Mathway interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Mathway
2 rounds | 4 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I started my coding journey on YouTube, where I first learned about data structures and algorithms. Then, I continued my preparation for data structures on LinkedIn.
Application story
I applied through a referral from a senior.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I could not give precise and optimized solutions to the questions asked.
Preparation
Duration: 4 months
Topics: Data Structures, Pointers, OOPS, System Design, Algorithms, Dynamic Programming, Linked Lists and Graphs
Tip
Tip 1: Learn common algorithms that heavily rely on data structures, such as sorting, searching, and graph traversal algorithms.
Tip 2: Understand how data structures play a crucial role in the efficiency of these algorithms.
Application process
Where: Referral
Eligibility: Above 6 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Include some projects on your resume.
Tip 2: Avoid putting false information on your resume.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration60 minutes
Interview date20 Oct 2022
Coding problem2
Apart from DSA, computer networking, and DBMS, we were presented with C++ questions focusing on topics like memory management, pointers, templates, exception handling, and file handling. We were assessed on our understanding of these concepts and our ability to write clean and efficient C++ code.
1. K - Sum Path In A Binary Tree
Moderate
35m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value and a number ‘K’. Your task is to print every path of the binary tree with the sum of nodes in the path as ‘K’.
Note:
1. The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
2. Output the paths in the order in which they exist in the tree from left to right. Example: In the below example, path {1,3} is followed by {3,1} and so on.
Example:
For K = 4 and tree given below:
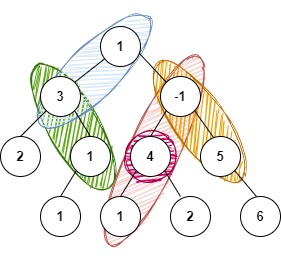
The possible paths are:
1 3
3 1
-1 4 1
4
-1 5
The sum of values of nodes of each of the above-mentioned paths gives a sum of 4.
Problem approach
The idea is simple: record all prefix sums in a hash table along the path. For current prefix sum x, check if (x - target)
appears in the hash table.
2. Validate Binary Tree Nodes
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given ‘N’ binary tree nodes numbered from 0 to N - 1 where node ‘i’ has two children LEFT_CHILD[i] and RIGHT_CODE[i]. Return ‘True’ if and only if all the given nodes form exactly one valid binary tree. If node ‘i’ has no left child then 'LEFT_CHILD[i]' will equal -1, similarly for the right child.
Example:
Let’s say we have n=4 nodes, 'LEFT_CHILD' = {1, -1, 3, -1} and
RIGHT_CHILD = {2, -1, -1, -1}. So the resulting tree will look like this:
It will return True as there is only one valid binary tree and each node has only one parent and there is only one root.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration90 minutes
Interview date20 Oct 2022
Coding problem2
1. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Moderate
30m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



For a given array with N elements, you need to find the length of the longest subsequence from the array such that all the elements of the subsequence are sorted in strictly increasing order.
Strictly Increasing Sequence is when each term in the sequence is larger than the preceding term.
For example:
[1, 2, 3, 4] is a strictly increasing array, while [2, 1, 4, 3] is not.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Naive Solution) :.
- The simplest approach to solving the problem is to generate all possible subarrays.
- For each subarray, check if the difference between adjacent elements remains the same throughout or not.
- Among all such subarrays satisfying the condition, store the length of the longest subarray and print it as the result.
TC : O(N^3), where N=size of the array
SC : O(1)
2. Next Greater Element
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array 'a' of size 'n'.
Print the Next Greater Element(NGE) for every element.
The Next Greater Element for an element 'x' is the first element on the right side of 'x' in the array, which is greater than 'x'.
If no greater elements exist to the right of 'x', consider the next greater element as -1.
For example:
Input: 'a' = [7, 12, 1, 20]
Output: NGE = [12, 20, 20, -1]
Explanation: For the given array,
- The next greater element for 7 is 12.
- The next greater element for 12 is 20.
- The next greater element for 1 is 20.
- There is no greater element for 20 on the right side. So we consider NGE as -1.
Problem approach
Approach 1 (Naive Solution):
1. Use two loops: the outer loop picks all the elements one by one.
2. The inner loop looks for the first greater element for the element picked by the outer loop.
3. If a greater element is found, then that element is printed as the next; otherwise, -1 is printed.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 8 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
8770 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Analytics Consultant
3 rounds | 10 problems
Interviewed by ZS
937 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
1 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
3406 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 2
4 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Expedia Group
2660 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






