approach to solve this in O(logN)

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
6 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
5570 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1130 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
7 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1122 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
6 rounds | 16 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
4070 views
3 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3713 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
2667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2336 views
0 comments
0 upvotes





