JUSPAY interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
JUSPAY
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Database Management Systems, Object Orientated Programing, Operating Systems, Computer Networks
Tip
Tip 1 : Consistency
Tip 2 : Never Give Up
Tip 3 : Learn from the mistakes
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Simple and short providing the required information
Tip 2 : Single page resume with showing all the multiple projects which have done.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration90 minutes
Interview date16 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
Round 1: Online Assessment
1. LCA Of Binary Tree
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of distinct integers and two nodes ‘X’ and ‘Y’. You are supposed to return the LCA (Lowest Common Ancestor) of ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
The LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ in the binary tree is the shared ancestor of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ that is located farthest from the root.
Note :
You may assume that given ‘X’ and ‘Y’ definitely exist in the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree
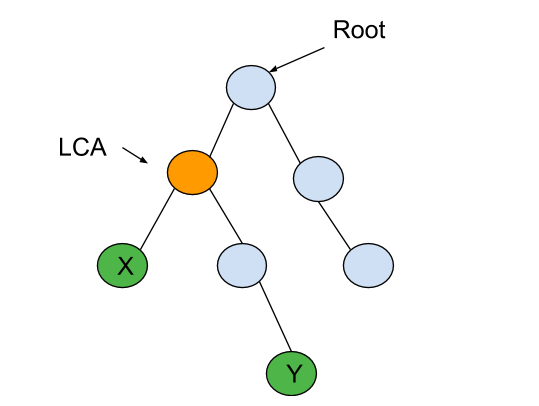
LCA of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ is highlighted in yellow colour.
Problem approach
We have discussed an efficient solution to find LCA in Binary Search Tree. In Binary Search Tree, using BST properties, we can find LCA in O(h) time where h is the height of the tree. Such an implementation is not possible in Binary Tree as keys Binary Tree nodes don’t follow any order. The following are different approaches to find LCA in Binary Tree.
Method 1: (By Storing root to n1 and root to n2 paths):
Following is a simple O(n) algorithm to find LCA of n1 and n2.
1) Find a path from the root to n1 and store it in a vector or array.
2) Find a path from the root to n2 and store it in another vector or array.
3) Traverse both paths till the values in arrays are the same. Return the common element just before the mismatch.
Time Complexity: The time complexity of the above solution is O(n). The tree is traversed twice, and then path arrays are compared.
Method 2 (Using Single Traversal)
Method 1 finds LCA in O(n) time but requires three tree traversals plus extra spaces for path arrays. If we assume that the keys n1 and n2 are present in Binary Tree, we can find LCA using a single traversal of Binary Tree and without extra storage for path arrays.
The idea is to traverse the tree starting from the root. If any of the given keys (n1 and n2) matches with the root, then the root is LCA (assuming that both keys are present). If the root doesn’t match with any of the keys, we recur for the left and right subtree. The node which has one key present in its left subtree and the other key present in the right subtree is the LCA. If both keys lie in the left subtree, then the left subtree has LCA also, otherwise, LCA lies in the right subtree.
Time Complexity: The time complexity of the above solution is O(n) as the method does a simple tree traversal in a bottom-up fashion.
2. Tree Traversals
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'N'
nodes, where the nodes have integer values.
Your task is to return the ln-Order, Pre-Order, and Post-Order traversals of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
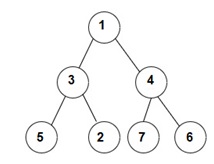
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
The Preorder traversal will be [1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 7, 6].
The Postorder traversal will be [5, 2, 3, 7, 6, 4, 1].
Problem approach
Inorder Traversal:
Algorithm Inorder(tree)
1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(left-subtree)
2. Visit the root.
3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(right-subtree)
Uses of Inorder
In the case of binary search trees (BST), Inorder traversal gives nodes in non-decreasing order. To get nodes of BST in non-increasing order, a variation of Inorder traversal where Inorder traversal s reversed can be used.
Preorder Traversal:
Algorithm Preorder(tree)
1. Visit the root.
2. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Preorder(left-subtree)
3. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Preorder(right-subtree)
Uses of Preorder
Preorder traversal is used to create a copy of the tree. Preorder traversal is also used to get prefix expression on an expression tree.
Postorder Traversal:
Algorithm Postorder(tree)
1. Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Postorder(left-subtree)
2. Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Postorder(right-subtree)
3. Visit the root.
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration120 minutes
Interview date17 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
Direct Interview With the CEO of Juspay.
1. Bridges In A Graph
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an undirected graph of V vertices and E edges. Your task is to find all the bridges in the given undirected graph. A bridge in any graph is defined as an edge which, when removed, makes the graph disconnected (or more precisely, increases the number of connected components in the graph).
For Example :
If the given graph is :
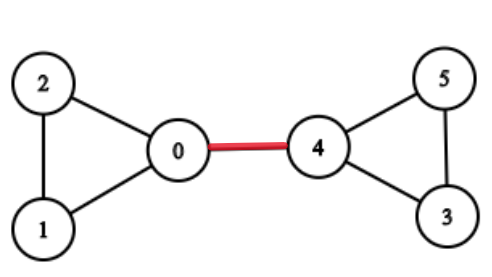
Then the edge between 0 and 4 is the bridge because if the edge between 0 and 4 is removed, then there will be no path left to reach from 0 to 4.and makes the graph disconnected, and increases the number of connected components.
Note :
There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
There are no parallel edges i.e no two vertices are directly connected by more than 1 edge.
2. N Queens
Hard
55m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an integer 'N'. For a given 'N' x 'N' chessboard, find a way to place 'N' queens such that no queen can attack any other queen on the chessboard.
A queen can be killed when it lies in the same row, or same column, or the same diagonal of any of the other queens. You have to print all such configurations.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by JUSPAY
2419 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 2 problems
Interviewed by JUSPAY
2928 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
1 rounds | 1 problems
Interviewed by JUSPAY
4938 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by JUSPAY
3858 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58030 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes







