MakeMyTrip interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Software Developer
MakeMyTrip
4 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Email Approach
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration65 minutes
Interview date15 May 2015
Coding problem1
There were 2 sections –
Aptitude and Logical Reasoning and MCQ based on Java question ,C++, coding for 20 min and 45 min respectively.
Section A- Not very difficult to clear this round although less time was a problem.
Section B- It contains 15 multiple choice question on c/c++,java and 4 simple coding questions
1. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



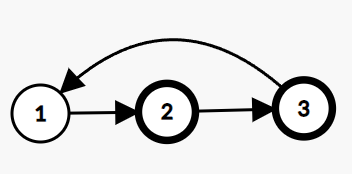
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
Floyd's algorithm can be used to solve this question.
Define two pointers slow and fast. Both point to the head node, fast is twice as fast as slow. There will be no cycle if it reaches the end. Otherwise, it will eventually catch up to the slow pointer somewhere in the cycle.
Let X be the distance from the first node to the node where the cycle begins, and let X+Y be the distance the slow pointer travels. To catch up, the fast pointer must travel 2X + 2Y. L is the cycle size. The total distance that the fast pointer has travelled over the slow pointer at the meeting point is what we call the full cycle.
X+Y+L = 2X+2Y
L=X+Y
Based on our calculation, slow pointer had already traveled one full cycle when it met fast pointer, and since it had originally travelled A before the cycle began, it had to travel A to reach the cycle's beginning!
After the two pointers meet, fast pointer can be made to point to head. And both slow and fast pointers are moved till they meet at a node. The node at which both the pointers meet is the beginning of the loop.
Pseudocode :
detectCycle(Node *head) {
Node *slow=head,*fast=head;
while(slow!=NULL && fast!=NULL && fast->next!=NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast)
{
fast = head;
while(slow!=fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return NULL; }
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration75 minutes
Interview date18 May 2015
Coding problem3
It was an online coding test in which 3 coding question were given.
1. Smallest Window
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given two strings S and X containing random characters. Your task is to find the smallest substring in S which contains all the characters present in X.
Example:
Let S = “abdd” and X = “bd”.
The windows in S which contain all the characters in X are: 'abdd', 'abd', 'bdd', 'bd'.
Out of these, the smallest substring in S which contains all the characters present in X is 'bd'.
All the other substring have a length larger than 'bd'.
Problem approach
The naïve approach is to generate all substrings of string1 and for each substring, check whether the substring contains all characters of string2. Finally, print the smallest substring containing all characters of string2.
The efficient solution is to use hashing. First check if the length of the string is less than the length of the given pattern, if yes then no such window can exist . Next, store the occurrence of characters of the given pattern in a array, say h_pat[]. Now use two pointer technique :
1. Start matching the characters of pattern with the characters of string , keep incrementing count if a character matches.
2. Check if (count == length of pattern string), if it matches then this means a window is found.
3. If such a window is found, try to minimize it by removing extra characters from the beginning of the current window.
4. Delete one character from first and again find this deleted key at right, once found apply step 2.
5. Update minimum length.
At last, print the minimum length window.
2. Find Smallest Integer
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'ARR' consisting of 'N' positive numbers and sorted in non-decreasing order, and your task is to find the smallest positive integer value that cannot be represented as a sum of elements of any proper subset of the given array.
An array 'B' is a subset of another array 'A' if each element of 'B' is present in 'A'.
For example:
For the given input array [1, 1, 3],
1 can be represented as the sum of elements of the subset [1],
2 can be represented as the sum of elements of a subset [1, 1],
3 can be represented as the sum of elements of a subset [3],
4 can be represented as the sum of elements of a subset [1, 3],
5 can be represented as the sum of elements of a subset [1, 1, 3]
So, the smallest positive integer value that cannot be represented as a sum of elements of any subset of a given array is 6.
Problem approach
The Brute force approach would be to find the sum of all the possible subsets and then compare sum with the sum of remaining elements.
A better approach would be to sort the array in descending order and then take the largest elements. Now, take elements from the largest, until we get strictly more than half of total sum of the given array. As soon as the current sum is greater than half of the total sum of the given array, return the subset so far.
3. Minimum steps to reach target by a Knight
Moderate
25m average time
60% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a square chessboard of size ‘N x N’. The position coordinates of the Knight and the position coordinates of the target are also given.
Your task is to find out the minimum steps a Knight will take to reach the target position.
Example:
knightPosition: {3,4}
targetPosition: {2,1}
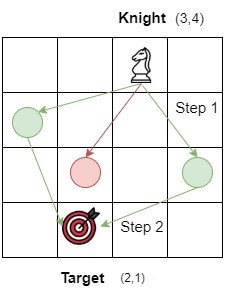
The knight can move from position (3,4) to positions (1,3), (2,2) and (4,2). Position (4,2) is selected and the ‘stepCount’ becomes 1. From position (4,2), the knight can directly jump to the position (2,1) which is the target point and ‘stepCount’ becomes 2 which is the final answer.
Note:
1. The coordinates are 1 indexed. So, the bottom left square is (1,1) and the top right square is (N, N).
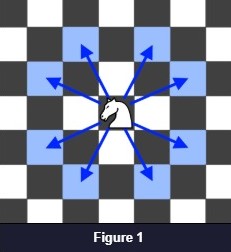
2. The knight can make 8 possible moves as given in figure 1.
3. A Knight moves 2 squares in one direction and 1 square in the perpendicular direction (or vice-versa).
Problem approach
This problem is similar to finding the shortest path in an unweighted graph. BFS can be used to solve this problem.
Make a queue that stores the coordinate and distance from its starting node for each cell. Try all 8 possible positions where a Knight can reach from its position. If reachable position is not already visited and is inside the board, we push this state into queue with distance 1 more than its parent state. Finally, we return distance of target position, when it gets pop out from queue.
Time Complexity : O(N^2) as in the worst case, all cells of board will be visited
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration60 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem4
It started with a discussion on the programs given in coding round. They asked me about my interest field after that they directly jumped into Networking, Linux and Ethical Hacking part looking my interest domain. They asked me various question on networking and linux.
Then they asked me to code a simple c program
1. Reverse Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
Problem approach
This can be solved both: recursively and iteratively.
The recursive approach is more intuitive. First reverse all the nodes after head. Then we need to set head to be the final node in the reversed list. We simply set its next node in the original list (head -> next) to point to it and sets its next to NULL. The recursive approach has a O(N) time complexity and auxiliary space complexity.
For solving the question is constant auxiliary space, iterative approach can be used. We maintain 3 pointers, current, next and previous, abbreviated as cur, n and prev respectively. All the events occur in a chain.
1. Assign prev=NULL, cur=head .
2. Next, repeat the below steps until no node is left to reverse:
1. Initialize n to be the node after cur. i.e. (n=cur->next)
2. Then make cur->next point to prev (next node pointer).
3. Then make prev now point to the cur node.
4. At last move cur also one node ahead to n.
The prev pointer will be the last non null node and hence the answer.
2. Networking Question
Port numbers of protocols like FTP,SMTP
Problem approach
Port number 20 is used for FTP data while port number 21 is used for FTP Control.
Port number 161 is used for SMTP.
3. Networking Question
Explain the OSI Model
Problem approach
Physical Layer
The lowest layer of the OSI Model is concerned with electrically or optically transmitting raw unstructured data bits across the network from the physical layer of the sending device to the physical layer of the receiving device. It can include specifications such as voltages, pin layout, cabling, and radio frequencies.
Data Link Layer
At the data link layer, directly connected nodes are used to perform node-to-node data transfer where data is packaged into frames. The data link layer also corrects errors that may have occurred at the physical layer.
The data link layer encompasses two sub-layers of its own. The first, media access control (MAC), provides flow control and multiplexing for device transmissions over a network. The second, the logical link control (LLC), provides flow and error control over the physical medium as well as identifies line protocols.
Network Layer
The network layer is responsible for receiving frames from the data link layer, and delivering them to their intended destinations among based on the addresses contained inside the frame. The network layer finds the destination by using logical addresses, such as IP (internet protocol). At this layer, routers are a crucial component used to quite literally route information where it needs to go between networks.
Transport Layer
The transport layer manages the delivery and error checking of data packets. It regulates the size, sequencing, and ultimately the transfer of data between systems and hosts. One of the most common examples of the transport layer is TCP or the Transmission Control Protocol.
Session Layer
The session layer controls the conversations between different computers. A session or connection between machines is set up, managed, and terminated at layer 5. Session layer services also include authentication and reconnections.
Presentation Layer
The presentation layer formats or translates data for the application layer based on the syntax or semantics that the application accepts. Because of this, it at times also called the syntax layer. This layer can also handle the encryption and decryption required by the application layer.
Application Layer
At this layer, both the end user and the application layer interact directly with the software application. This layer sees network services provided to end-user applications such as a web browser or Office 365. The application layer identifies communication partners, resource availability, and synchronizes communication.
4. OS Question
How to copy files in Linux ?
Problem approach
The cp command is the primary method for copying files and directories in Linux. Virtually all Linux distributions can use cp. The basic format of the command is: cp [additional_option] source_file target_file
For example:
cp my_file.txt my_file2.txt
This Linux command creates a copy of the my_file.txt file and renames the new file to my_file2.txt.
04
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration45 minutes
Interview date19 May 2015
Coding problem0
This round was started with two puzzles. I got stuck in the first puzzle itself but in this round the interviewer was checking our approach, our logical thinking. Then I was given one program and was asked to optimize it. Question was simple based on hash map. Next question was based on ethical hacking. I was asked to explain SQL attack.
The interview ended with some discussions over my project.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
Software Developer
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by MakeMyTrip
1572 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 13 problems
Interviewed by MakeMyTrip
1466 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by MakeMyTrip
1168 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Engineer
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by MakeMyTrip
825 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
Software Developer
5 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
3986 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
6 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by SAP Labs
2872 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Software Developer
3 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1201 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






