KLA interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Associate Professional
KLA
2 rounds | 3 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 6 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, DBMS, Full Stack, .Net
Tip
Tip 1: Concentrate on all the data structures and algorithms and practice at least 100 easy and 80 medium and 30-40 hard questions before the placements
Tip 2: Pick a coding language like 'Python' and practice well in that, so that during the hackathon we won't need to waste time exploring the language
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Current arrears shouldn't be there
Resume tip
Tip 1: As many projects as we have in the resume as good as it is.
Tip 2: Whatever is there in the resume we need to be strong in those areas. If we couldn't answer a question asked from the resume it would create a bad impression on us
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration90 minutes
Interview date8 Feb 2022
Coding problem2
This round was held around 4pm and it happened in online mode in hackerank platform. We were supposed to turn on our camera and mic during the whole round.
1. Container With Most Water
Moderate
15m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a sequence of ‘N’ space-separated non-negative integers A[1],A[2],A[3],......A[i]…...A[n]. Where each number of the sequence represents the height of the line drawn at point 'i'. Hence on the cartesian plane, each line is drawn from coordinate ('i',0) to coordinate ('i', 'A[i]'), here ‘i’ ranges from 1 to ‘N’. Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most area of water.
Note :
1. You can not slant the container i.e. the height of the water is equal to the minimum height of the two lines which define the container.
2. Do not print anything, you just need to return the area of the container with maximum water.
Example
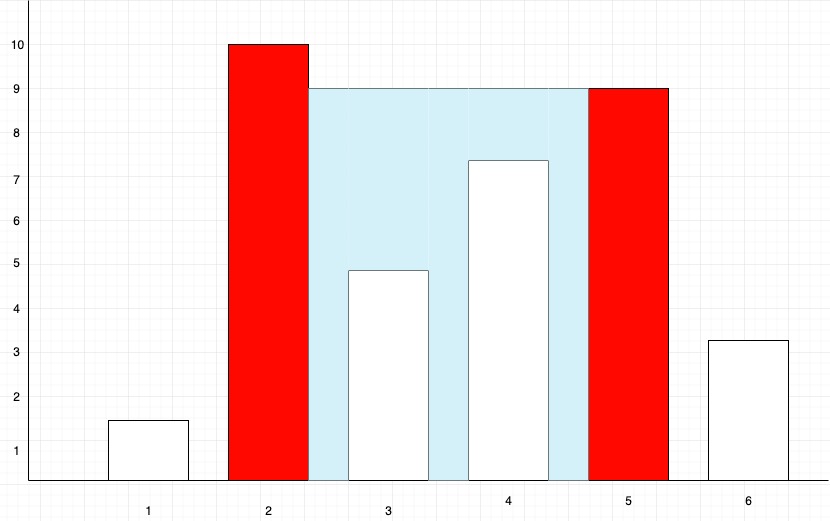
For the above Diagram, the first red marked line is formed between coordinates (2,0) and (2,10), and the second red-marked line is formed between coordinates (5,0) and (5,9). The area of water contained between these two lines is (height* width) = (5-2)* 9 = 27, which is the maximum area contained between any two lines present on the plane. So in this case, we will return 3* 9=27.
Problem approach
Since we assume there is a better answer in the sub-range of [i, j], then this optimal range must be contained by either [i + 1, j] or [i, j - 1], or both.
Let's assume [i + 1, j] doesn't contain the optimal range, but [i, j - 1] contains it. Then this means two things:
the optimal range is not in [i + 1, j - 1], otherwise, [i + 1, j] will contain it.
The optimal range contains the block [i, i + 1] (since this is the part which exists in [i, j - 1] but not in [i+1, j]).
However, notice that, len(i, j - 1) < len(i, j), and in the range [i, j], the area is constrained by the height of h[i] (even in the case h[i] == h[j]). Thus, in the range [i, j - 1], even all pillar are no shorter than h[j], the maximum area is smaller than the area formed by i & j, which contradicts our assumption there is a better answer in the sub-range of [i, j]. This contradiction suggests [i + 1, j] contains the optimal sub-range, if such sub-range exists.
According to above theorem, we can design the algorithm, whenever h[i] < h[j], we advance the pointer i.
2. Number of Islands
Easy
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a non-empty grid consisting of only 0s and 1s. You have to find the number of islands in the given grid.
An island is a group of 1s (representing land) connected horizontally, vertically or diagonally. You can assume that all four edges of the grid are surrounded by 0s (representing water).
Problem approach
Use matrix Breadth-first search to solve the problem
02
Round
Hard
Online Coding Test
Duration720 mintues
Interview date17 Feb 2021
Coding problem1
Hackathon
1. Technical question
Regarding image processing
Problem approach
Converted image into 2D array and applied BFS and DFS to solve it

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by KLA
717 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by KLA
4951 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Associate Professional
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
521 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Professional
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Associate Professional
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by CIS - Cyber Infrastructure
496 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






