Magicbricks interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
Magicbricks
3 rounds | 5 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Coding Test - Pen and paper
Duration60 minutes
Interview date16 May 2015
Coding problem2
It comprised of general aptitude questions and two coding questions. It was an offline test.
1. N Queens
Hard
55m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an integer 'N'. For a given 'N' x 'N' chessboard, find a way to place 'N' queens such that no queen can attack any other queen on the chessboard.
A queen can be killed when it lies in the same row, or same column, or the same diagonal of any of the other queens. You have to print all such configurations.
Problem approach
DFS can be used to solve this problem. The idea is to place queens in different columns one by one, starting from the leftmost column. As we cannot place 2 queens in the same column, when we place the queen in the nth column and if its valid position, dfs again starting n+1 th column and try placing the next queen in all the rows of n+1th column and find a valid position. If no valid queen row found in n+1th row, backtrack and go to nth column, and change the queen position to the next row and repeat the process.
2. Sort 0 1 2
Easy
22m average time
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given an integer array/list(ARR) of size 'N'. It only contains 0s, 1s and 2s. Write a solution to sort this array/list.
Note :
Try to solve the problem in 'Single Scan'. ' Single Scan' refers to iterating over the array/list just once or to put it in other words, you will be visiting each element in the array/list just once.
Problem approach
The simple approach is to simply count the number of 0’s, 1’s, and 2’s. Then, place all 0’s at the beginning of the array followed by 1’s and 2's. The time complexity of this approach would be O(n) and space complexity O(1).
However, the approach requires two traversals of the array. The question can also be solved in a single scan of the array by maintaining the correct order of 0’s, 1’s, and 2’s using variables.
We divide the array into four groups using three pointers. Let us name these pointers as low, mid, and high.
1. a[0…low-1] only zeroes
2. a[low..mid-1] only ones
3. a[mid…high] unknown
4. a[high+1..n-1] only twos
Algorithm :
1. Initialise three pointers low = 0, mid = 0 and high = n -1
2. Run a while loop until mid<=high :
2.1 If (a[mid] ==0), then swap the element with the element low and increment low and mid (low++ and mid++).
2.2 If (a[mid] ==1), then increment mid (mid++).
2.3 If (a[mid] ==2), then swap it with an element in high range and decrement high (high--).
02
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date18 May 2015
Coding problem2
After having a technical discussion about my CV. He gave me two questions to code.
1. Ninja and substrings
Easy
20m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in companies



Ninja has been given a string 'STR' containing only lowercase alphabetic characters. Ninja has to find the number of all the different possible substrings of size two that appear in 'STR' as contiguous substrings.
For example:
If the string is “abcd”, then all possible substrings of size two are { “ab”, “bc”, “cd”}.
Problem approach
The brute force solution is to check for every index in the string whether the sub-string can be formed at that index or not. To implement this, run a nested loop traversing the given string and check for sub-string from every index in the inner loop.
Time Complexity : O(n^2)
The solution can be optimised by using KMP Algorithm. The KMP matching algorithm uses degenerating property (pattern having same sub-patterns appearing more than once in the pattern) of the pattern. The basic idea behind KMP algorithm is: whenever we detect a mismatch (after some matches), we already know some of the characters in the text of the next window.
Pseudocode:
Find Prefix:
Begin
length := 0
prefArray[0] := 0
for all character index i of pattern, do
if pattern[i] = pattern[length], then
increase length by 1
prefArray[i] := length
else
if length !=0 then
length := prefArray[length - 1]
decrease i by 1
else
prefArray[i] := 0
done
End
KMP Algorithm:
Begin
n := size of text
m := size of pattern
call findPrefix(pattern, m, prefArray)
while i < n, do
if text[i] = pattern[j], then
increase i and j by 1
if j = m, then
print the location (i-j) as there is the pattern
j := prefArray[j-1]
else if i < n AND pattern[j] != text[i] then
if j != 0 then
j := prefArray[j - 1]
else
increase i by 1
done
End
2. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
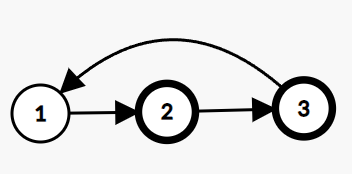
Problem approach
Floyd's algorithm can be used to solve this question.
Define two pointers slow and fast. Both point to the head node, fast is twice as fast as slow. There will be no cycle if it reaches the end. Otherwise, it will eventually catch up to the slow pointer somewhere in the cycle.
Let X be the distance from the first node to the node where the cycle begins, and let X+Y be the distance the slow pointer travels. To catch up, the fast pointer must travel 2X + 2Y. L is the cycle size. The total distance that the fast pointer has travelled over the slow pointer at the meeting point is what we call the full cycle.
X+Y+L = 2X+2Y
L=X+Y
Based on our calculation, slow pointer had already traveled one full cycle when it met fast pointer, and since it had originally travelled A before the cycle began, it had to travel A to reach the cycle's beginning!
After the two pointers meet, fast pointer can be made to point to head. And both slow and fast pointers are moved till they meet at a node. The node at which both the pointers meet is the beginning of the loop.
Pseudocode :
detectCycle(Node *head) {
Node *slow=head,*fast=head;
while(slow!=NULL && fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
{
fast = head;
while(slow!=fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL; }
03
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 minutes
Interview date18 May 2015
Coding problem1
This was supposed to be the HR round but out of surprise the interviewer started by giving me a question to code.
After I approached this question with the right solution he just asked about my family. After that he said to wait. After half an hour the results were announced. A total of three students were hired and I was amongst one of them.
1. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
A stack can be used to solve this question.
We traverse the given string s and if we:
1. see open bracket we put it to stack
2. see closed bracket, then it must be equal to bracket in the top of our stack, so we check it and if it is true, we remove this pair of brackets.
3. In the end, if and only if we have empty stack, we have valid string.
Complexity: time complexity is O(n): we put and pop each element of string from our stack only once. Space complexity is O(n).

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by Magicbricks
896 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6543 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3566 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1201 views
0 comments
0 upvotes










